
About This Quiz
Do you know know the difference between asteroids and meteoroids? Gas giants and terrestrial planets? The distance a light-year measures and why no object can move faster than the speed of light? If you answered yes to these questions, you're in good company. Astronomers have been fascinated by space and its contents for thousands of years. In fact, the ancient Greeks were creating mathematical models to explain the stars and planetary systems as far back as the 4th century BCE. From Galileo Galilei to Johannes Kepler to Albert Einstein, some of the most brilliant minds in human history have been responsible for the way the universe and its physical laws are currently understood.Â
Whether you're an amateur astronomer, a celestial body-inspector or someone who would enthusiastically volunteer to go to Mars in a heartbeat, this quiz will take you on a trip to the furthest corners of the Milky Way galaxy (make sure to say "hello!" to Voyager 1 and 2 as you fly by.) Answer at least 11 of these space-themed questions correctly and join the ranks of other famous astronomers, mathematicians and physicists.Â
Are you ready to test your knowledge of all things astronomy? Get out your map of the solar system, grab your telescope and let's get started!
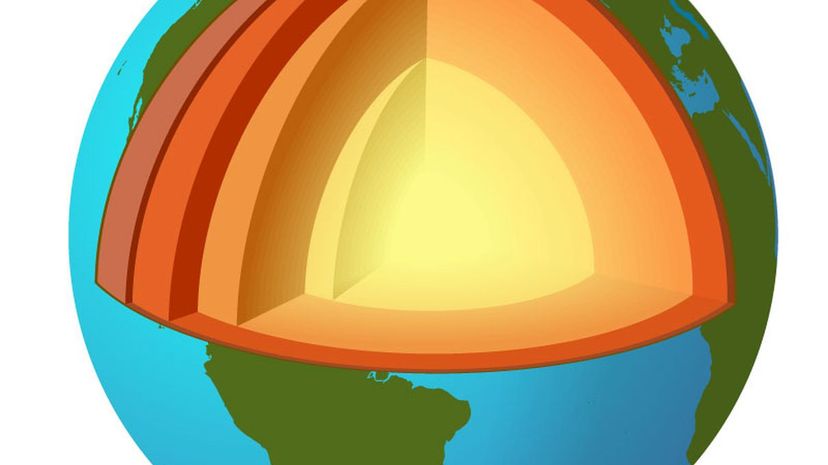

According to the dynamo theory, the Earth's outer core contains a self-sustaining magnetic field generator consisting of perpetually moving liquid iron. This motion creates electric currents, a product of electrons actively moving through the liquid metal, which then becomes a magnetic field.

Thought to be invented by German scientist Friedrich Bessel in 1838, a light-year measures the distance light travels in a year, a staggering 6 trillion miles over 365 days (or, to put it another way, 6 million million miles.)
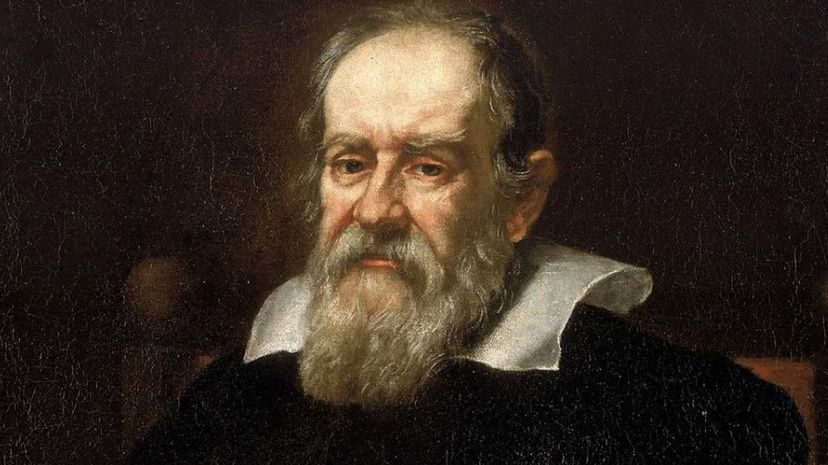

Although Nicolaus Copernicus initially proposed the idea of heliocentrism (which stated that the sun was the center of the solar system), it was Galileo who was able to actually disprove the commonly accepted belief that the Earth was the center of the solar system (also known as geocentrism.)
Advertisement
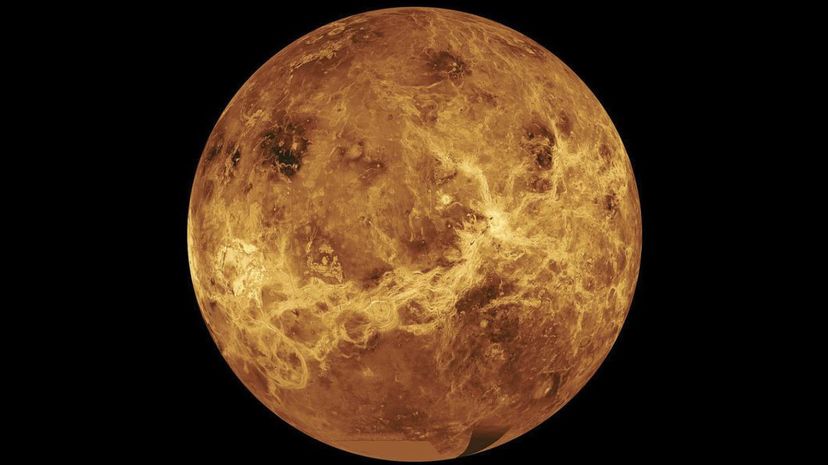

