
About This Quiz
Humanity is on a mission to send a human-crewed spaceship to Mars, but we still don't know everything there is to know about our bodies. It's understandable that we still haven't completely figured out our genetic code, but you'd think we would have at least discovered all the organs and structures in our own body!
In 2013, scientists discovered a new ligament in the knee called the anterolateral ligament that supports your anterior cruciate ligament. Who knows, maybe we'll find a new elbow ligament next.Â
In 2018, scientists discovered a new organ called the interstitium. The interstitium is located just below the surface of your skin and is filled with fluid. Researchers think that it functions as a shock absorber. But hey, if it took scientists thousands of years to discover it, it seems unfair to test you on it, so we'll give you that one as a free pass.
Do you know your body well enough to get a perfect score on this quiz? We hope you know the significant organs like your brain, heart, lungs, liver and intestines. But how about the smaller organs like you thymus gland? You are familiar with your thymus gland, aren't you? Let's find out!
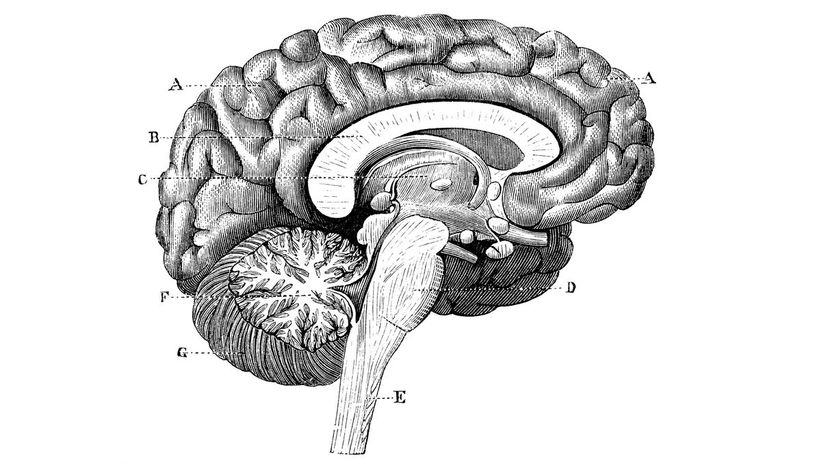
Have you ever let your sleep schedule slide so that you were staying up late and sleeping in half the day? Once your sleep schedule is off, it can be hard to get back on track because your pineal gland starts producing melatonin at inappropriate times.
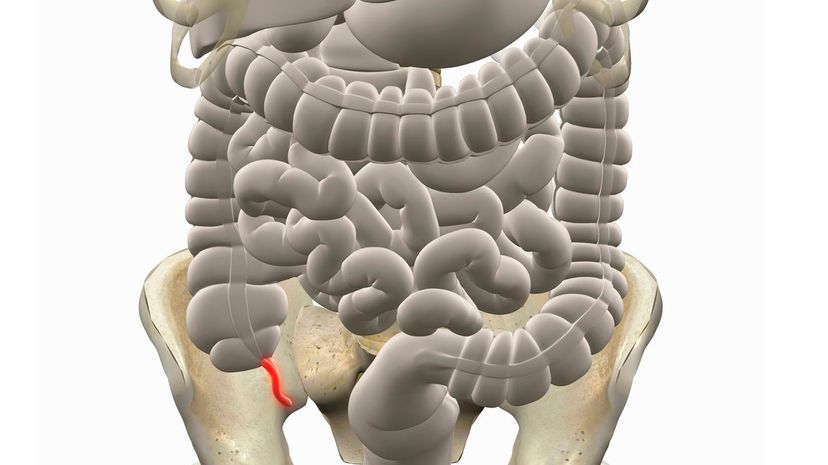
Getting an appendectomy is one of the most common emergency surgeries. It's was long thought that the appendix served no function in modern humans, but some scientists now believe it may play a role in protecting healthy bacteria after a stomach illness.
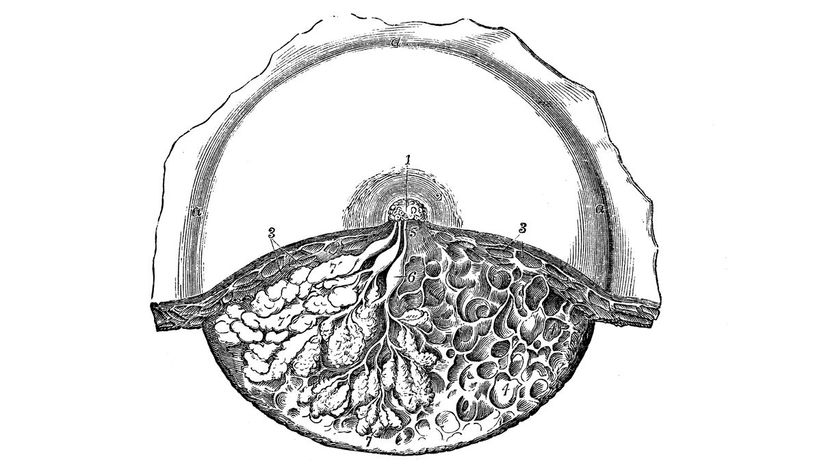
Both men and women have mammary glands for milk production. In women, the glands become developed after estrogen levels increase. In cases of extreme hormonal imbalances, men can also produce milk.
Advertisement

You might not think of your skin as an organ, but it's the largest organ in your body based on the surface area. Like any other organ, it can become damaged if you don't take care of it properly. So wear your sunscreen!
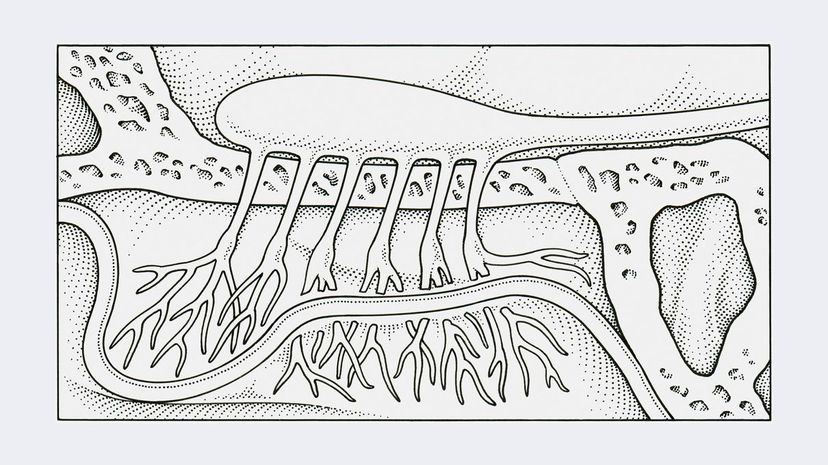
Your olfactory bulb is located on the base of your brain and extends in a series of 'roots' into your nasal cavity. If this organ became damaged, not only would your sense of smell be destroyed, but you might not enjoy your meals as much either. Don't believe us? Try eating your next meal with your nose plugged.
