
About This Quiz
Since humans have existed on Earth, they've been curious about science. Oh, sure, the ancient Egyptians and Mesopotamians didn't have giant telescopes that could see into the vastness of space or powerful microscopes that could examine tiny particles. But they still performed scientific experiments to better understand the nature of the world and the universe. And for thousands of years since, people have continually made advancements in medicine, science and astronomy, adding to people's understanding of natural phenomena such as volcanoes, earthquakes and hurricanes.
Let's face it: the world would be a much darker place without the invaluable contributions of scientists ... and not just because they harnessed electricity! Scientists have helped us cure diseases, effectively use our natural resources, predict hurricanes and tornadoes, travel to the moon and so much more. We have scientists like Galileo, Copernicus, Curie and Darwin to thank for our longer lifespans, brighter futures and richer knowledge of the world.
So whether you built a volcano model in school or played with a chemistry set as a kid, see how many of these scientists you can identify by their official titles. We promise not to blind you with science! Maybe you should see an ophthalmologist for that ...
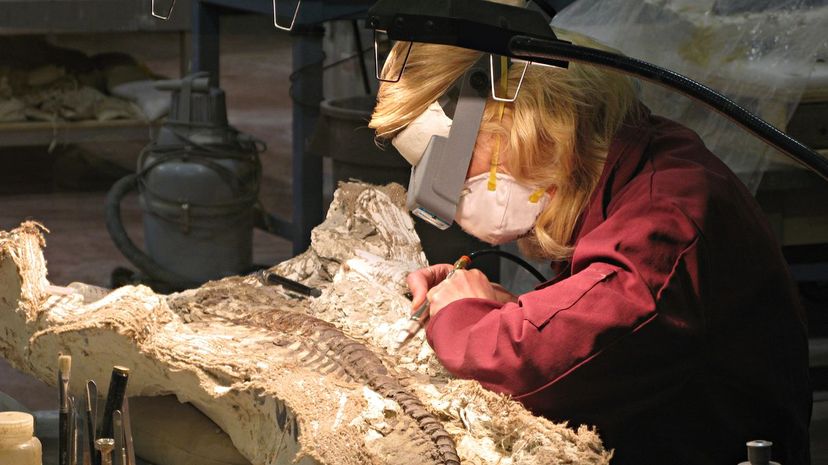

You have paleontologists to thank for the dinosaur bones you see displayed at the museum. Paleontologists study ancient fossils to discover what life was like thousands of years ago.
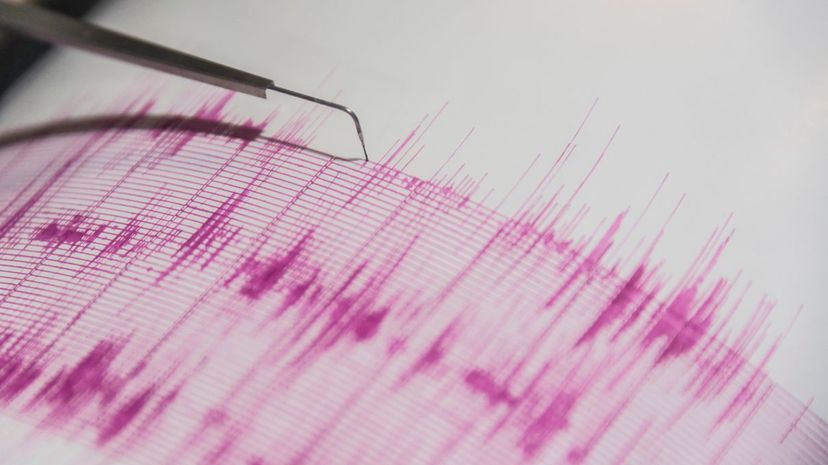