In order for a planet to be considered a gas giant, it needs to be mostly made up of gases such as helium and hydrogen. Venus is considered a terrestrial planet, meaning it is mainly composed of rock and metal.
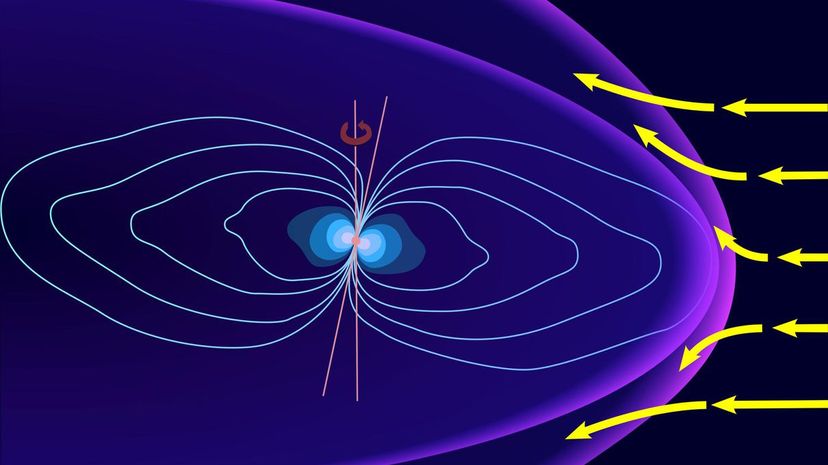
The Earth's magnetic field protects from solar wind, a steady stream of charged particles emitted by the sun's upper atmosphere (called the corona.) The aurora borealis, also known as the Northern Lights, occur when the atmosphere becomes charged after coming into contact with solar winds.
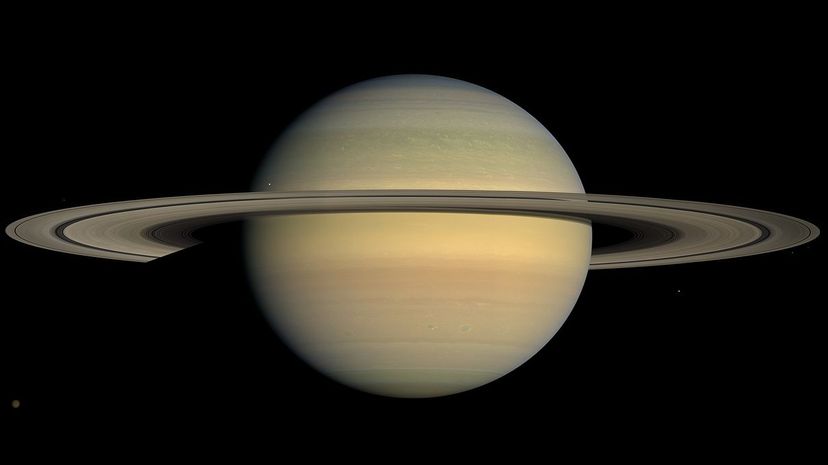
The second-largest planet in the solar system, Saturn is a gas giant that is famous for its spectacular planetary rings, Saturn is the fifth-brightest object in the solar system and can be seen with the naked eye from Earth during certain times of the year.
Advertisement
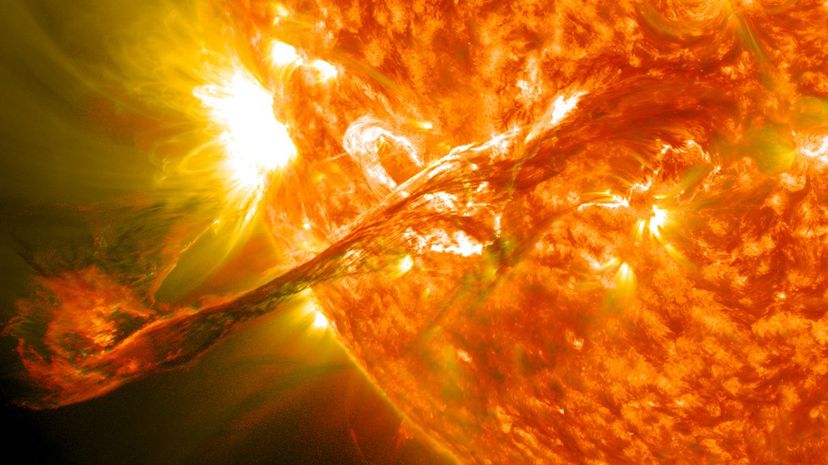

With an estimated diameter of 870,000 miles, the sun is by far the largest celestial body in our solar system. The Earth, on the other hand, is only 7,917 miles in diameter. Based on these measurements, about 1,300,000 Earths could fit inside the sun.
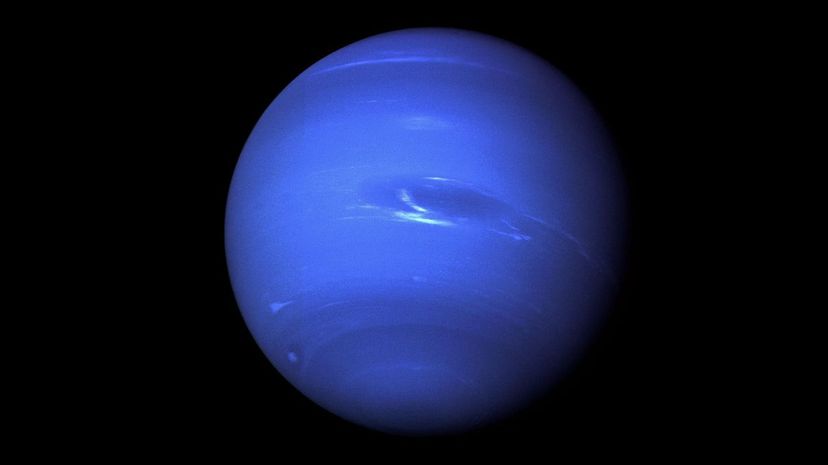

The densest of all the gas giant planets, Neptune is almost 3 billion miles away from the sun (its exact distance depends on its orbital location.) The Voyager 2 is the only spacecraft to have ever passed Neptune, giving scientists the first detailed pictures of this remote planet in 1989.

