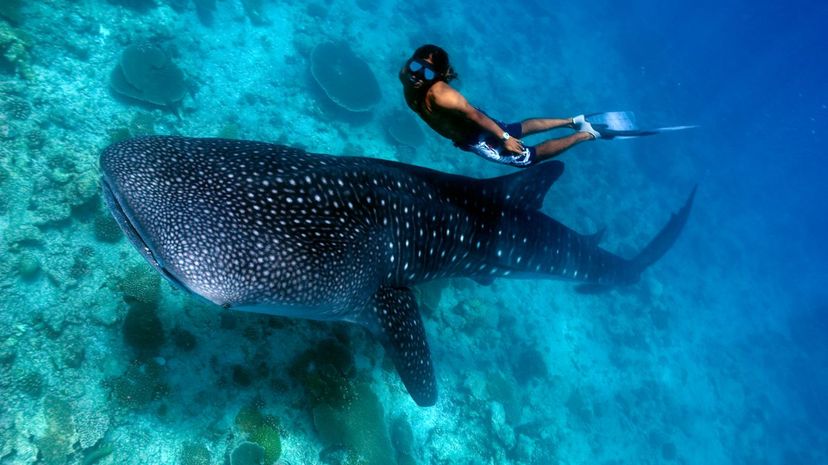

About This Quiz
"Are you ready to dive into the world of sharks and test your knowledge? From the infamous great white to the gentle nurse shark, this shark identification quiz will challenge your skills in identifying different types of these fascinating creatures. Don't let the fear instilled by movies like ""Jaws"" cloud your judgment - most shark species are harmless or only attack humans by mistake. Take a bite out of this quiz to see if you can recognize 40 different types of sharks!
Despite their fierce reputation, sharks are actually more endangered by humans than the other way around. With threats like overfishing, pollution, and habitat loss, many shark species are facing the risk of extinction. It's crucial for us to respect these ocean predators, learn about their importance in the ecosystem, and work towards their protection. So, join us in this fin-tastic quiz to show off your shark identification skills and spread awareness about these amazing creatures!
Whether you're a shark enthusiast or just looking to challenge yourself, this quiz is the perfect opportunity to learn more about these incredible animals. From the massive whale shark to the elusive goblin shark, you'll have the chance to test your knowledge and maybe even discover some new species along the way. So, jump in and see if you have what it takes to identify these different types of sharks! Good luck!
"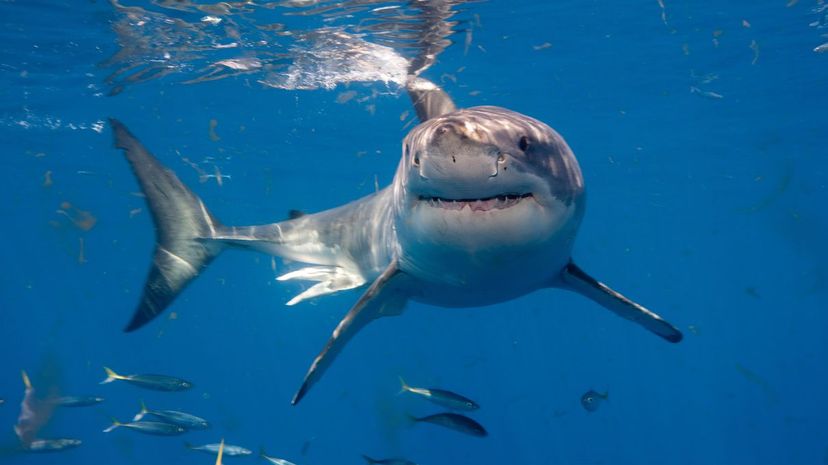
The great white shark is certainly a formidable predator, largely due to its immense size: Some can grow up to 20 feet long! The only predator they seem to fear is the orca, also known as the killer whale.
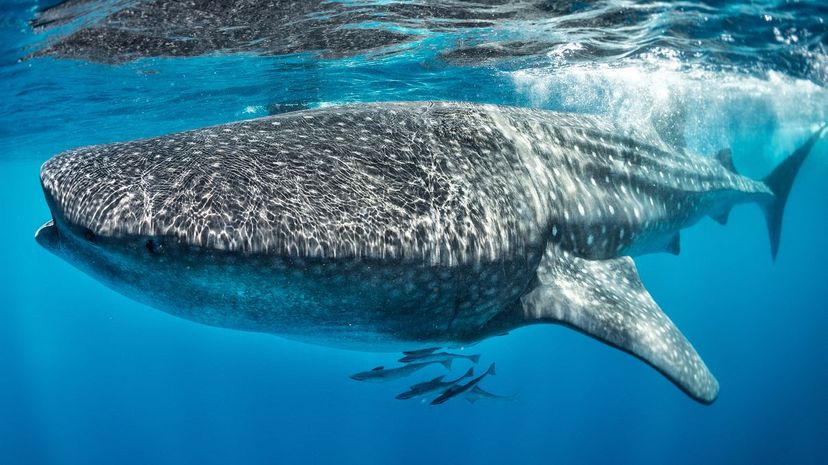

Despite their tremendous size, whale sharks are harmless to humans. As filter feeders, they eat plankton and tiny fish with their large gaping mouths. Some scientists believe they can live to be 130!
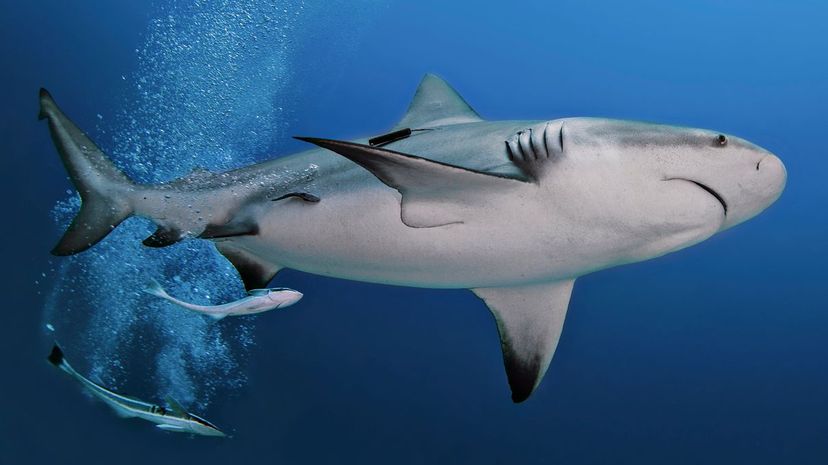

Because the bull shark can swim in both seawater and freshwater, it's been discovered as far as 700 miles up the Mississippi River. Bull sharks get their name for their bullish shape and temperament.
Advertisement
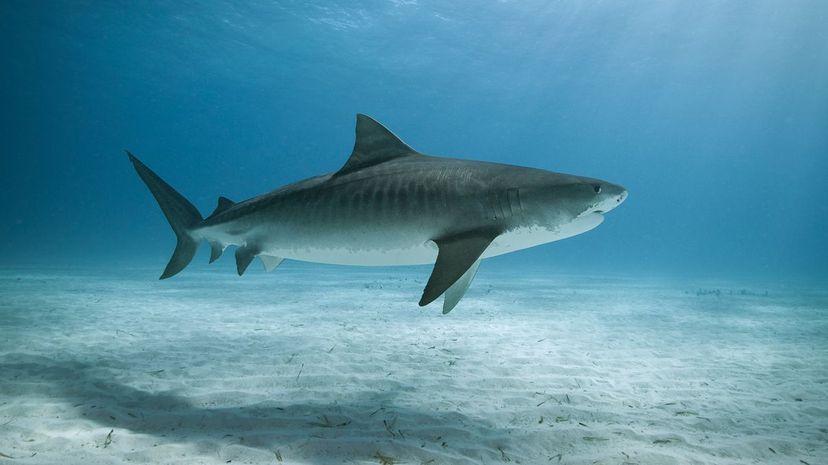