People once thought that earthquakes were caused by angry gods or subterranean gases. Seismologists study seismic waves through the Earth to better understand and predict earthquakes and tsunamis.
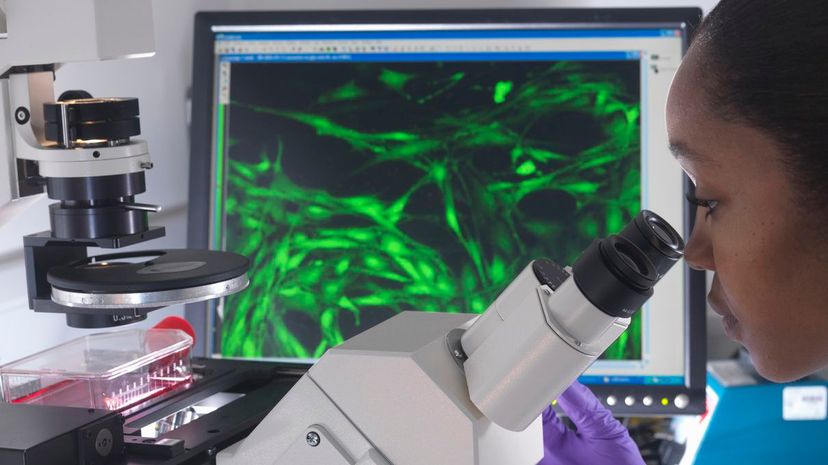

Cytologists explore the functions and structure of cells to aid in medical research. They are concerned with both eukaryotes, which have a nucleus, and prokaryotes, which include bacteria.
Advertisement

Have you ever wondered how your parents' traits got passed down to you? Geneticists could tell you how; they study genes and heredity. They owe Gregor Mendel some thanks for his early work in the field.

Remember learning about igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks in school? A petrologist studies those three kinds of rocks and how they form. Petrology and mineralogy often go hand in hand.
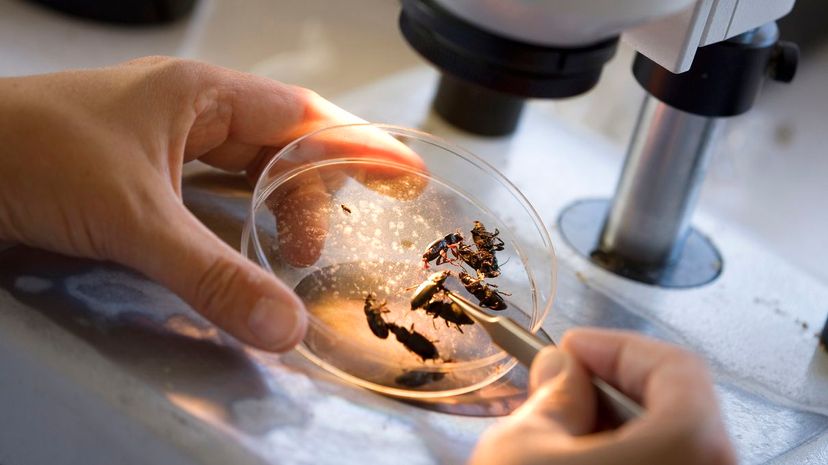
Entomology, or the study of insects, is a particular branch of zoology. Since there are potentially millions of species of insects — many unclassified — entomologists have plenty of subjects to study!
Advertisement
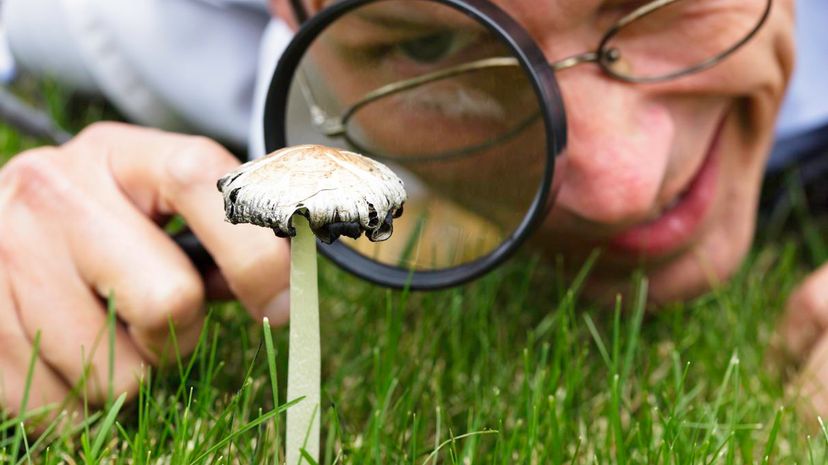