When considering this aspect of Einstein's Special Theory of Relativity, it's important to understand that when it comes to physics, mass is energy. Specifically, as an object accelerates its energy increases as it meets resistance, therefore increasing its overall mass (or energy.)
Advertisement
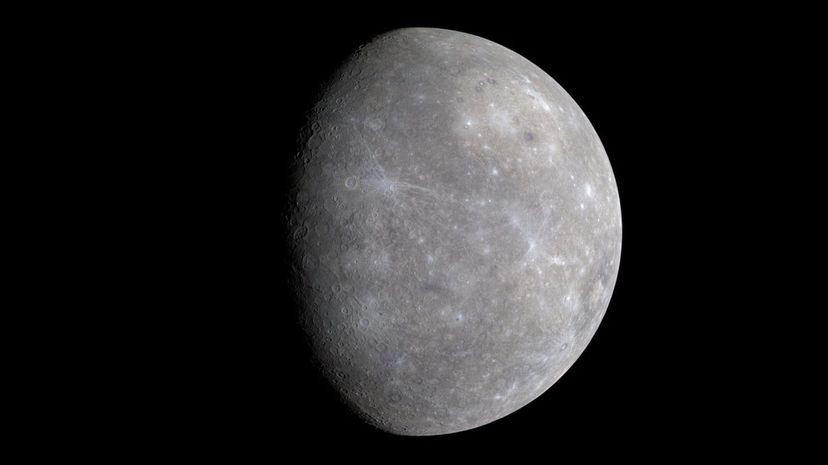

A solar day on Mercury (or, the amount of time between noon and noon the following day) is the same duration as 176 Earth days or 1,407 Earth hours. Surprisingly, a year on Mercury is 88 Earth days because it orbits the sun faster than it spins on its axis..
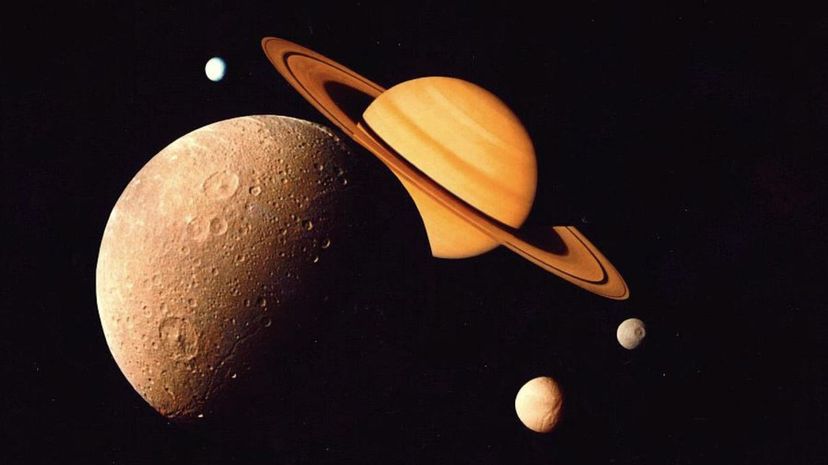

Like other members of the gas giant family, the vast majority of of Saturn's atmosphere (an estimated 96 percent) is made of hydrogen gas along with helium, methane and ammonia. Scientists have measured winds reaching up to almost 1,650 feet per second in the planet's upper atmosphere.
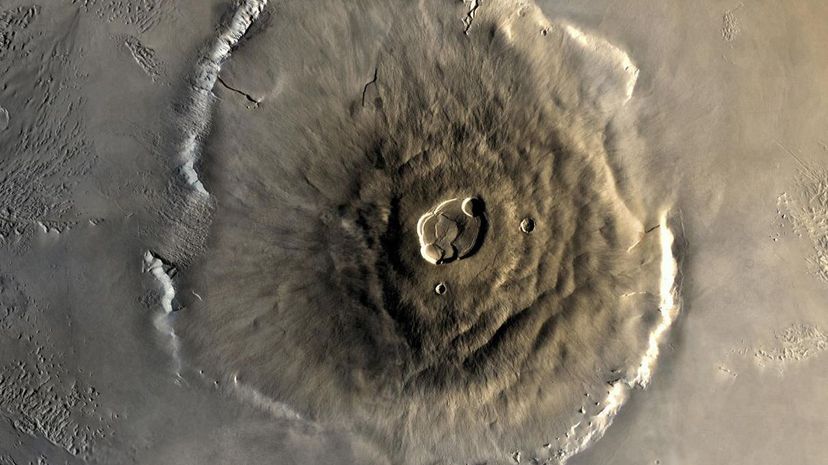
The planet Mars is home to Olympus Mons, the tallest known volcano in the solar system. 13 miles high and 373 miles in diameter, this volcano is still considered active by many scientists despite having been formed billions of years ago.
Advertisement