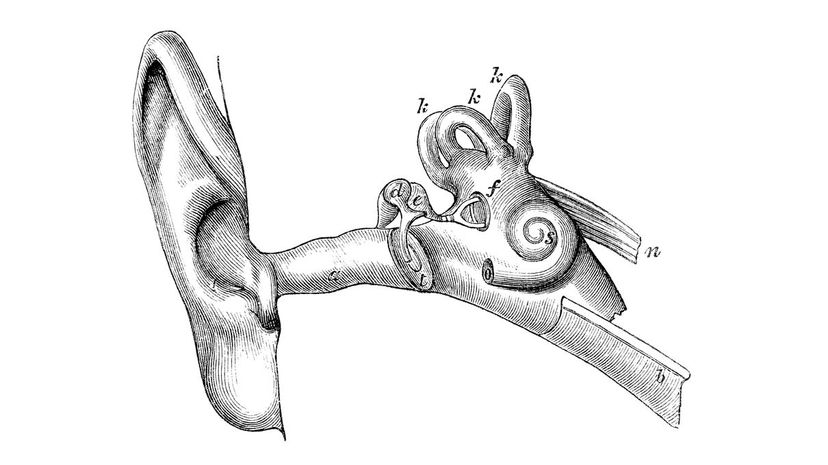
Your snail-shaped cochlea converts sound waves into neural signals that your brain can interpret. Damage to this organ can lead to hearing loss. Unfortunately, it isn't able to heal itself, so damage is usually permanent.
Advertisement
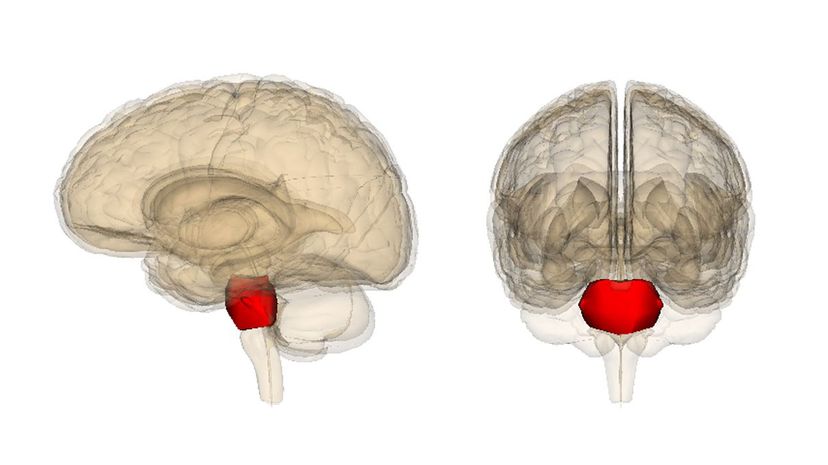
The pons is a critical part of your brainstem that regulates sleep, swallowing, bladder function, facial expressions, taste and other functions. You wouldn't be able to survive without your pons since your body wouldn't have a way to transmit information from your spine to your brain.
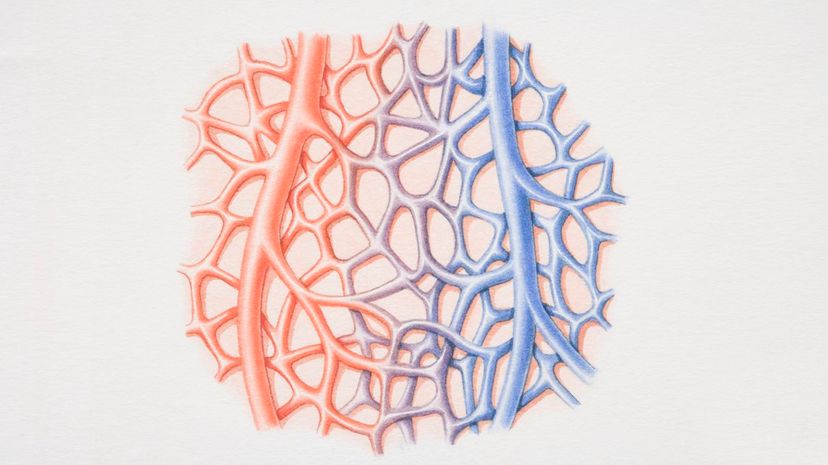
Your capillaries are the smallest type of blood vessels. Your arteries carry blood away from your heart and become smaller arterioles. These arterioles eventually become capillaries, which allow for the exchange of oxygen and nutrients.
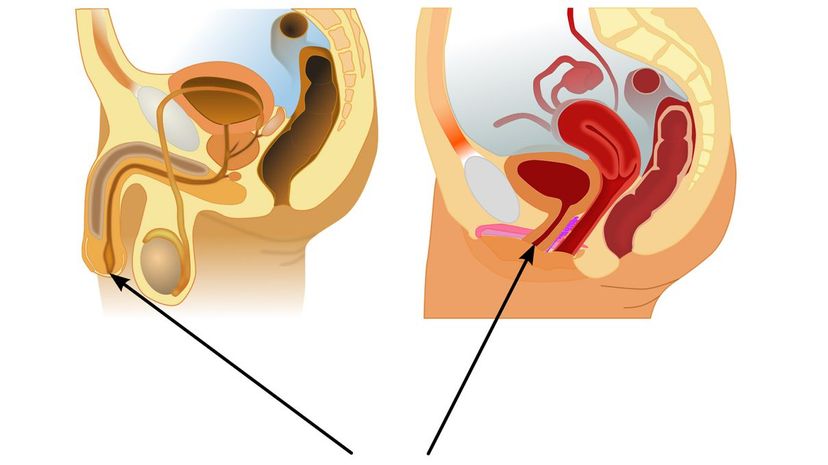
Your urethra creates a passageway from your bladder to your ... well, toilet. Both men and women have this organ. However, women have a shorter urethra, which makes them more susceptible to bladder infections.
Advertisement

Your esophagus connects your mouth to your stomach. Can you guess how long it is? From your throat to your stomach, it runs about 8 inches long. Obviously, in a bigger person, it's going to be slightly longer.
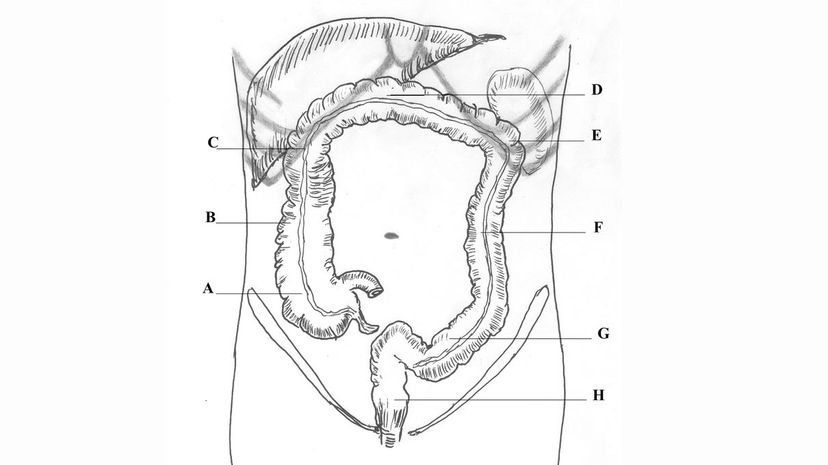
Your large intestines serve as the final stage of your food's journey. Despite their name as 'large,' your large intestines are only about a quarter of the length of your small intestines. In the average person, the long intestines measure about 5 feet long.