Before you go eating any wild mushrooms, you should consult with a mycologist. This type of scientist knows all about fungi and can determine whether wild mushrooms are toxic or not.
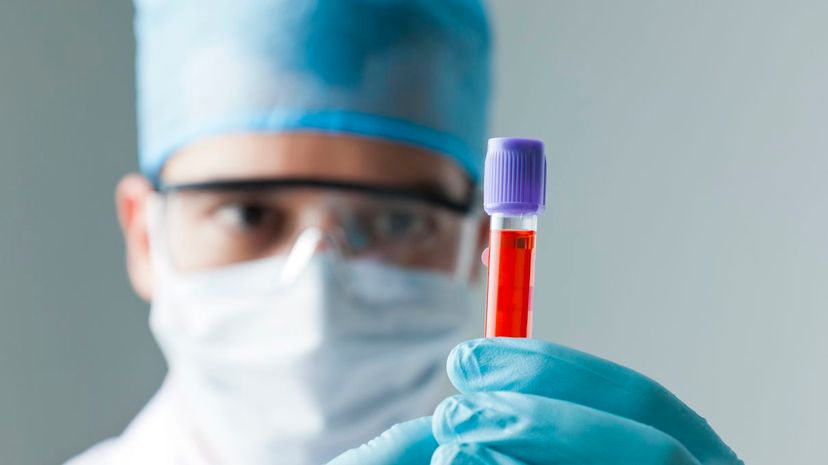

Hematologists research the diseases related to blood, such as blood clots, hemophilia, leukemia and lymphoma. People with these afflictions have hematologists to thank for their treatment plans.
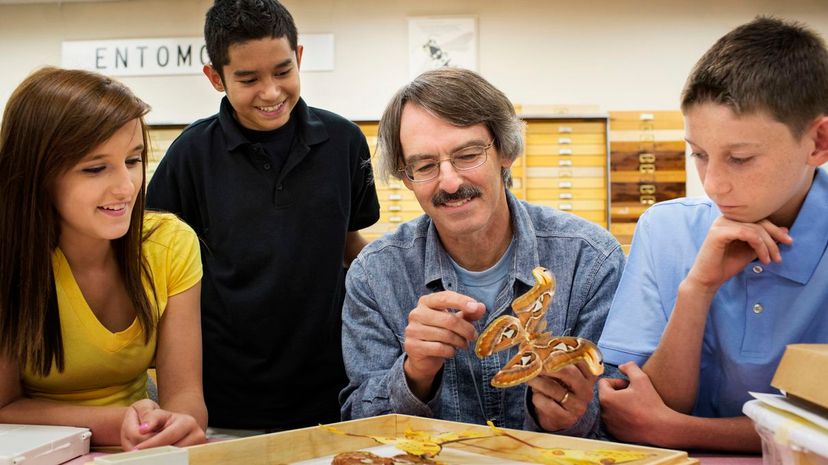

Lepidopterology, or the scientific study of butterflies and moths, is a branch of entomology. Historically, European lepidopterists have traveled to places like Australia and Brazil to find new specimens.
Advertisement
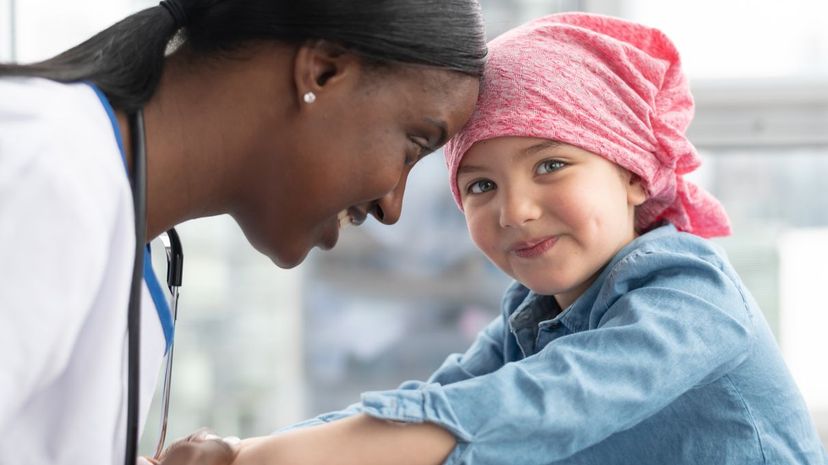