The fierce tiger shark comes in second place (after the great white) for fatal shark attacks on people. Its stripes fade over time, and the tiger shark can reach a length of 16 feet.
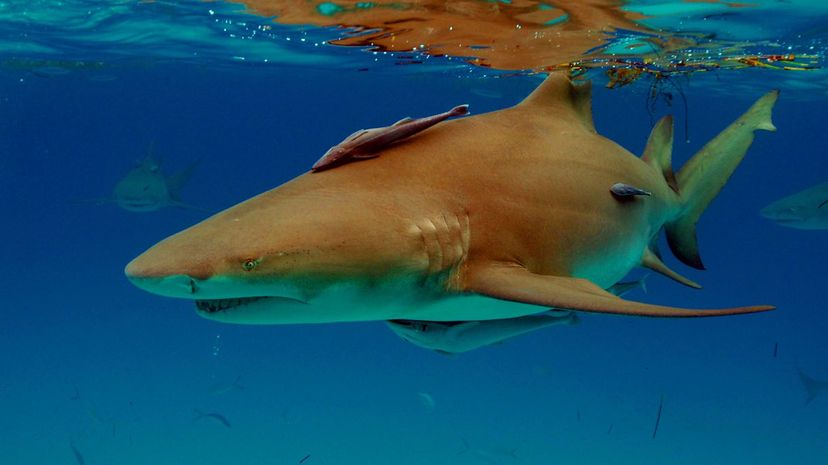

Lemon sharks tend to live in communities and travel back to the same location to reproduce. These nocturnal hunters use electroreceptors to find fish and pose no substantial risk to humans.
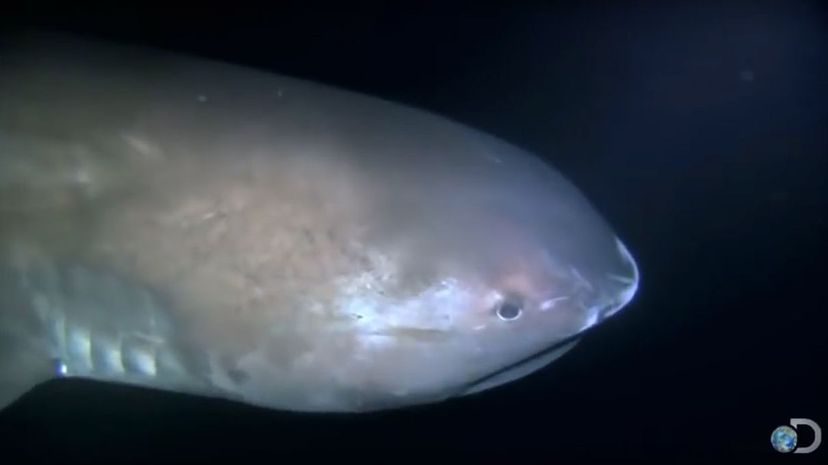
So few megamouth sharks have been captured that scientists don't know too much about it, except that it's a filter feeder like the whale shark and basking shark. It has a bulbous head and a wide mouth.
Advertisement
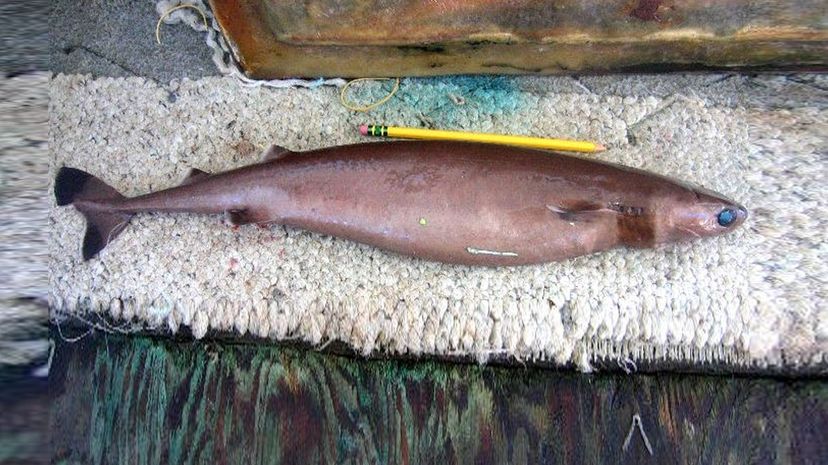

Although reaching only 22 inches in length, the cookiecutter shark is not afraid to take a bite or two out of much larger animals. It gets its name from the way it extracts "plugs" of flesh from prey.
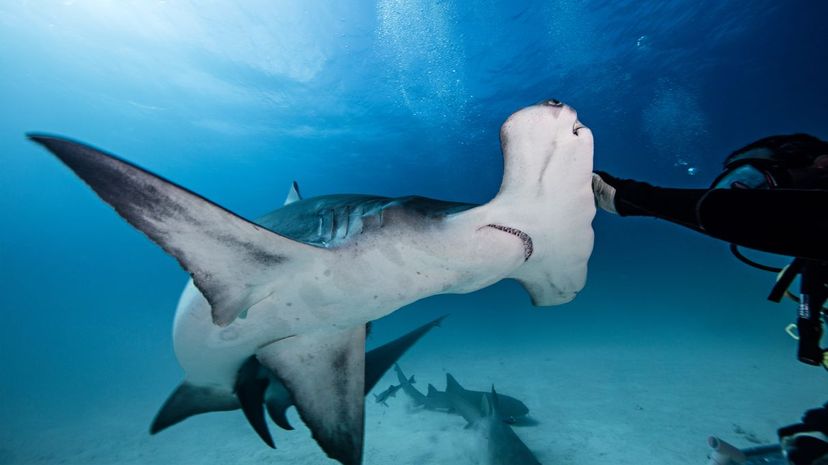

Hammerhead sharks are unique in that they swim together in schools in the daytime and hunt alone at night. Scientists believe the shark's hammer-like head gives it 360-degree vision.
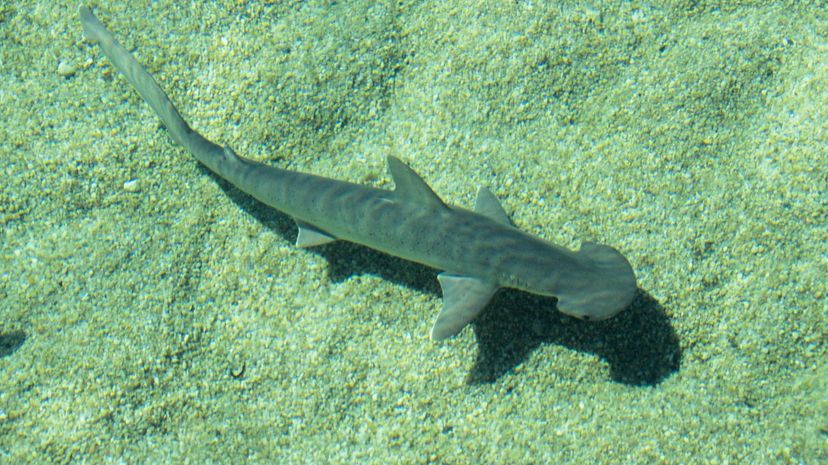