A star's brightness is entirely dependent on its temperature, which affects the light wavelengths being emitted. A very hot star has more energy and emits a shorter wavelength light, this makes the star appear blue. A cooler star, on the other hand, emits longer wavelength light and will appear red.
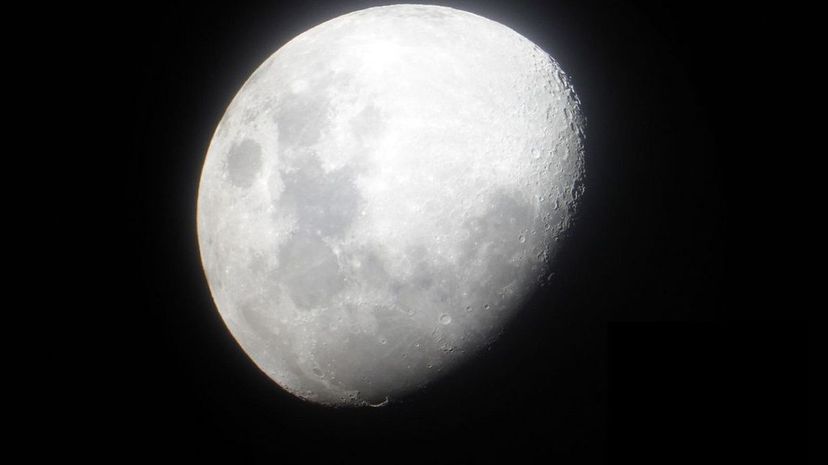

Because the Earth and the moon are made of similar matter, the giant-impact hypothesis, which suggests that 4.5 billion years ago a celestial body the size of Mars collided with Earth and produced extensive debris that eventually became the moon, is currently the most accepted theory.
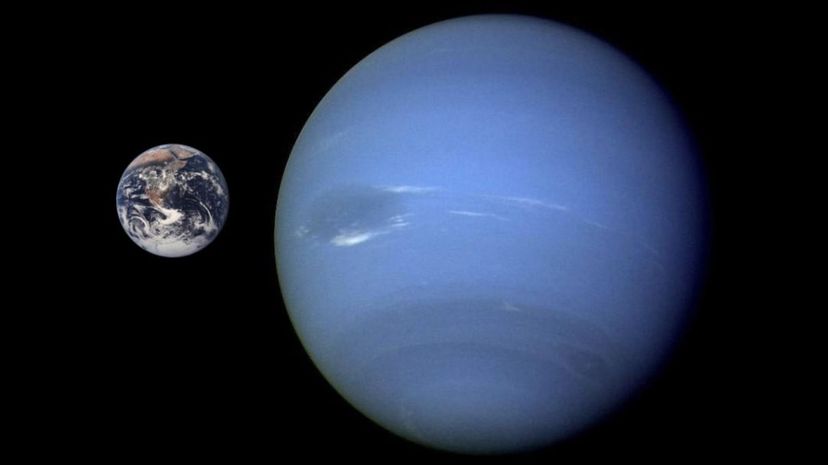

After observing the five closest planets to the sun, the Romans decided to name them after their most powerful gods. When Neptune was discovered in 1846, astronomers decided to carry on the tradition of naming planets after Roman gods and christened the planet Neptune, god of the sea.
Advertisement
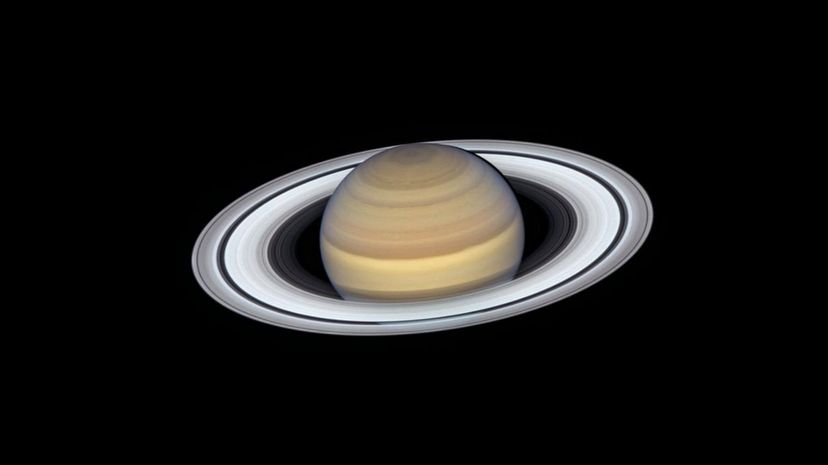

As of 2019, Saturn has 62 moons. 53 of these moons have been confirmed by scientists and nine moons are still unconfirmed. Recently, Saturn's largest moon, Titan, has been a source of fascination for astronomers due to its environment, which is thought to contain oceans and canals.
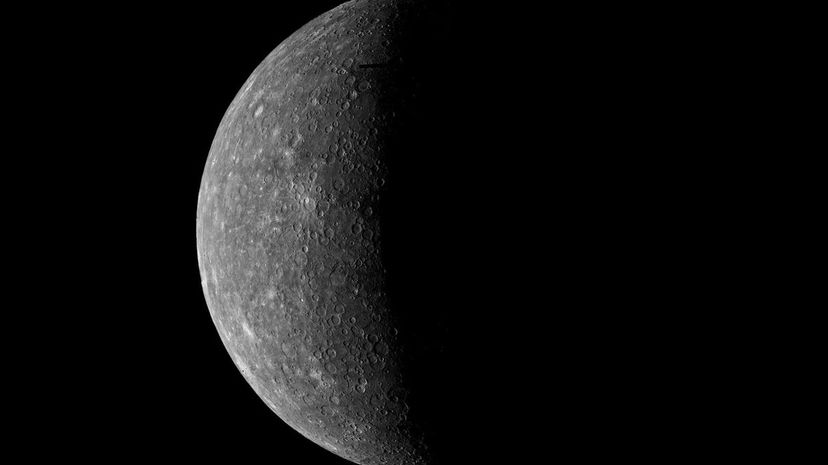