The word "oncology" comes from the Greek for "study of tumors." Oncologists stay busy studying the causes of cancer and researching ways to cure it. They also list risk factors to avoid.
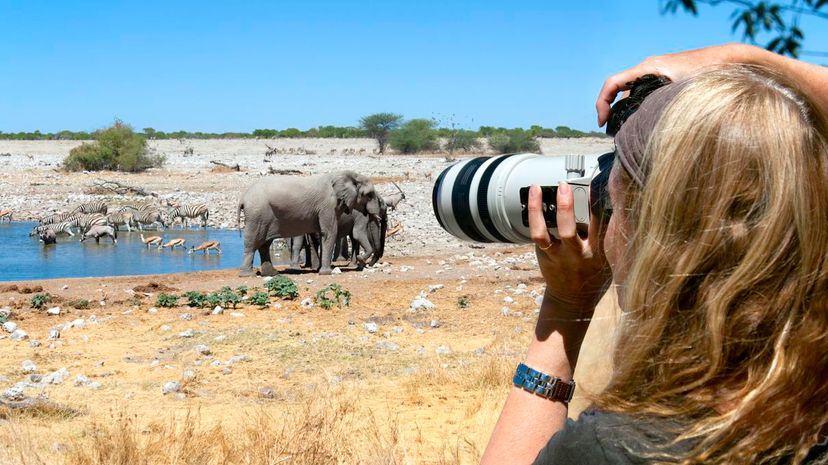

A zoologist is a type of biologist who specifically studies all animals, including ones that are extinct. Zoologists also research animals' habitats and how they fare in their ecosystems.
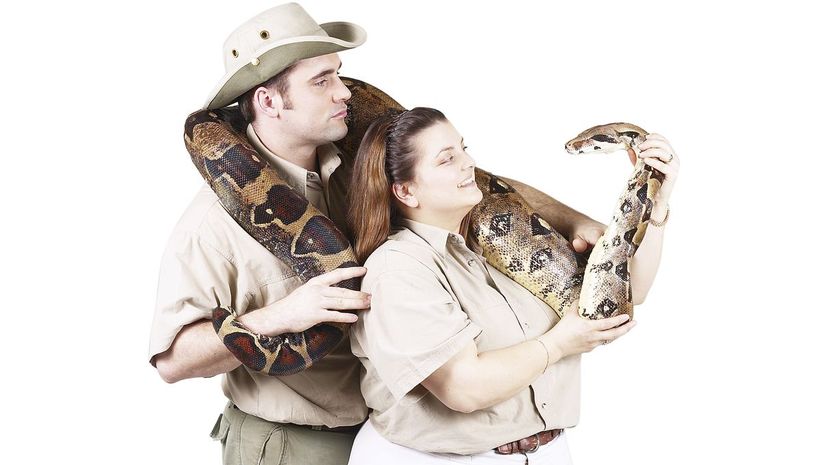