We suppose the bonnethead's head may resemble a bonnet, although it could also be described as a shovel or a taco! This shark only grows to about three feet in length and eats plants as well as fish.
Advertisement
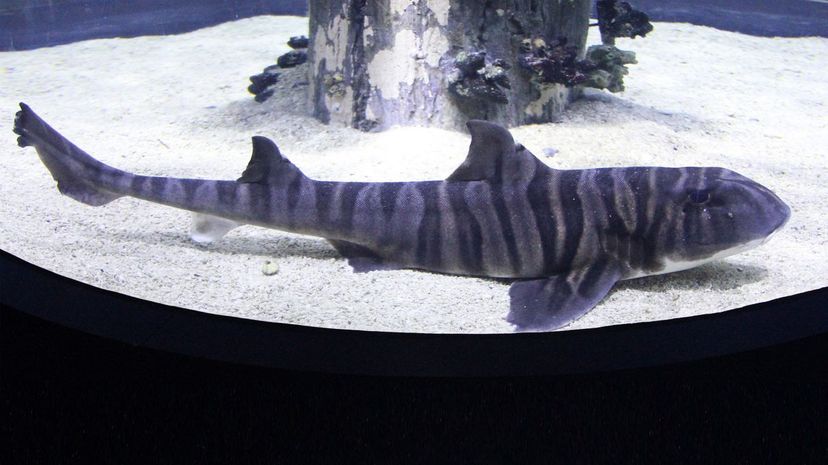

While young zebra sharks have a stripe pattern, those stripes morph into spots as the shark ages. Zebra sharks spend their days lying still on the ocean floor but come out to hunt at night.
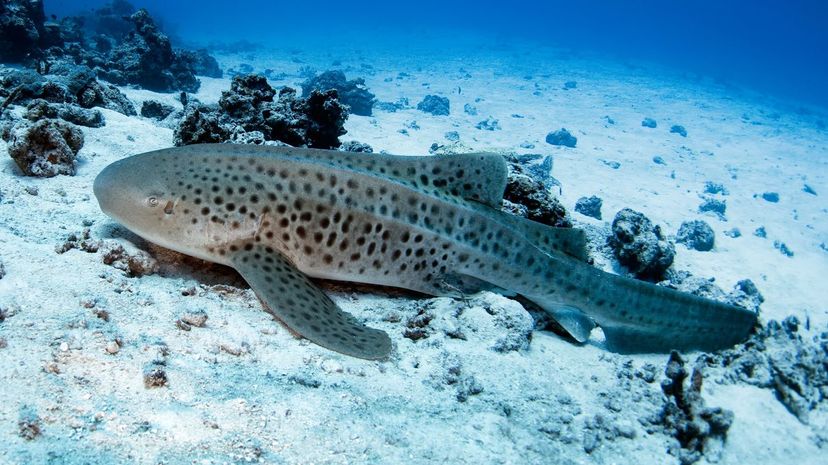

Named for the distinctive spots and "saddles" on its back, the leopard shark swims in schools, usually at night. Although they're commonly spotted near the coasts, they don't threaten humans.
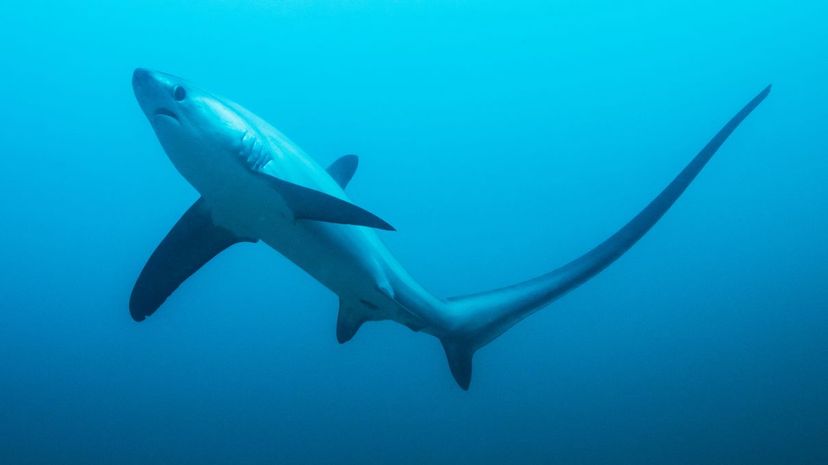

The solitary thresher shark lives in temperate and tropical oceans. It's named for its long tail, which is often as long as the shark's body. Threshers use this tail to stun prey.
Advertisement
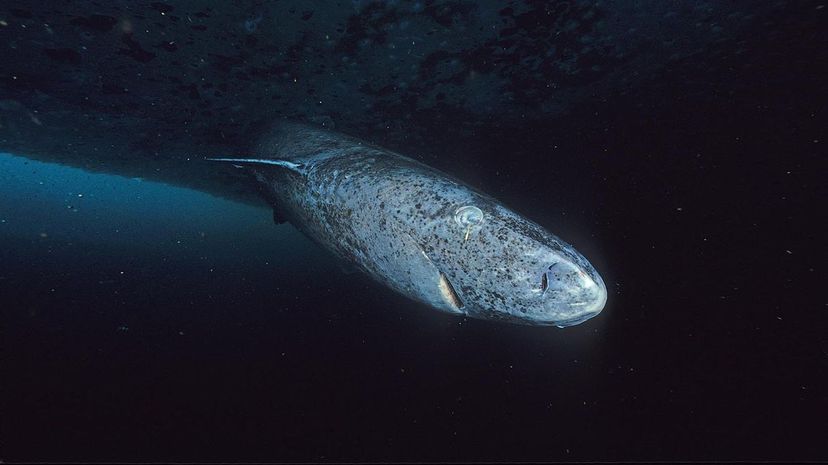

Researchers used radiocarbon dating to determine that Greenland sharks are the longest-living vertebrates in the world. They can grow up to 24 feet long, and they live in the North Atlantic and Arctic Oceans.
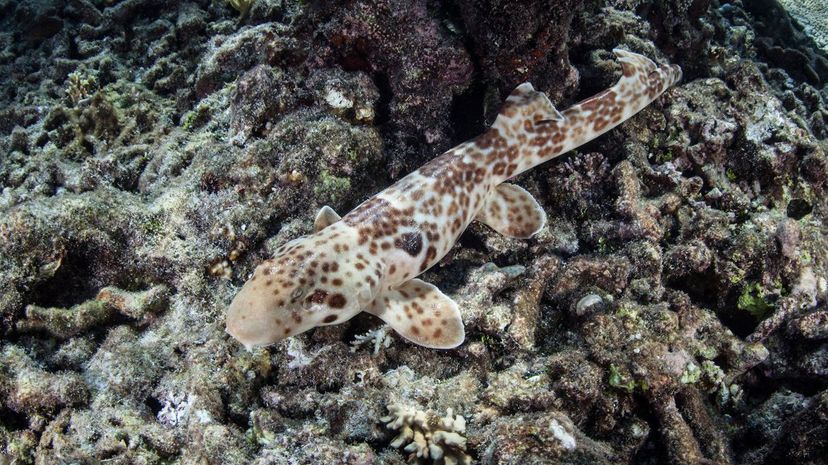