Mercury is only 3,032 miles in diameter, about a third of the size of Earth, and it continues to grow smaller as time passes. This phenomenon is caused by the planet's iron core, which is gradually cooling and solidifying, making the planet itself shrink as a result.
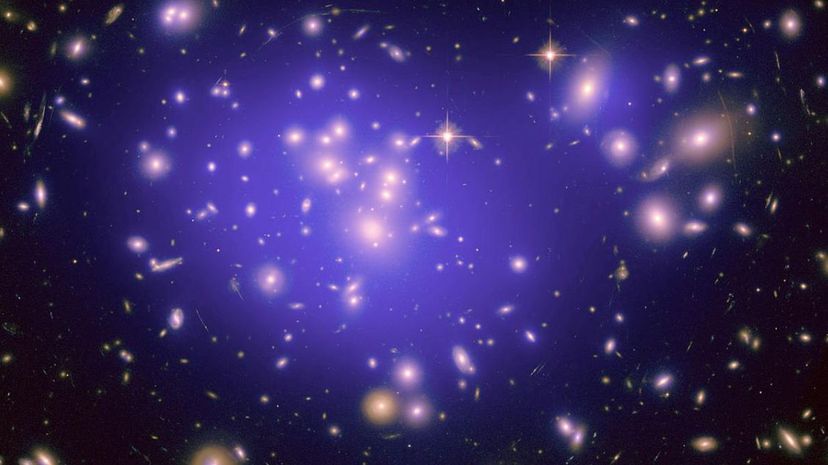

Dark matter, which is undetectable by scientific instruments, is a type of matter scientists have hypothesized to be responsible for the mass of the universe. Dark matter is aptly named as it is not believed to give off any radiation, light or X-rays.
Advertisement
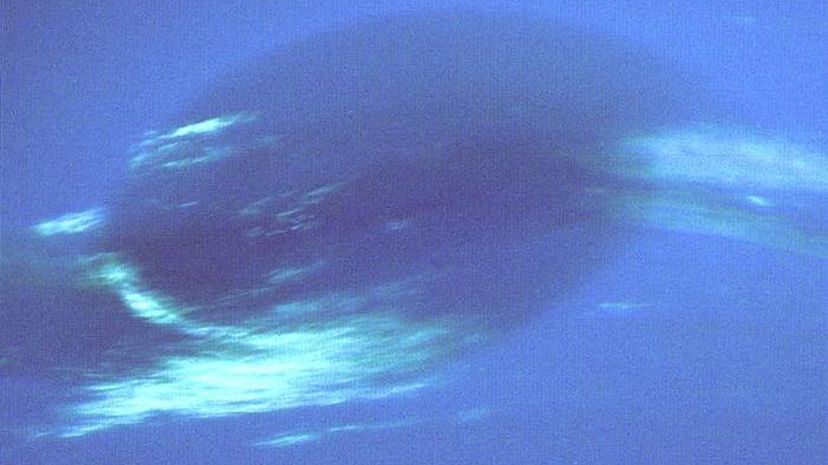

With winds thought to have reached over 1,590 feet per second, the Great Dark Spot on the planet Neptune was first observed when the Voyager 2 passed the planet in 1989. In 1994, Neptune was observed using the Hubble Space Telescope and the Great Dark Spot had vanished.
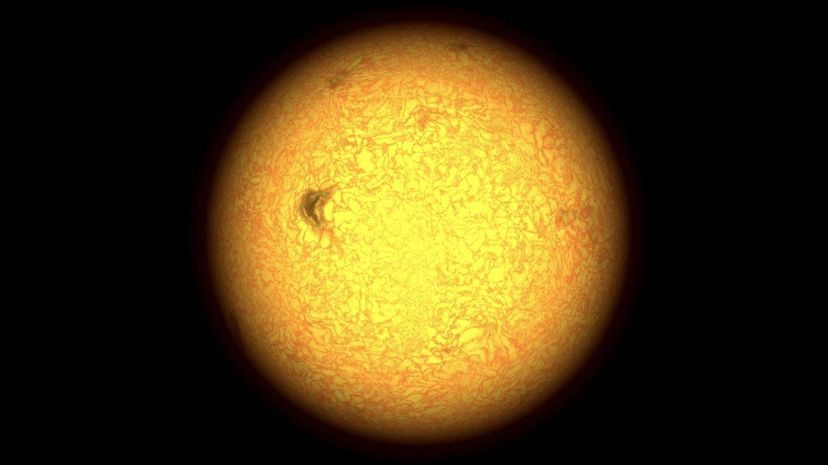

The sun is currently a yellow dwarf star (technically called a G V star) and is about halfway through its hydrogen-burning life cycle. The sun burns 600 million tons of hydrogen every second, producing enough energy to self-sustain for the next 10 billion years.

Stars are able to hold their shape without continuously expanding because of their own gravity. The weight of any given star is what keeps its shape (also explained as the fine balance between outgoing gas pressure and how gravity pulls this pressure inward.)
Advertisement
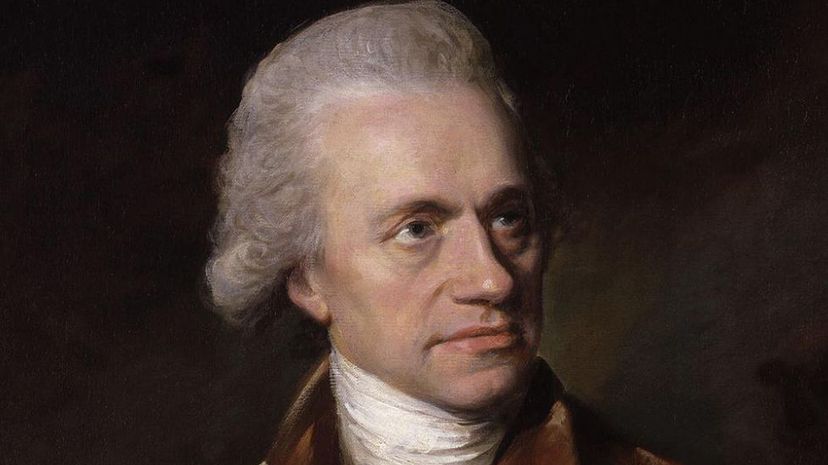