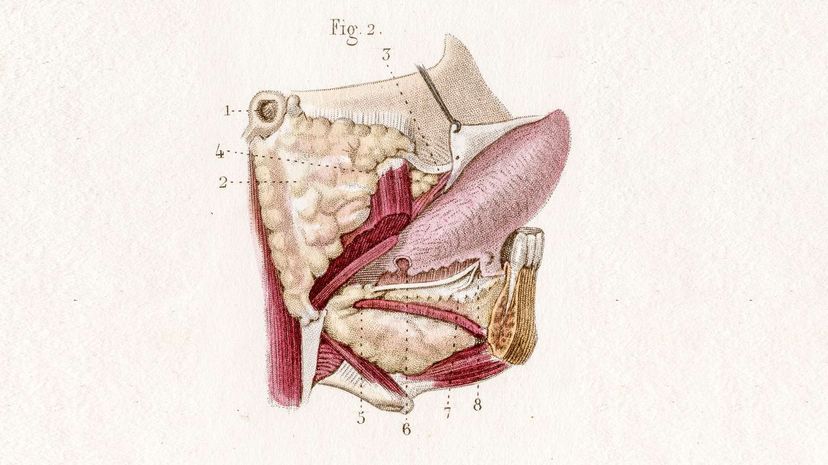
If you've ever noticed your mouth start watering in anticipation before you walked into a restaurant, you can thank your salivary glands. You have six glands in total. Can you guess how much saliva they produce in a day? More than two liters (67oz.)!
Advertisement
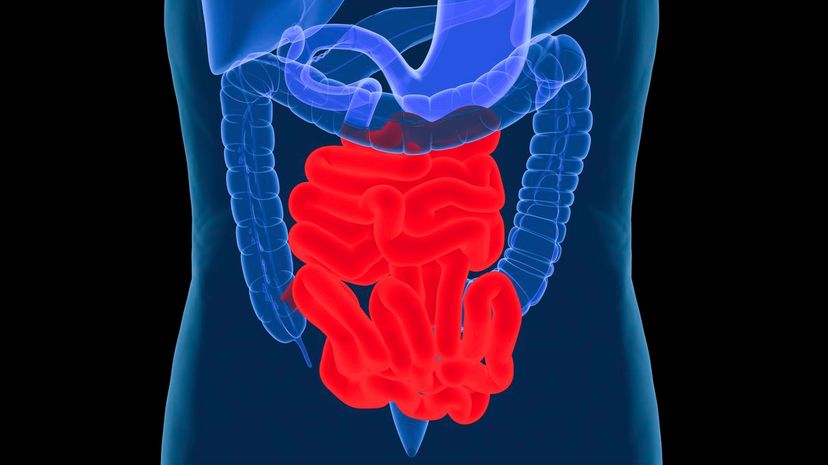
Your small intestines measure roughly 20 feet. Whereas your stomach is responsible for breaking down food and your large intestines are responsible for absorbing water, the main job of your small intestines is to absorb nutrients.
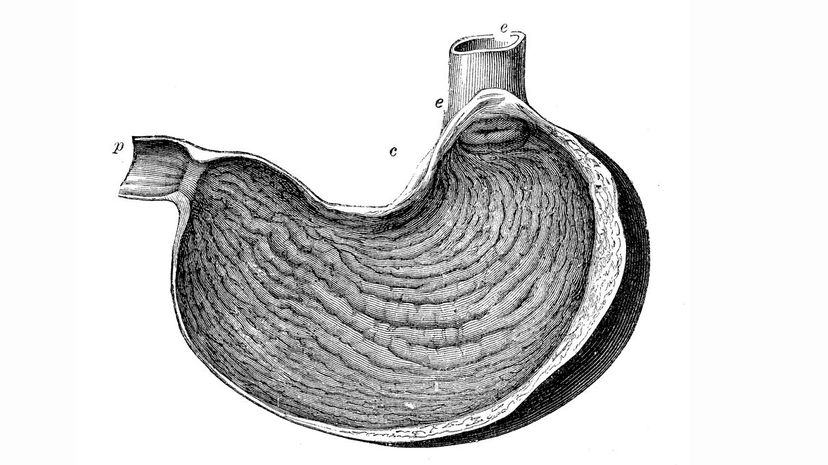
Besides breaking food, your stomach also releases a hormone called ghrelin. When your stomach is empty, it produces this 'hunger hormone' that signals to your brain that it's time to eat. If you're trying to lose weight, you can reduce ghrelin by eating filling, low-calorie foods.
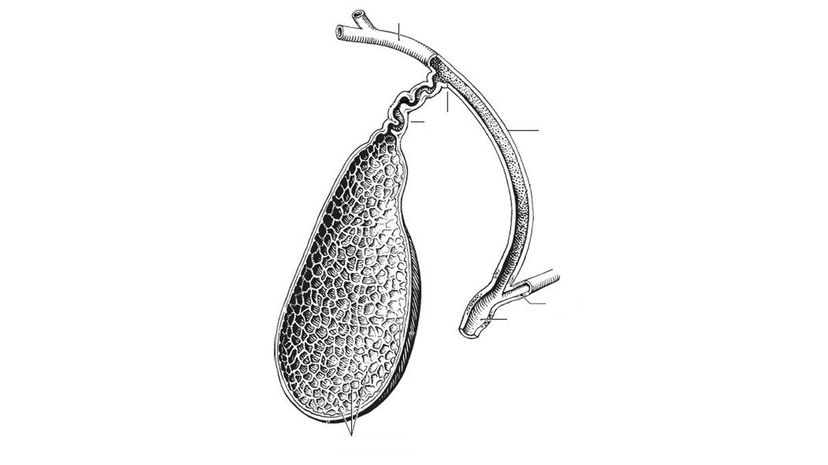

Your gallbladder stores bile produced by your liver to help break down fatty foods. You can survive without your gallbladder, but your doctor will probably prescribe a low-fat diet. Without a gallbladder, bile flows directly from the liver to the small intestines.