The epaulette shark has distinctive spots behind its fins, calling to mind the epaulettes on military uniforms. These sharks primarily live in the warm waters around Australia and New Guinea.
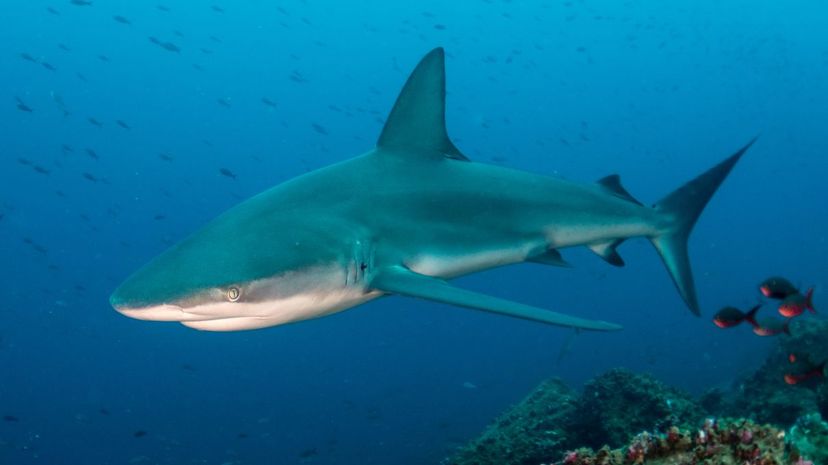

The scientists who named this shark found it in the Galapagos Islands, hence the name. The shark can reach about 10 feet in length and likes to snack on bony fish, octopuses and squids.
Advertisement
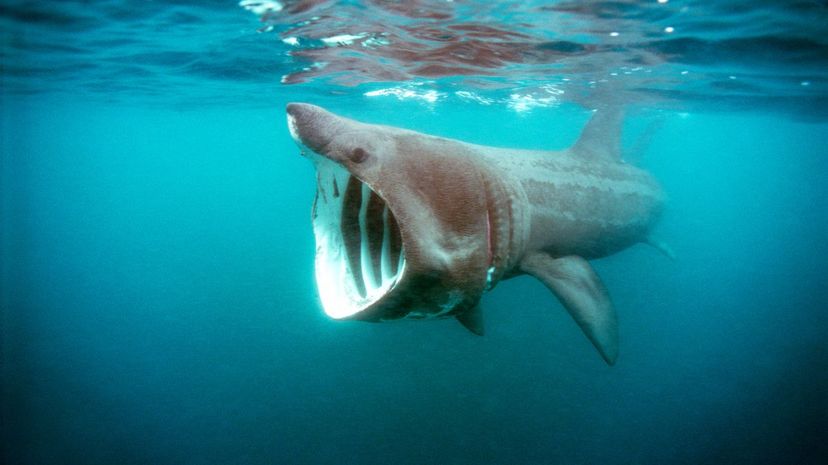

Along with the whale shark and megamouth, the basking shark eats primarily plankton as a filter feeder. And while it can grow up to 26 feet long, it's a slow swimmer and not an aggressive species.
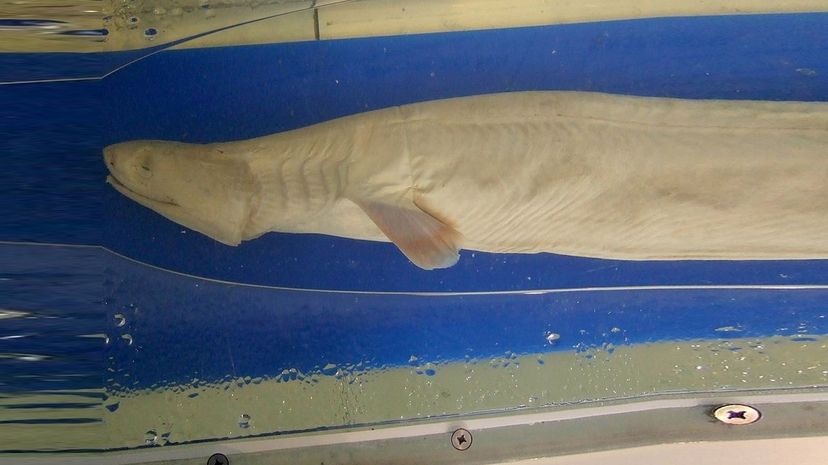

It's a good thing this shark typically stays thousands of feet underwater, because it looks simply terrifying! The frilled shark has a long, eel-like body and a stretchy mouth that lets it eat prey whole.
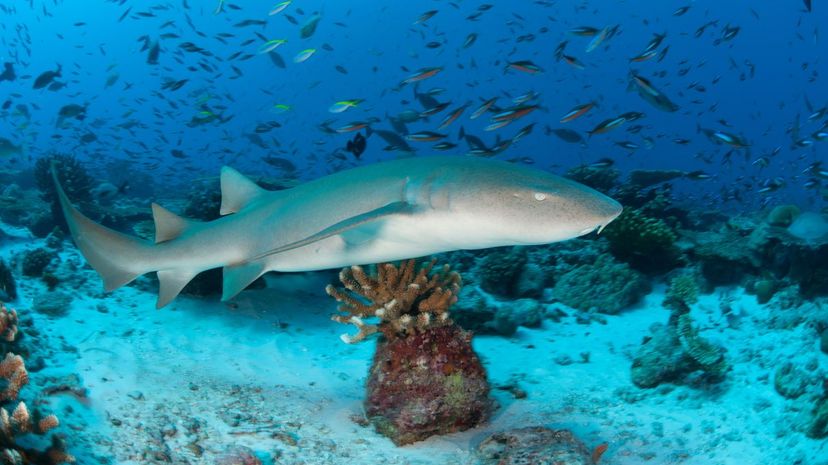

Don't underestimate the nurse shark! Even though it tends to be slow and inactive, it ranks fourth in shark attacks on people. Nurse sharks are brown in color and grow up to 10 feet long.
Advertisement
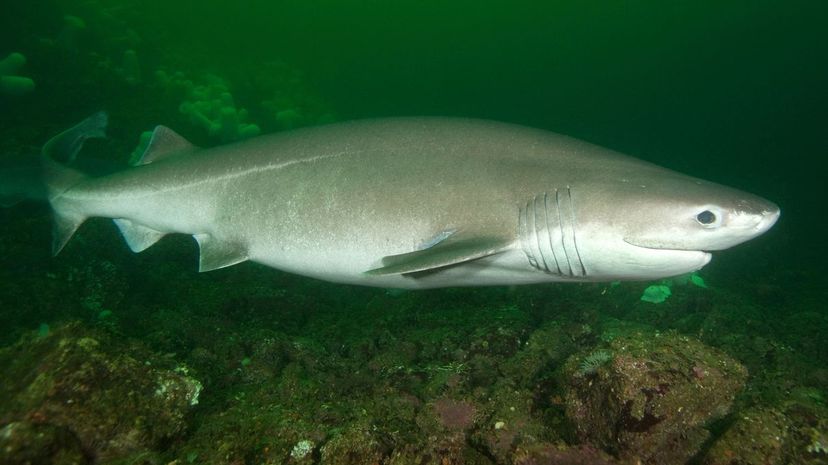