Uranus remained undetected by humans until 1781 when William Herschel misidentified the planet as a comet. Using a telescope, Herschel observed what he thought was a star until he noticed it passing in front of other stars. This "star" turned out to be the planet Uranus.
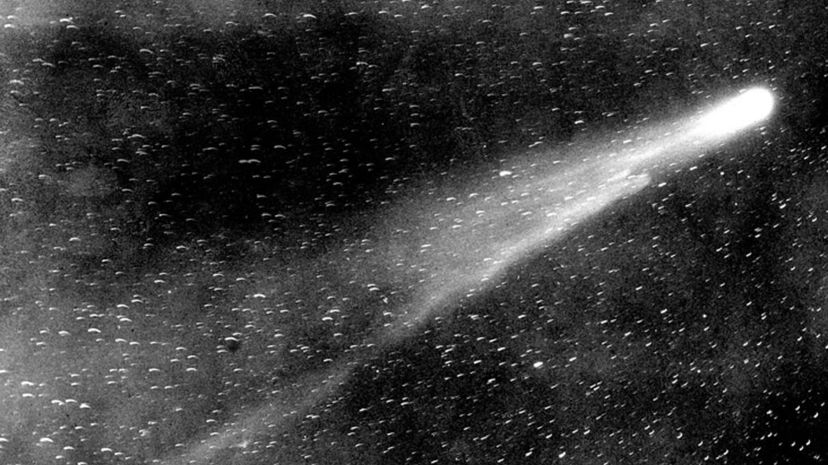

Halley's comet has a long history of being observed by humans and go as far back as Babylonian times. The next time Halley's comet will pass by Earth close enough to be observed will be in the year 2061 (give or take a a few years.)
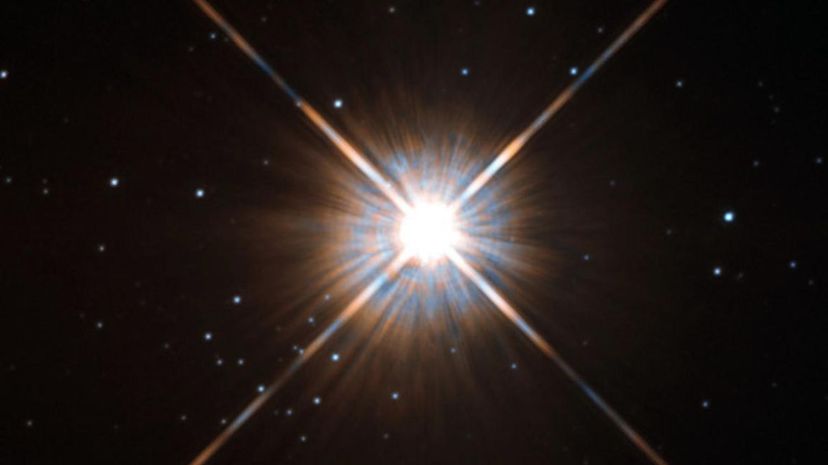

Proxima Centauri is the name of the star closest to Earth after the sun (although close is a relative term.) About 4.2 light-years away -almost 2.5 trillion miles - it would take approximately 75,000 years to get there using the most innovative space travel technology currently available.
Advertisement
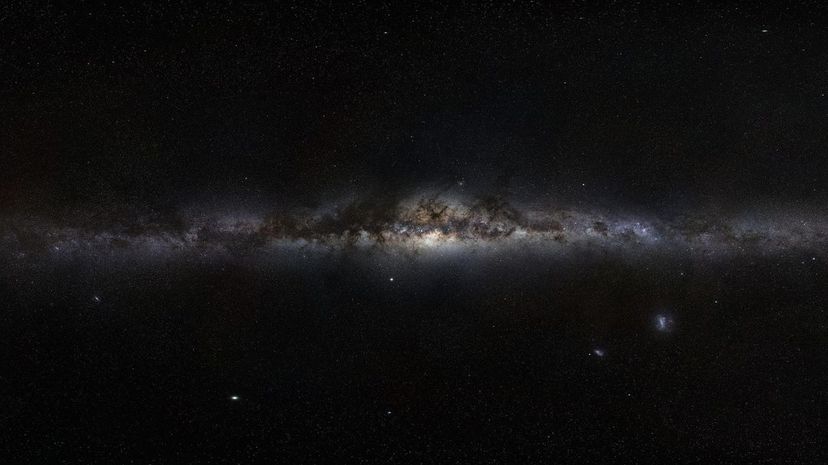

While there is no way to know the exact number of stars in the Milky Way galaxy, scientists estimate there are about 200 billion (with some estimates as low as 100 billion and some as high as 400 billion.)
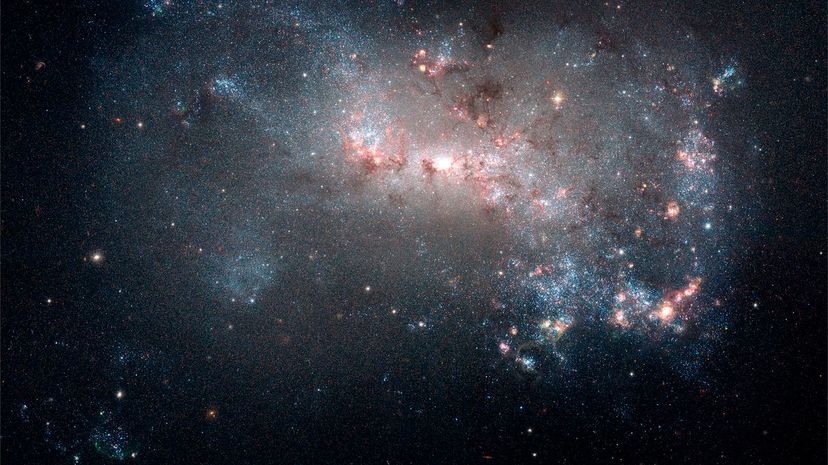