Advertisement
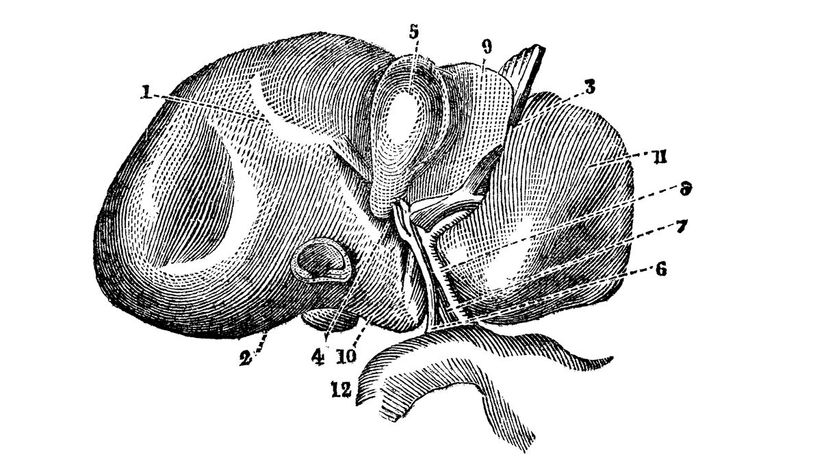
Most of your organs only have one or two functions, but your liver has dozens. Some of its many jobs include storing sugar to keep your blood sugar balanced, creating hormones, making proteins and filtering blood.
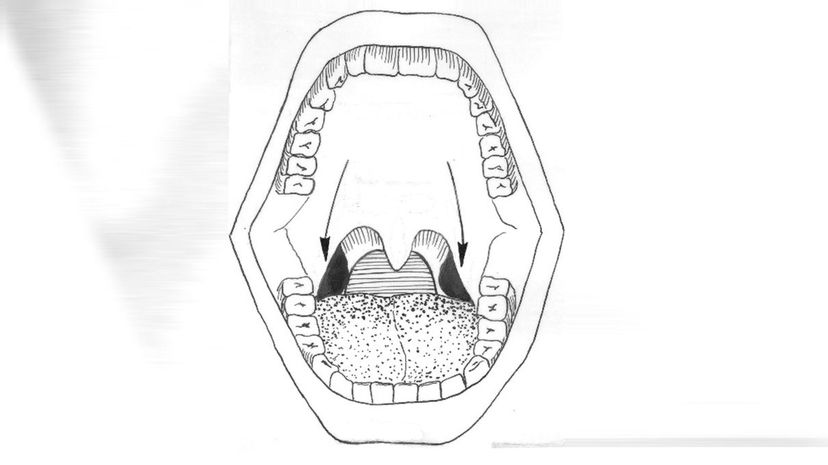
Did you get your tonsils removed as a kid? Many people do if they become infected repeatedly, and it's thought that people have been performing tonsillectomies for thousands of years! Your tonsils are a lymph organ, which means they play a role in boosting your immune system.
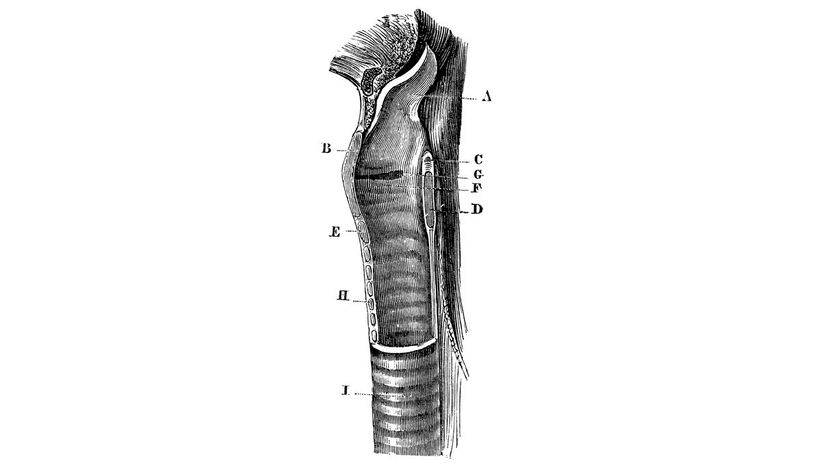
Your larynx is more commonly known as your voice box. You can see it on the front of your throat if you tilt your head up. Your larynx produces sound, but unless you want to speak in Morse code, you still need your mouth to differentiate between different consonant and vowel sounds.
Advertisement

Take a deep breath and feel your lungs expand in your chest. Did you know that your right lung has more lobes than your left? Your left lung only has two lobes instead of three to make room for your heart.
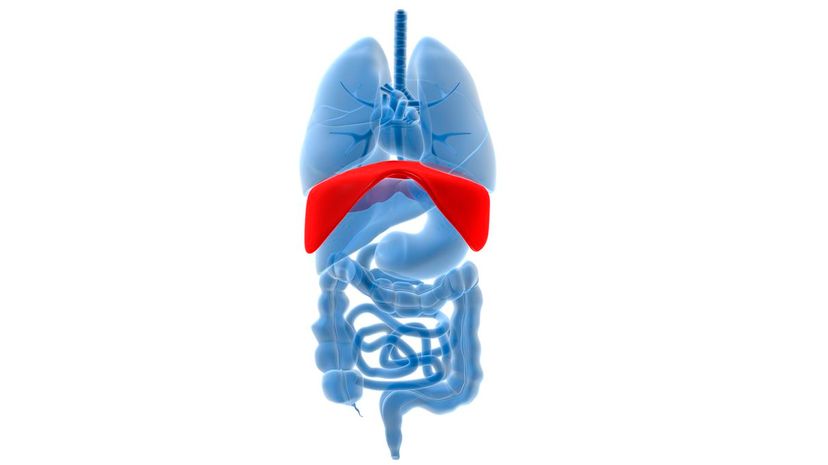
If you take a deep breath that engages your whole stomach region, you're breathing with your diaphragm. If you're a teacher or somebody who speaks loudly regularly, you're probably already familiar with the power of the diaphragm.
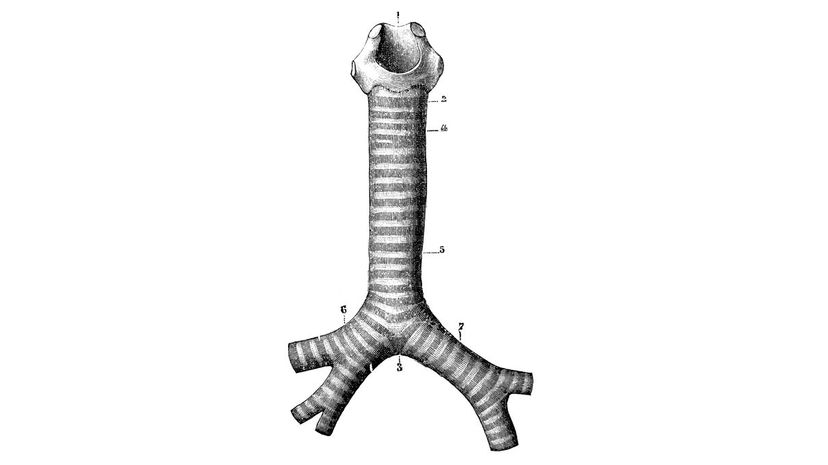
Don't let your trachea get clogged or you won't be able to breathe. For most people, their 'windpipe' is only about an inch in diameter, and in children, it's even smaller. No wonder they put those chocking hazard signs on toys.