As the name suggests, the bluntnose sixgill shark has a blunt snout and six gills - and can grow up to 26 feet long! This shark also has fluorescent blue-green eyes, the better to terrify its prey!
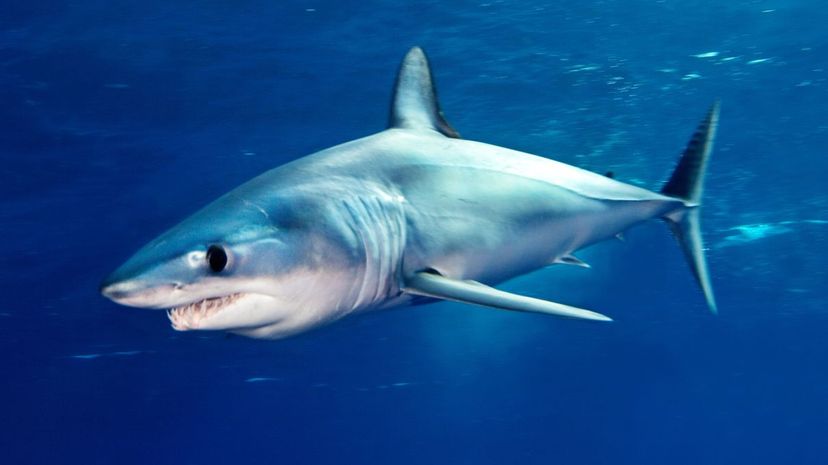

There are two types of mako sharks alive today: shortfin and longfin. A type of mackerel shark, the mako is blue and grey in color. The shortfin mako is the fastest shark, reaching speeds of 42 mph.
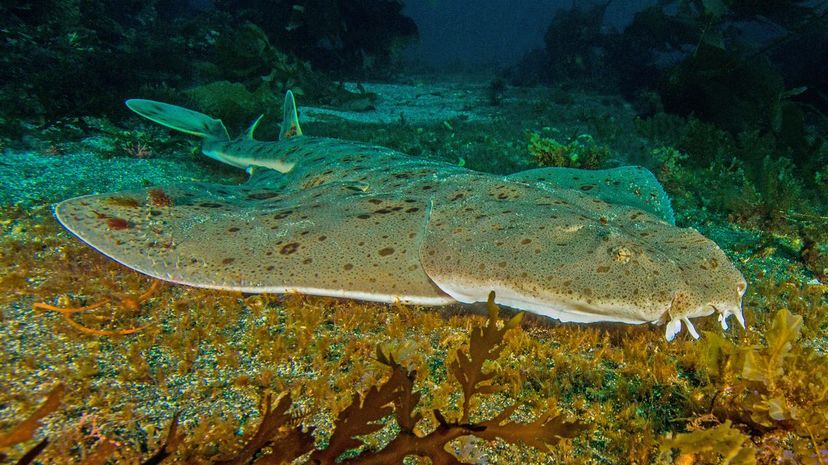

With is flat body and wide pectoral fins, the angel shark looks like a ray. The shark lies motionless in the sand until the prey is overhead; then it lunges upward and captures its meal.
Advertisement
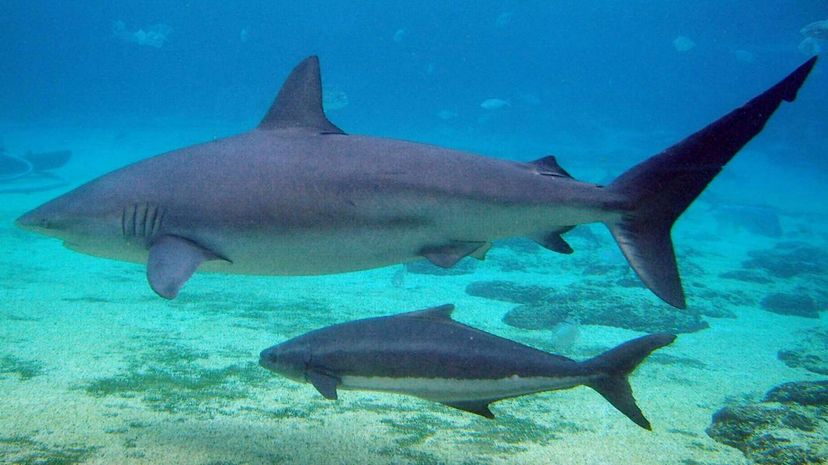

Dusky sharks have no natural predators - except for humans. Because dusky sharks have slow reproductive cycles, they're vulnerable to being overfished. They will also eat anything, including garbage.
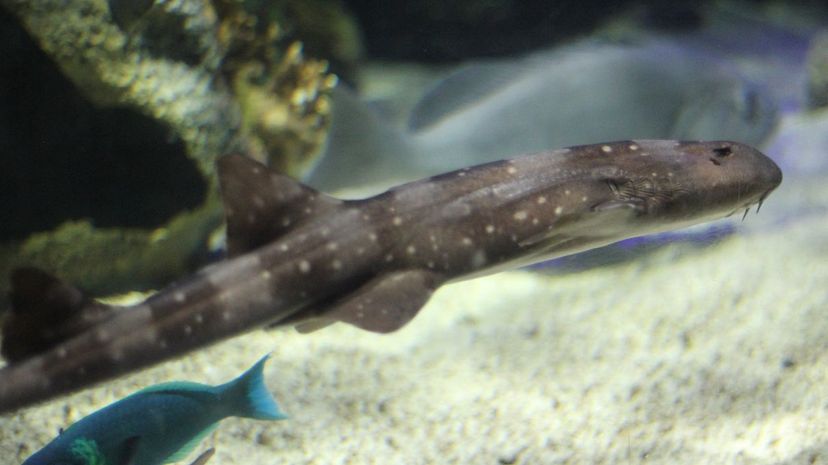

Whitespotted bamboo sharks grow to only 24 to 37 inches, so some people keep them as pets. They have an easily recognizable appearance, with a round snout, narrow body, brown stripes and white spots.
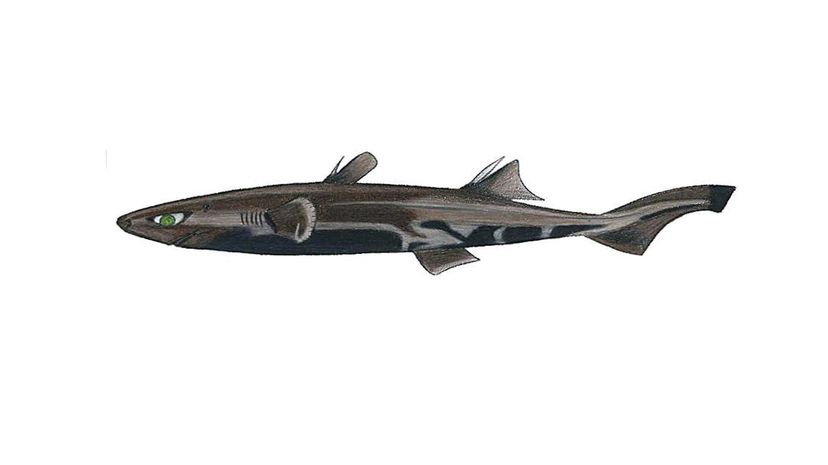