Herpetology, which comes from the Greek for "creeping animal," is the study of amphibians and reptiles. That covers a lot of cold-blooded animals, from lizards, snakes and turtles to frogs, salamanders and toads.
Advertisement
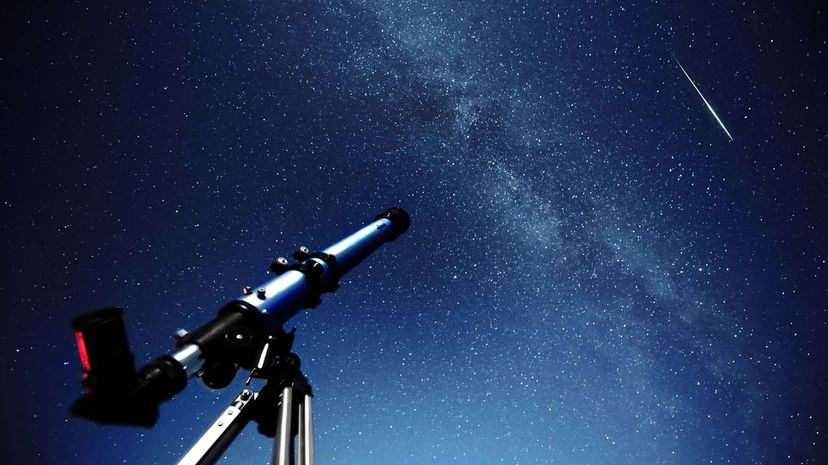

If you ever need someone to explain the Big Bang Theory to you, you can ask a cosmologist. Cosmology is focused on understanding the origins and evolution of the universe. That's some pretty vast stuff!
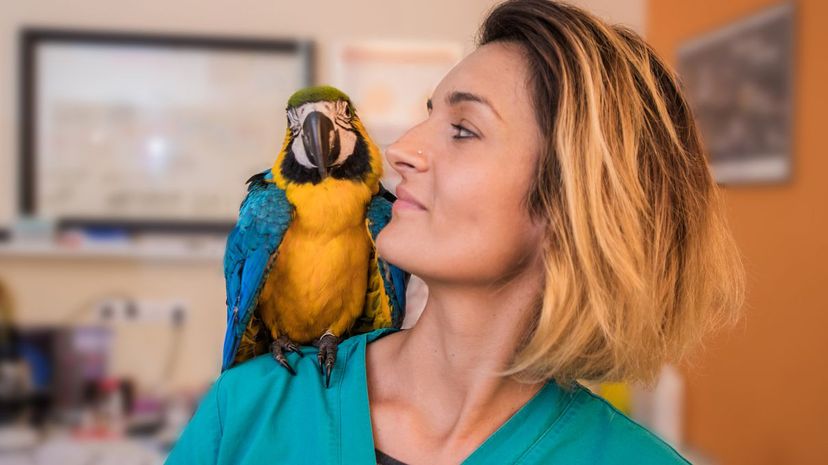

Since the Stone Age, when people drew pictures of birds, people have been curious about avian species. Ornithologists seek to understand the behavior of birds, such as their migration patterns.
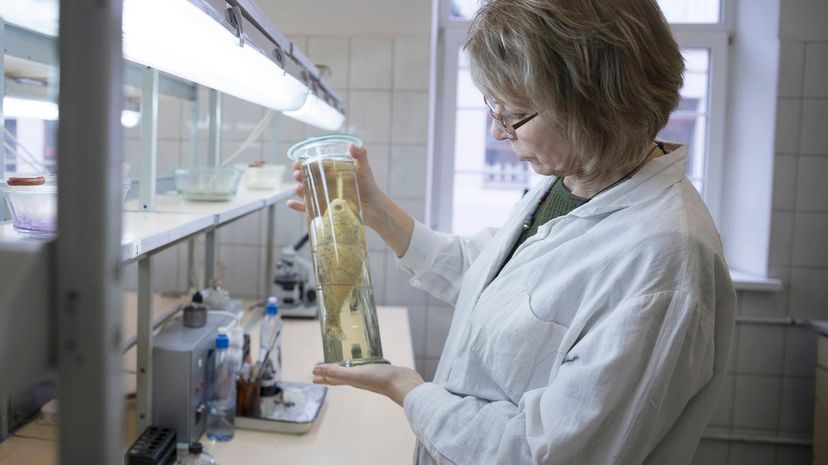

An ichthyologist is a kind of zoologist that studies fish, and they have plenty of species to choose from. According to a global database of fish, ichthyologists discover hundreds of new fish species every year.
Advertisement

Dendrologists know all about wooded plants, like trees, shrubs and vines. They often use leaf shape to identify the type of tree. Although it's similar in some ways, dendrology is distinct from botany.