Galaxies that form many new stars very quickly are called starbursts. This phenomenon is often seen when two galaxies come together, forming gigantic molecular clouds containing enough dense gas and dust to produce new stars at a much faster rate.
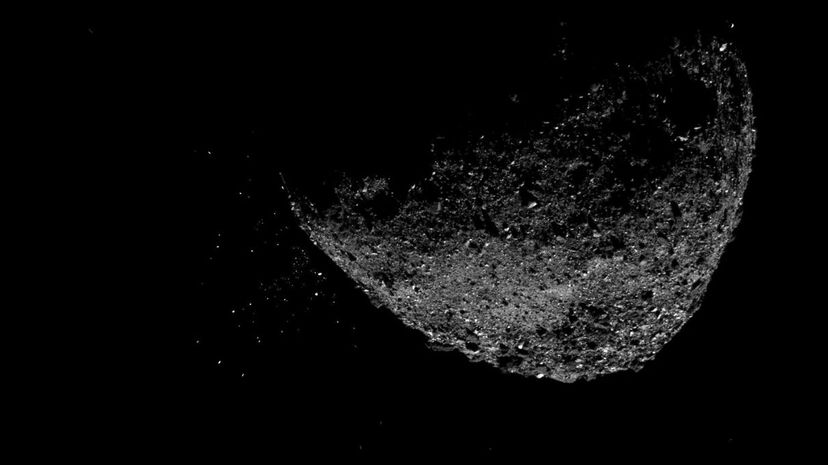
Asteroids can be anywhere from 30 feet to well over a hundred miles in diameter, and anything under 30 feet is considered a meteorite. Asteroids are often found orbiting the sun in a 20 million-mile area between Mars and Jupiter.
Advertisement

Although Venus is the second closest planet to the sun, the average surface temperature is much hotter than that of Mercury. Because of its dense atmosphere, the average surface temperature of Venus hovers around 863 degrees Fahrenheit.

The smallest of all the planets in the solar system, Mercury has a diameter of 3,030 miles. Earth's moon, which is the fifth-largest moon in the solar system, has a slightly smaller diameter of 2,159 miles - just slightly larger than the US/Mexico border.
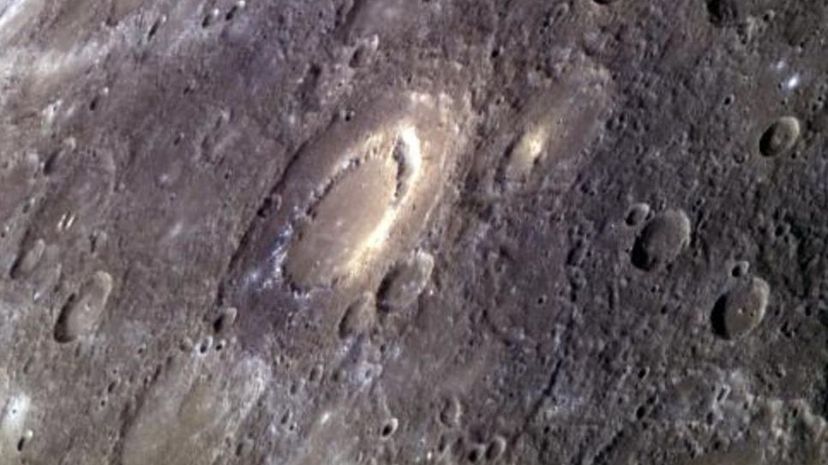

Poor Mercury! With its lack of a protective atmosphere, liquids that could help erode impact sites and proximity to the sun, Mercury is the most cratered planet in the solar system (at least the craters are well-named after great artists and writers.)
Advertisement
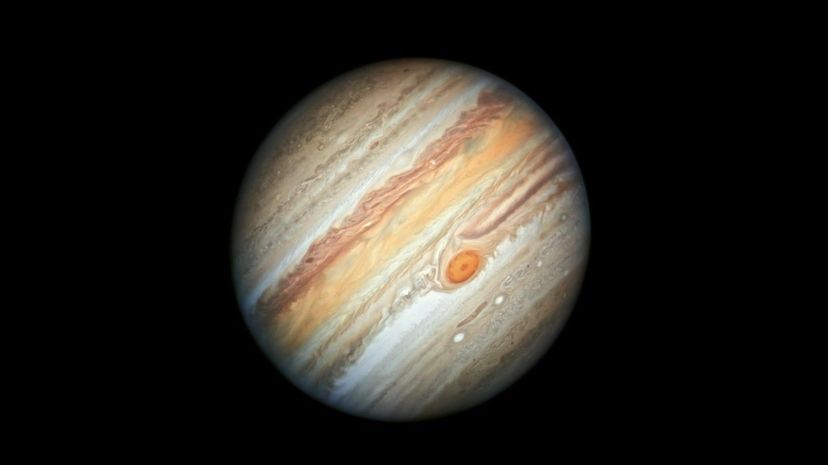