Advertisement
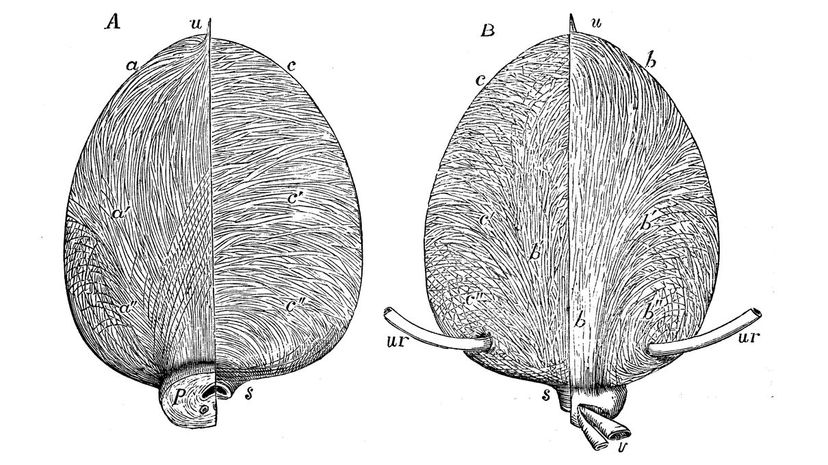
Do you know what your bladder is connected to? Two tubes called ureters connect your kidneys to your bladder. It's your kidneys' job to create urine, and your bladder's duty to hold it. For most people, the bladder holds between one and two cups of liquid.
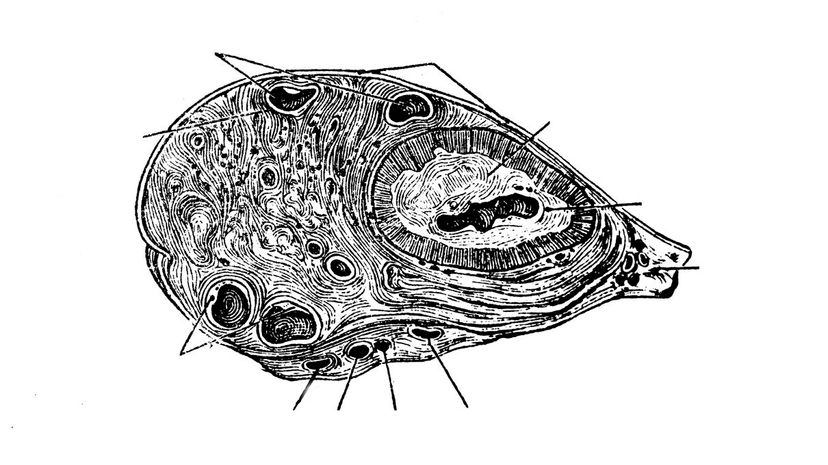
The ovaries serve several functions. They contain the eggs used for fertilization, but they're also the leading site of estrogen production. Ovaries also produce a small amount of testosterone (much less than men produce).
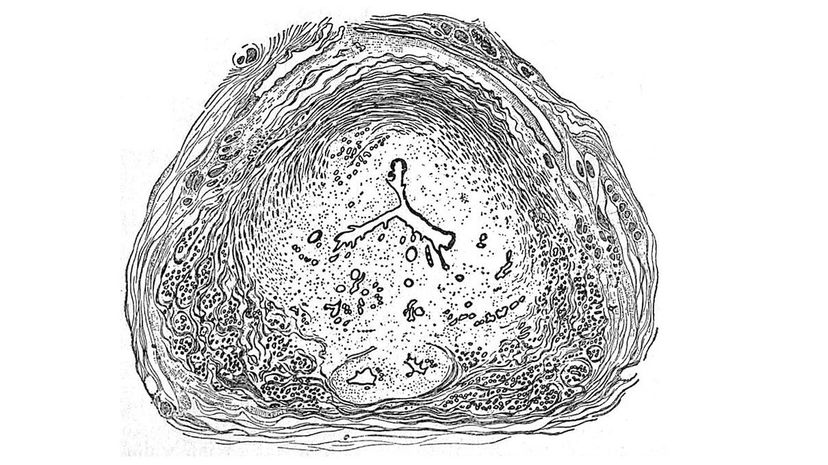
The walnut-sized prostate creates seminal fluid, which mixes with sperm to make semen. Prostate cancer is one of the most common causes of death in older men. Almost 4% of men die of prostate cancer.
Advertisement
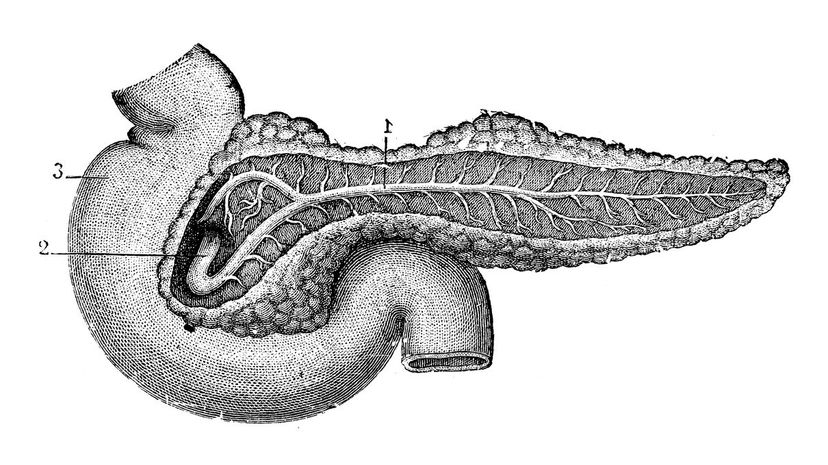
Your pancreas produces insulin, which regulates your blood sugar. Cancer of the pancreas is usually fatal because it's hard to detect in the early stages. Right now, the survival rate of pancreatic cancer is about 20%.
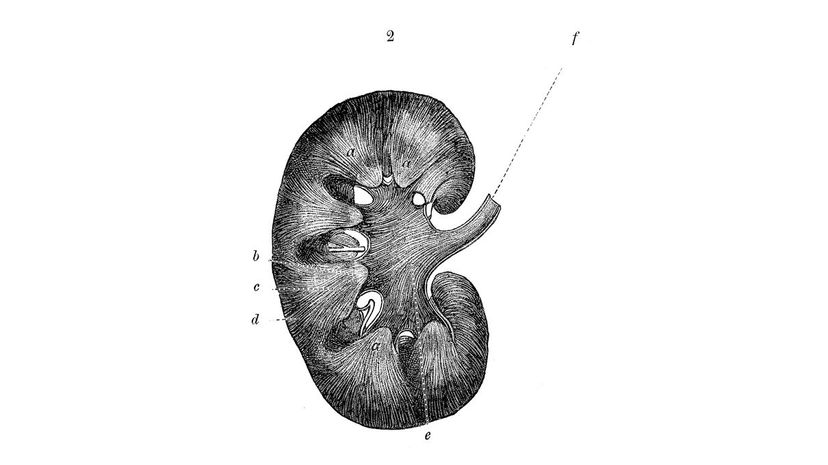
Your kidneys act like Brita filters for your blood. Anything that needs to be removed is sent to your bladder for excretion. Your kidneys are also responsible for regulating your mineral balance.