Immunology is considered a branch of biology because it studies living beings — specifically, their immune systems. Thus, immunologists are concerned with organs like the thymus, spleen and liver.

Glaciologists study glaciers and other large bodies of ice, tracking the movement and melting of glaciers around the world. Astroglaciologists look for ice on other planets and moons.
Advertisement

Speleology is the study of caves and how they form and change over time. Sometimes speleologists are confused with spelunkers or cavers — people who explore caves for fun. But both groups need solid caving skills.
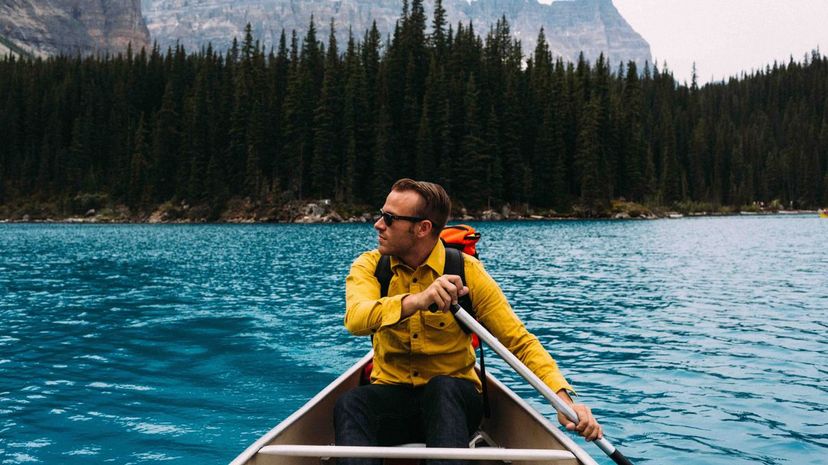

Limnologists are scientists who study inland aquatic ecosystems, such as lakes, rivers, wetlands and ponds. This field of study focuses on the physical and chemical traits of inland bodies of water.

Primatologists study primates to better understand their behavior and evolution over time. An interesting fact: women make up the majority of scientists seeking Ph.D.s in primatology.
Advertisement
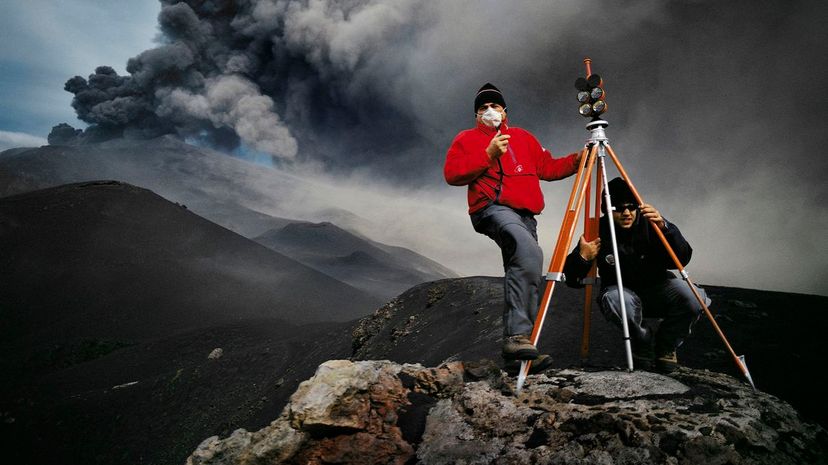