Growing only about seven inches, the dwarf lantern shark is the smallest known shark in the world. Most are found in the Caribbean near Colombia and Venezuela. Females have two or three pups at a time.
Advertisement
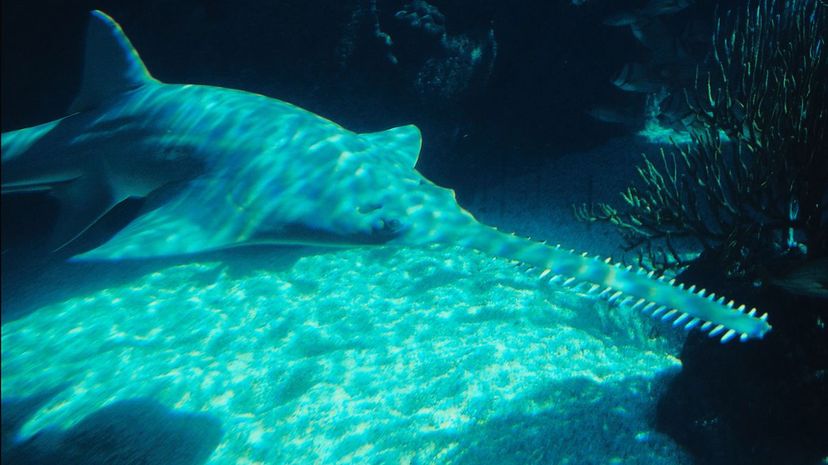

Even though this shark stays pretty deep, it's well known for its long snout edged with teeth, giving it a saw-like appearance. The shark uses this saw to disable its prey (and sometimes predators).
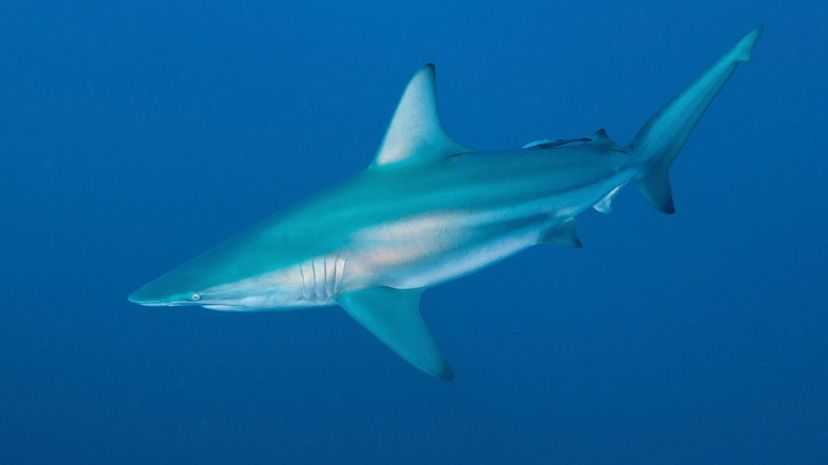

Blacktip sharks get their name from the black coloring on the tips of their fins. They can leap out of the water to catch fish, and females return to the place of their birth to reproduce themselves.
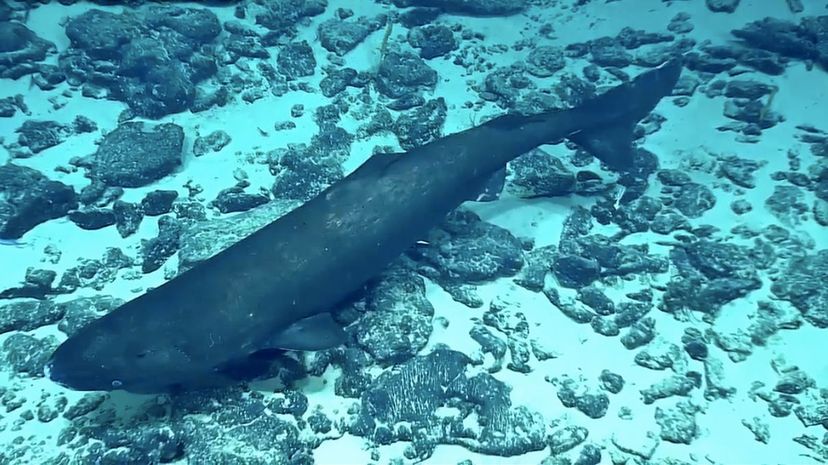

The Pacific sleeper shark is a stealthy predator because of the way it effortlessly glides through deep waters. It uses suction to draw food into its mouth and chops it up with spiky teeth.
Advertisement
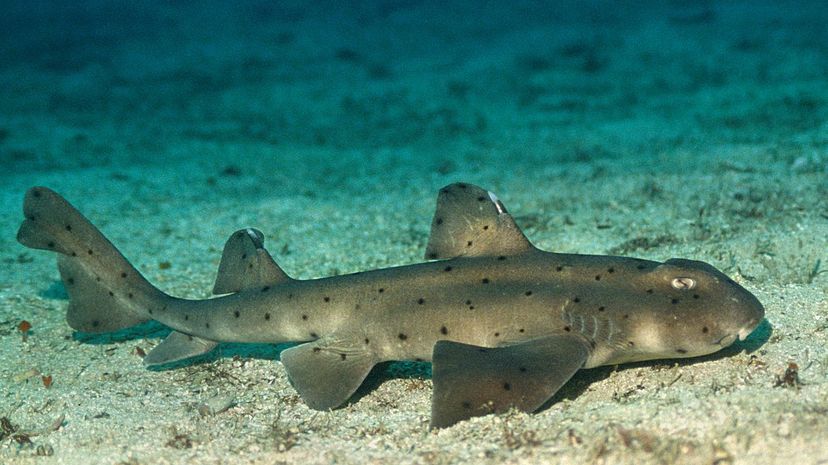

The horn shark has a distinctive appearance with ridges over the eyes and spots over its brown or grey body. It is typically active at night and will leave humans alone if the favor is returned!
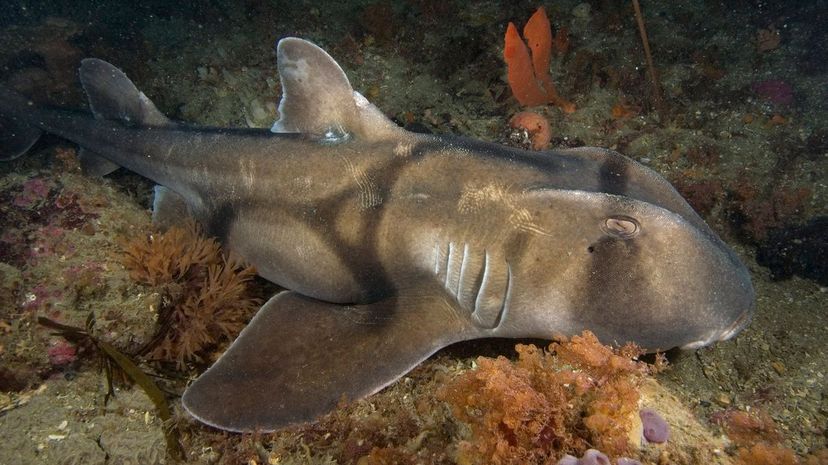

The Port Jackson shark lives in the waters around Australia and migrates south for summers and north for winters. Its distinctive markings make it look like it's wearing a harness.
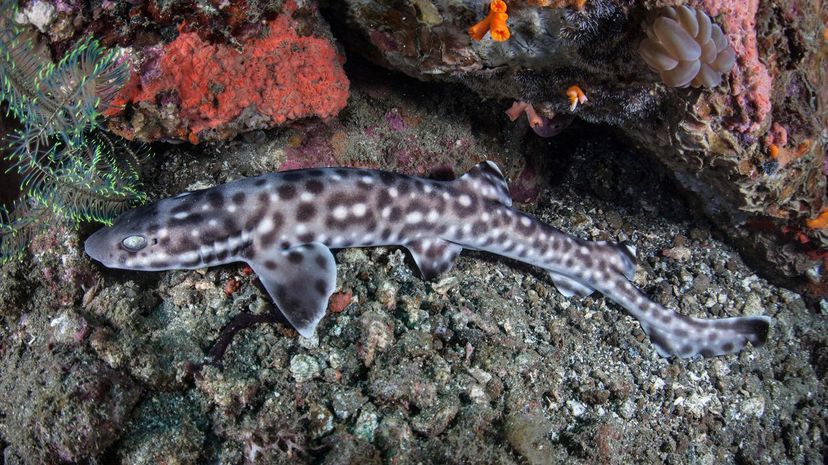