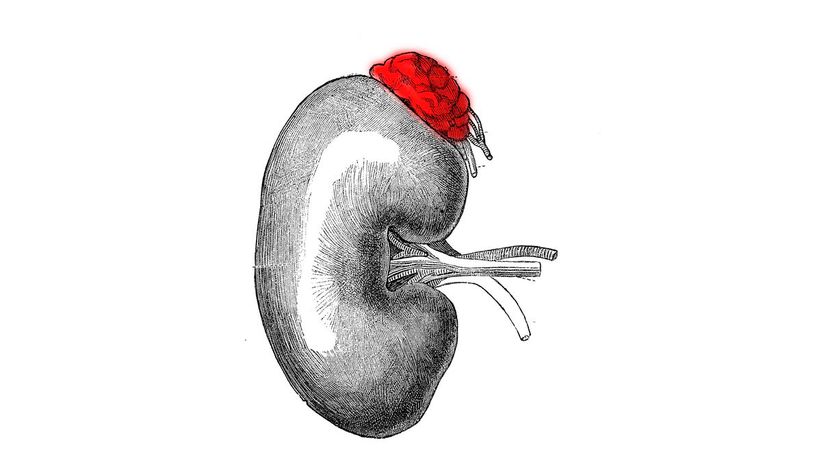
Your adrenal glands produce several other essential hormones besides adrenaline. These include your stress hormone cortisol and your sodium-saving hormone aldosterone. They also produce a small amount of testosterone.
Advertisement
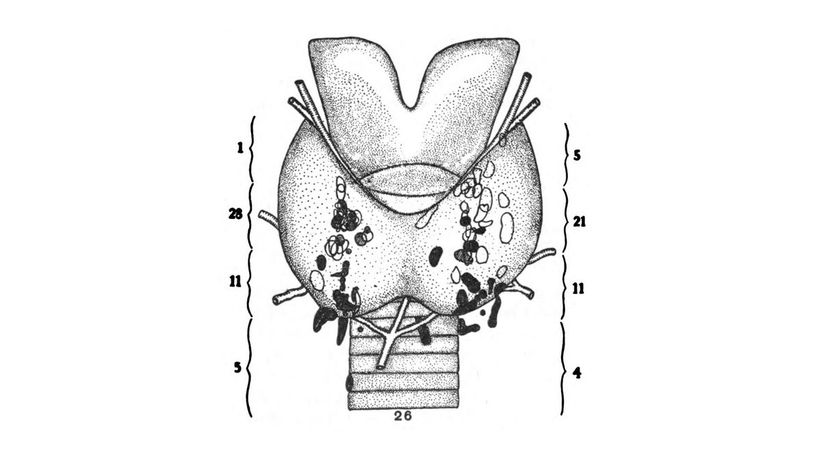
Your parathyroid glands are located behind your thyroid glands in the front of your throat. Do you know what their function is? They release parathyroid hormone, which plays a role in your body's calcium balance.
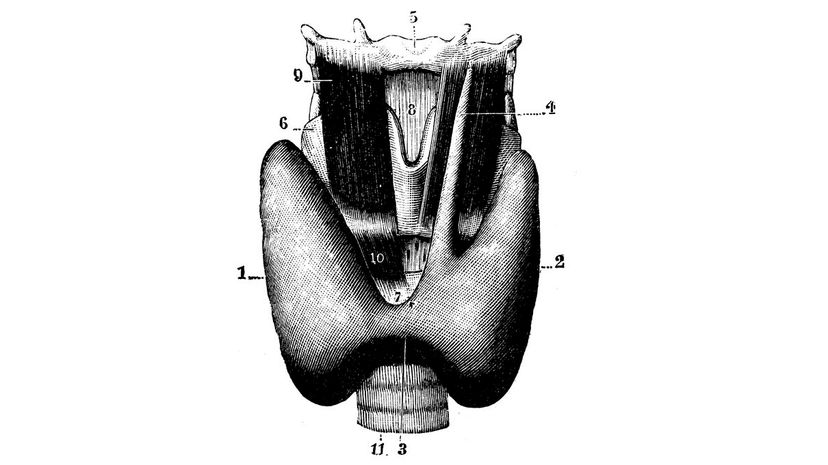
Your thyroid gland is responsible for regulating your metabolism. If your thyroid hormone levels drop, you'll usually notice a decline in your energy levels and weight gain. The opposite is true for when your thyroid is overactive.
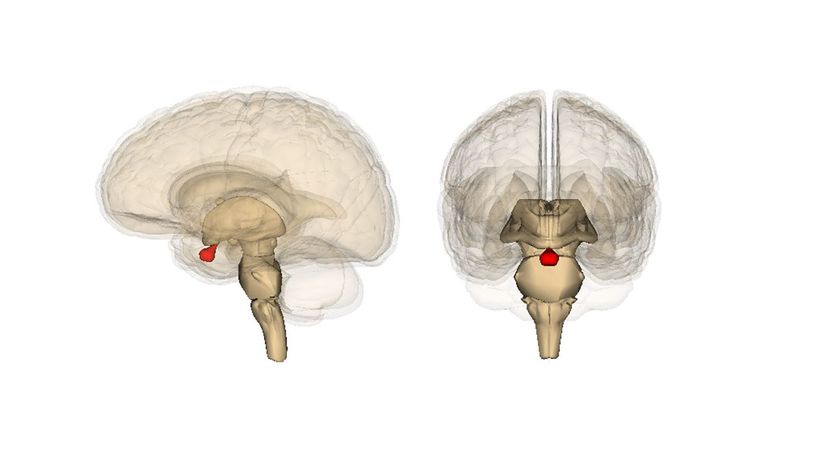
Your pituitary gland produces human growth hormone, which is essential for the production of new muscle, bone and connective tissue. Have you ever heard of athletes taking HGH for performance benefits? It's the same hormone that your body produces naturally.