With a diameter of 3,273 miles, Ganymede is not only the largest moon to orbit Jupiter, but it's also the largest moon in the entire solar system. Galileo Galilei discovered Ganymede in 1610, but it was Johannes Kepler who suggested naming the moon after the Greek mythological figure.
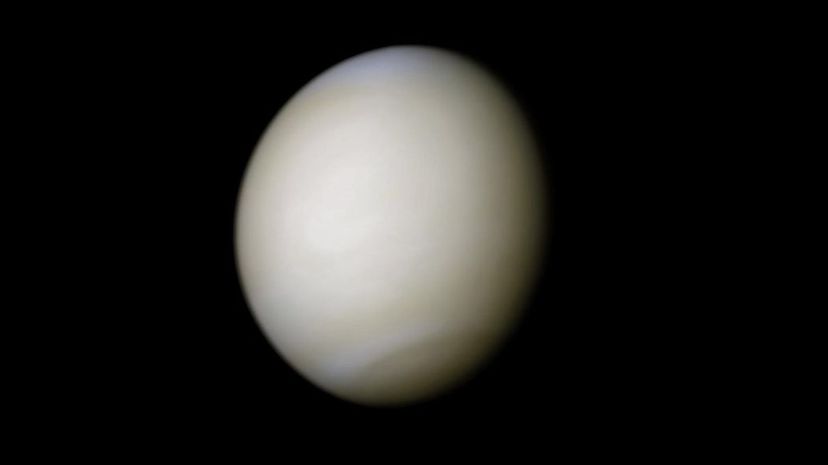

Despite the fact that Venus is Earth's next-door neighbor, it has a completely inhospitable atmosphere made almost entirely of carbon dioxide. Venus is also home to impenetrable clouds composed of sulphuric acid (which is why astronomers are unable to see what the surface of Venus looks like.)
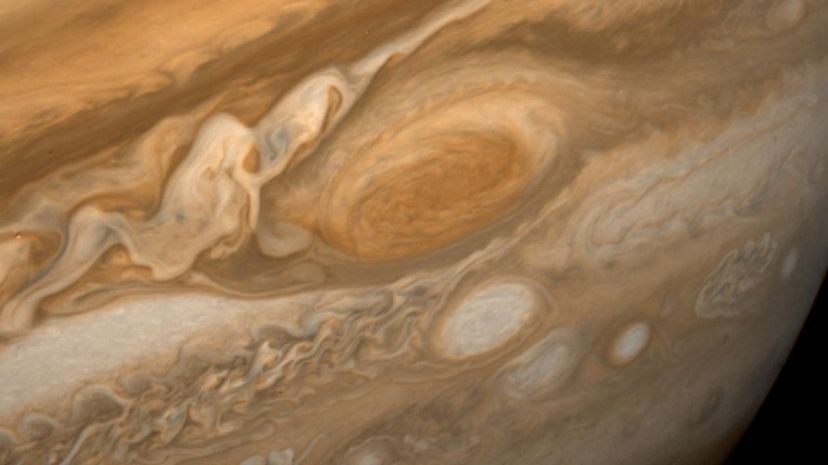

The Great Red Spot on Jupiter has been observed by astronomers for at least 350 years and is believed to be a massive anticyclonic storm. It has a diameter of 10,160 miles across (larger than the diameter of Earth by about a third) and was first observed by the Voyager 1 spacecraft in 1979.
Advertisement
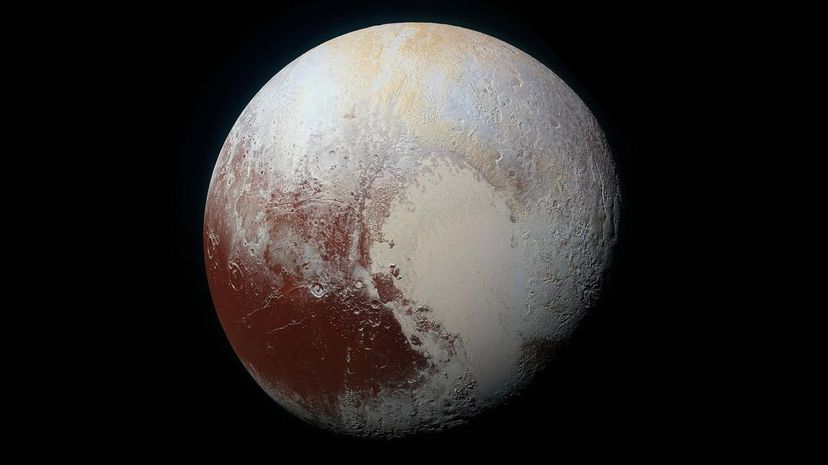

When the dwarf planet Eris, which is considerably larger than Pluto, was first discovered in 2005, the International Astronomical Union moved to redefine the requirements that a celestial body must meet in order to be classified as a planet. As a result, Pluto was demoted to dwarf planet status.
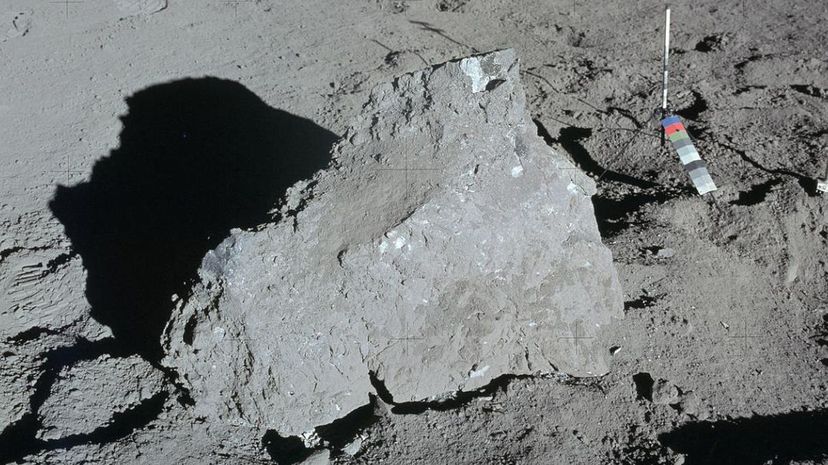

Lunar rocks have been an important tool for astronomers, both in terms of how the moon was formed as well as offering clues about the Earth's origin and the formation and long history of the inner solar system in general.