Catsharks live in tropical and temperate waters around the world and may have earned their name from their cat-like eyes. Most catsharks are small and have patterns of spots or stripes.
Advertisement
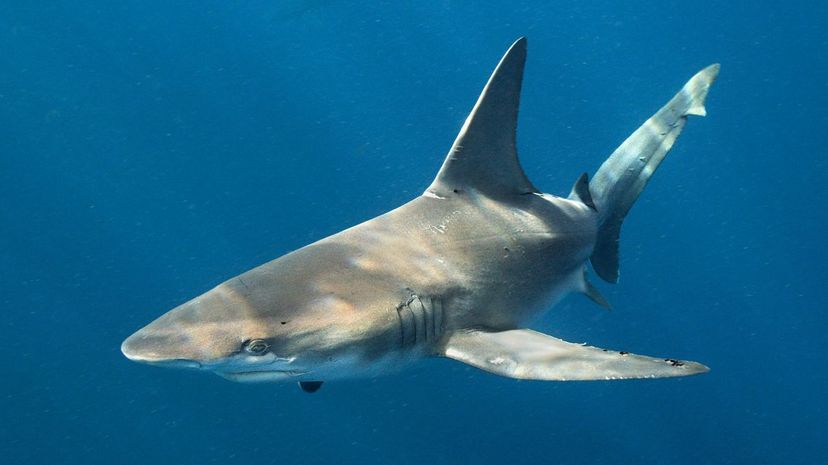

Although the sandbar shark somewhat resembles bull sharks, it's typically harmless to humans. It prefers to eat rays, fish and crabs and must watch out for predators like tiger sharks and great whites.
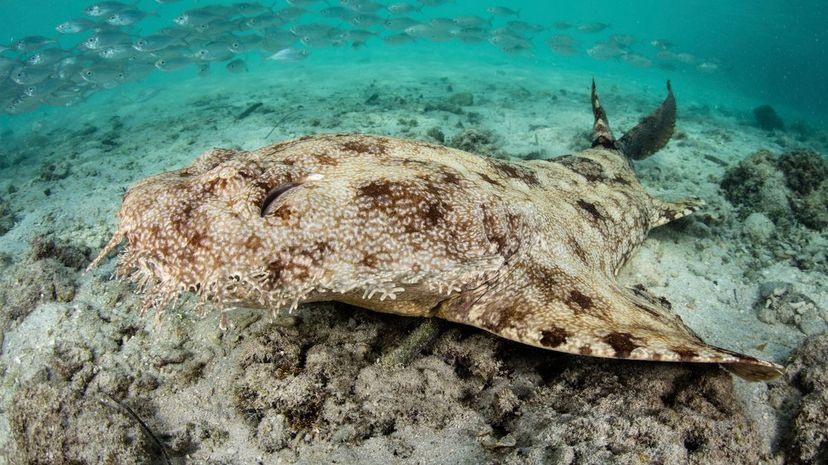

Wobbegongs live around Australia and Indonesia; their name comes from the Aboriginal word for "shaggy beard" due to the "whiskers" around the mouth. Wobbegongs rest on the seafloor and ambush fish.
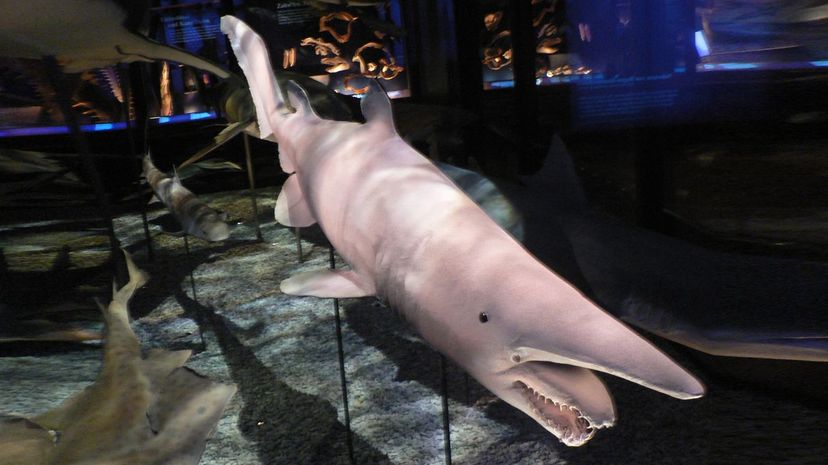

The goblin shark looks like it auditioned for a role in "Alien." The pinkish shark has a long, pointy snout and jaws that extend to gobble prey. Lucky for us, goblin sharks are rare.
Advertisement
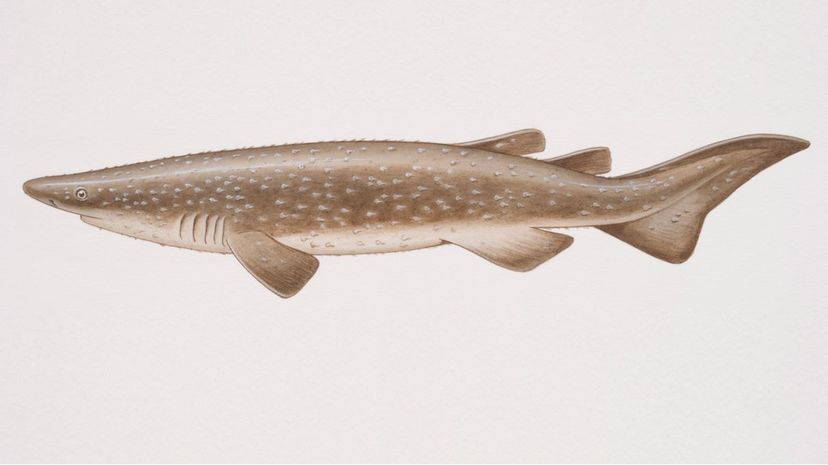

The bramble shark has a cylindrical form that tapers at the head. People rarely bump into this shark because it usually stays at great depths (up to 3,000 feet), feeding on fish and other sharks.
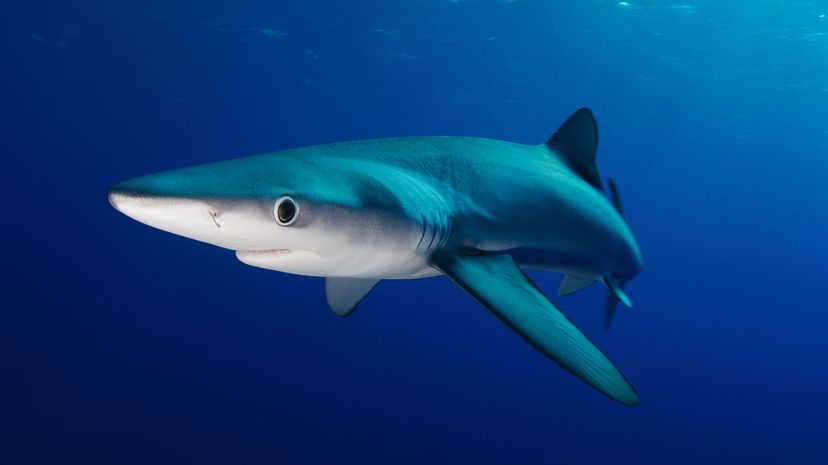