Advertisement
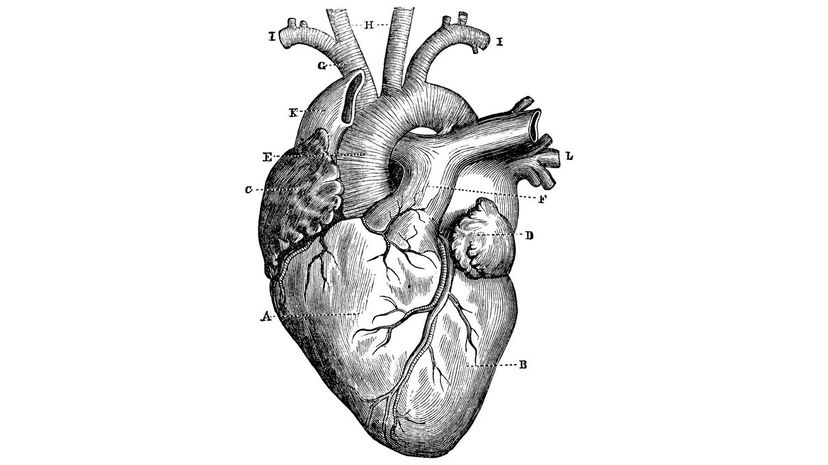
It may not look like the kind of heart you see on Valentine's Day, but your heart (along with your brain) is the most important organ in your body. Amazingly enough, surgeons are now able to perform complete heart transplants.
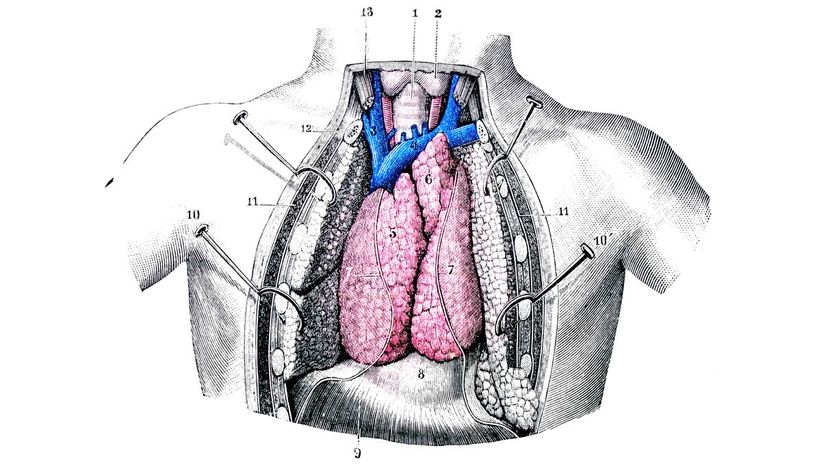
Your thymus gland store T-cells that help your body adapt to foreign invaders. Once you become an adult, your thymus gland is replaced by fat. It's essential for small children with developing immune systems.
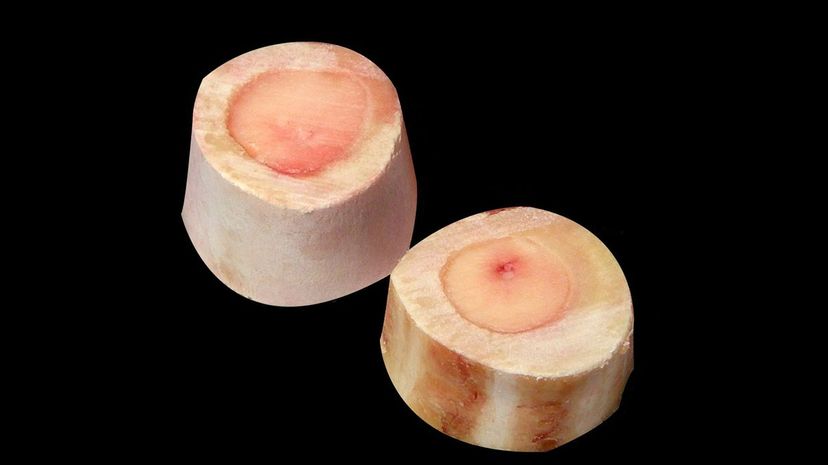

Your bone marrow is the site of hematopoiesis or the production of new blood cells. A large portion of your bodyweight is bone marrow. In the average person, the bone marrow makes up about 4% of the total mass.
Advertisement
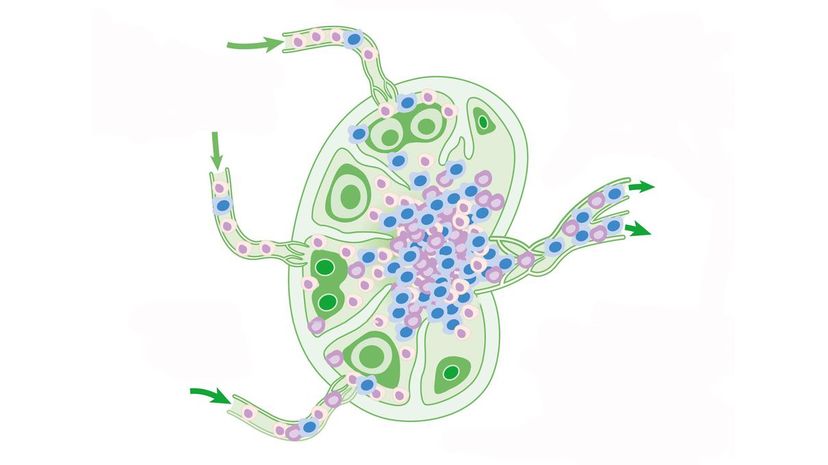
Your lymph nodes are connected by a serious of tubes called lymphatic vessels. When you have an infection, your lymph nodes can become swollen as your body tries to fight it off. Unfortunately, cancer can spread through your lymph system.
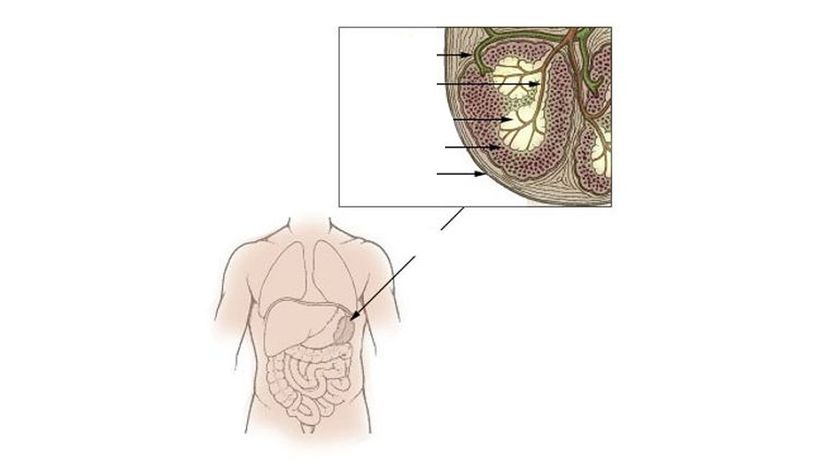
As your blood flows throw your spleen, the organ checks your blood cells for damage. If the red blood cells are old or damaged, it breaks them down. Your body also uses your spleen to store extra blood.
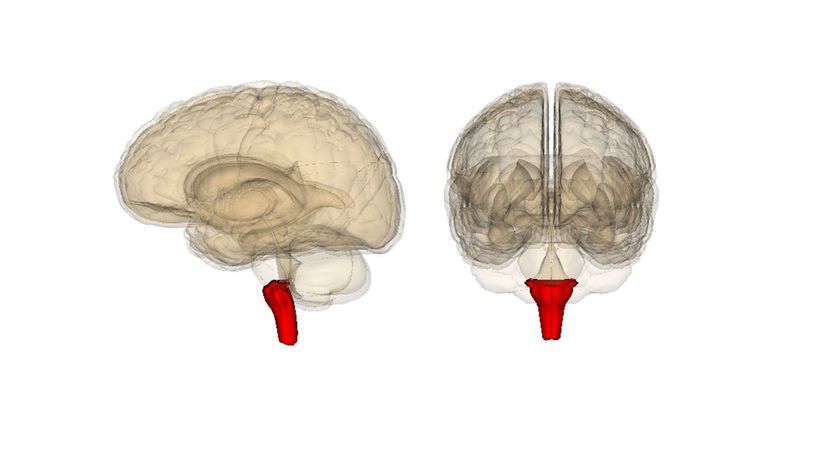
Your medulla oblongata is the part of your brain stem responsible for several essential processes including digestion, controlling your heart and swallowing. It's the lowest part of your brain before it transitions into your spinal cord.
Advertisement
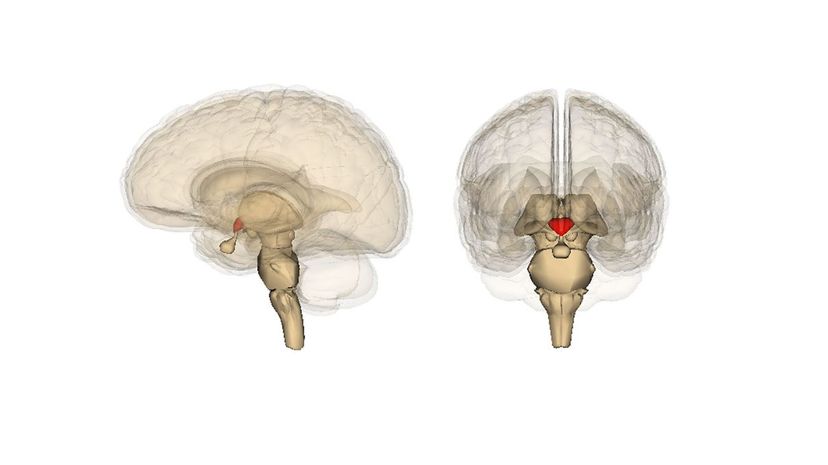
Your hypothalamus may only be a small part of your brain, but it plays a critical role in regulating the hormones in your body to make sure their concentration doesn't get too high or too low. It also regulates your body temperature.
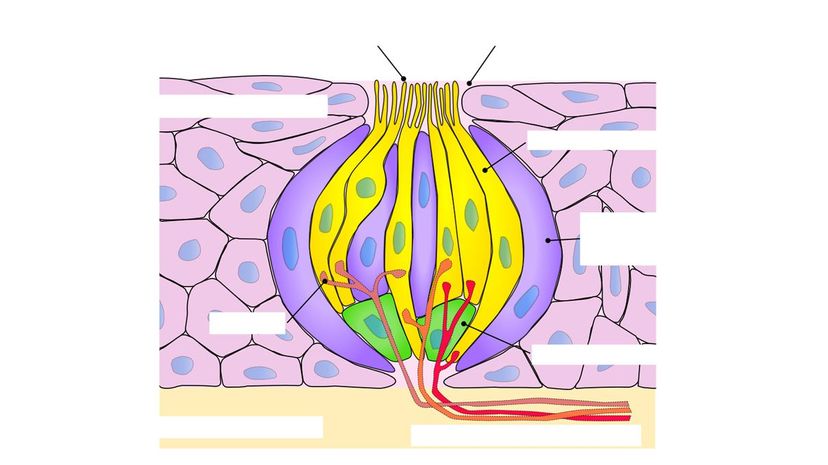
You may have learned that there are four types of taste buds: sweet, sour, salt and bitter. However, there's a fifth type of flavor called umami. It's the savory taste of meats and some fermented products.
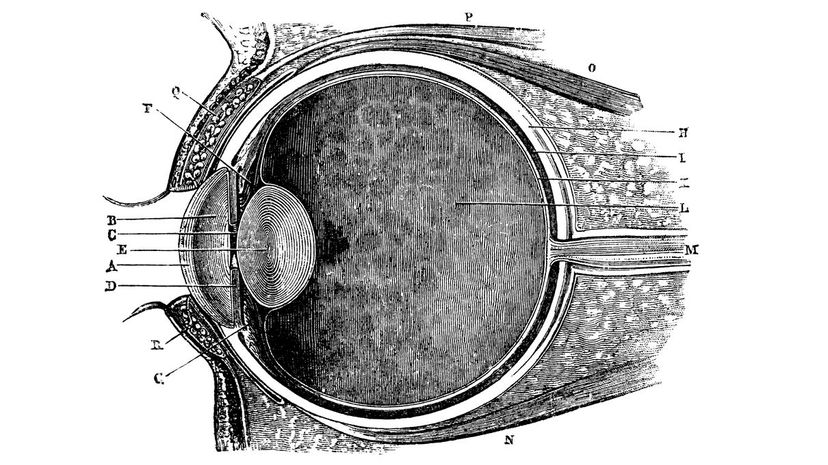
Your retina is the part of your eye that senses light and sends information to your optic nerve. It's located along the back of your eyeball so that light hits it after passing through your pupil.
Advertisement
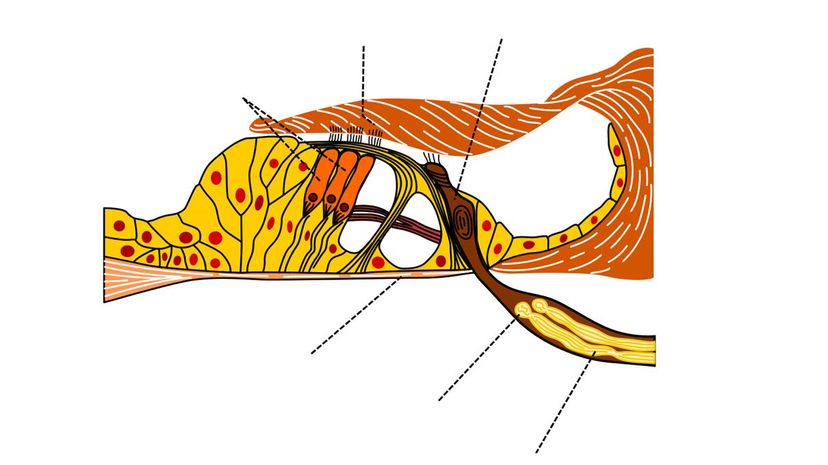
Your organ of Corti is located inside of your cochlea and helps with the transduction of sound vibrations into neural impulses. It was first discovered in 1851 by an Italian scientist.