So named because of their blue color on top, blue sharks have large round eyes and a slender build. Blue sharks eat smaller sharks, but they too find themselves hunted by tiger sharks.
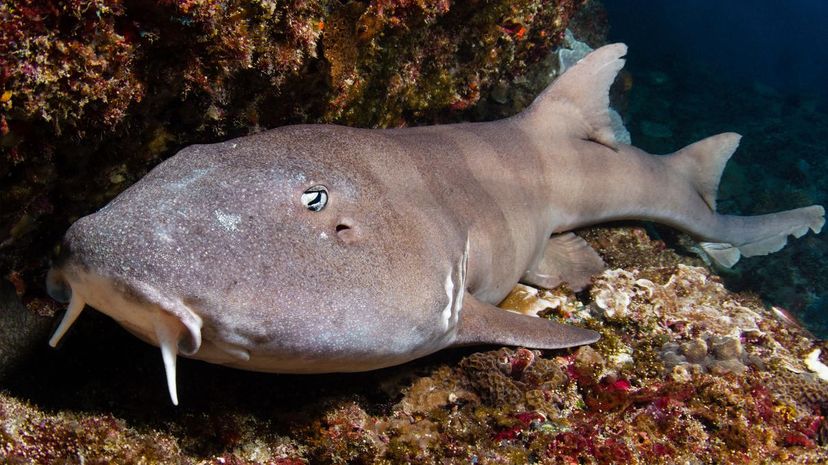

Young brown-banded bamboo sharks have thick brown bands, the adults tend to lose this pattern. This hardy shark makes it home in tidal pools and coral reefs, typically between Japan and Australia.
Advertisement
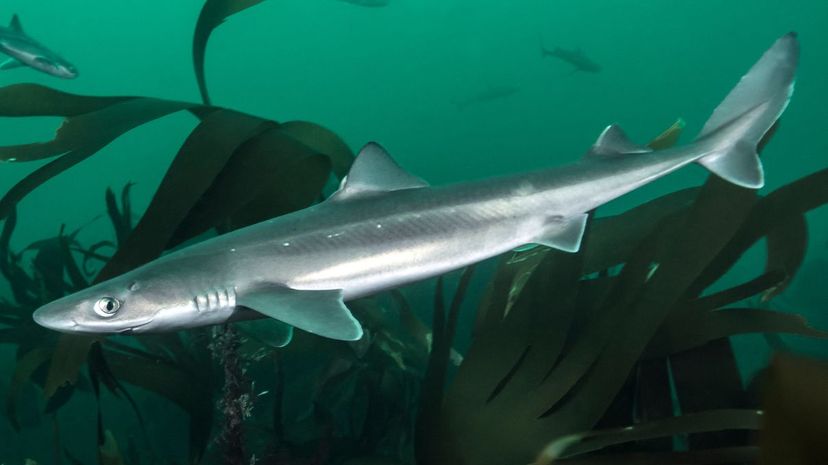

The spiny dogfish has two spines near its dorsal fins that it uses defensively against predators. This aggressive shark prefers to hunt in large packs, sometimes numbering in the thousands.
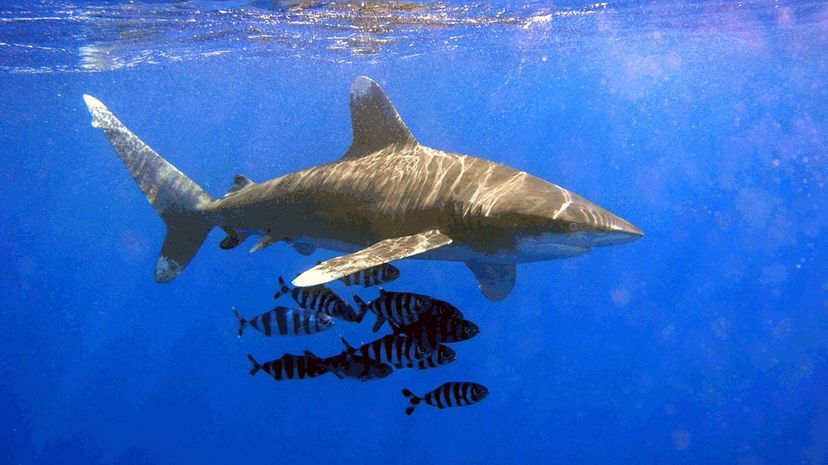

Residing in temperate and tropical waters, the oceanic whitetip shark takes part in feeding frenzies. If your ship or plane crashed in the sea, you'd be most worried about this shark.
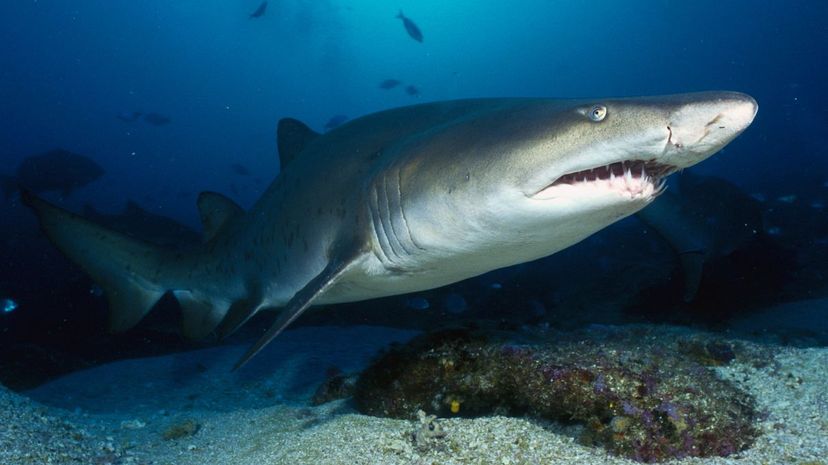

The sand tiger shark is unrelated to the more vicious tiger shark. It lives in sandy shorelines around the world and has the unique ability to gulp water, which helps it float effortlessly.
Advertisement
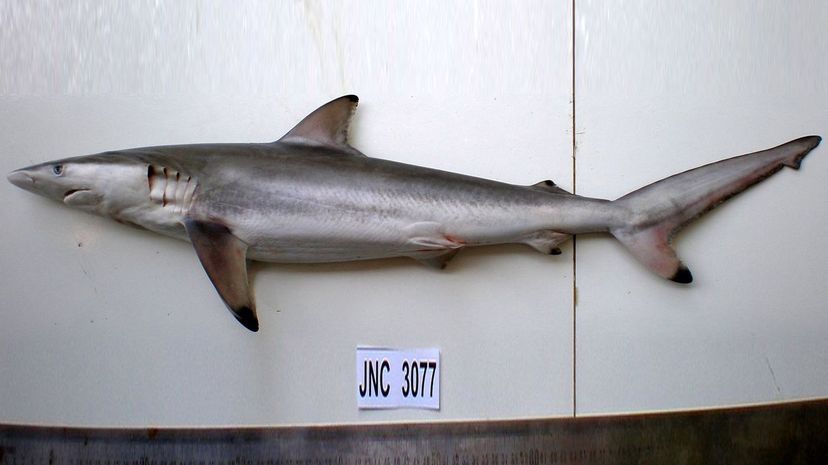

The spinner shark attacks schools of fish by swimming up vertically and spinning on its axis, leaping out of the water at the end. Because they swallow small fish whole, they usually leave humans alone.