A volcanologist is a type of geologist who focuses on volcanoes, magma and lava. These scientists study the history of volcanoes and what causes them to erupt, so they can better predict future eruptions.
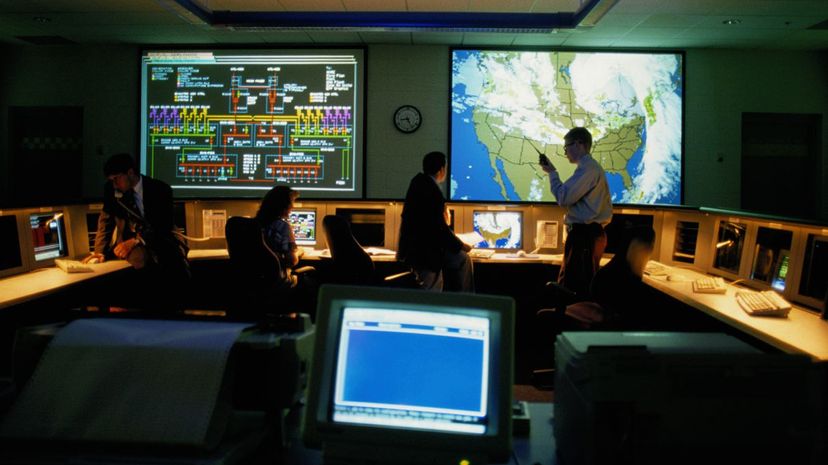

The Greek word "meteorology" literally means "the study of things high in the air." Meteorologists study changes in the atmosphere to predict the weather. For instance, we rely on them to warn us about hurricanes.
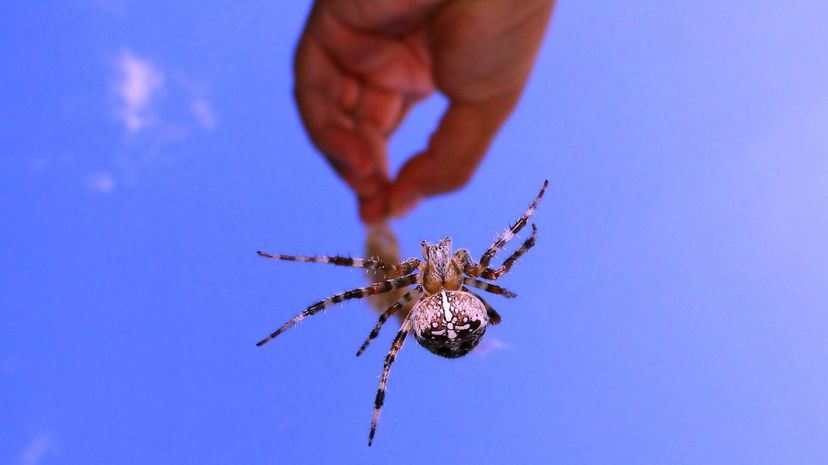

If you need a spider expert, an arachnologist is your safest bet. These scientists study arachnids, including spiders, scorpions and daddy longlegs. They'll know whether or not a particular spider is venomous.
Advertisement
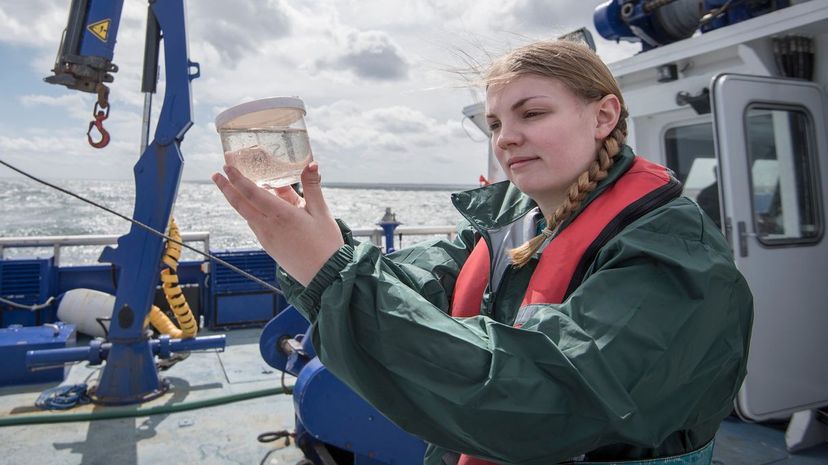

Since the oceans cover about 71% of Earth's surface, marine biologists have a lot of ground to cover, so to speak. They study marine life to better understand how such life affects the overall environment.
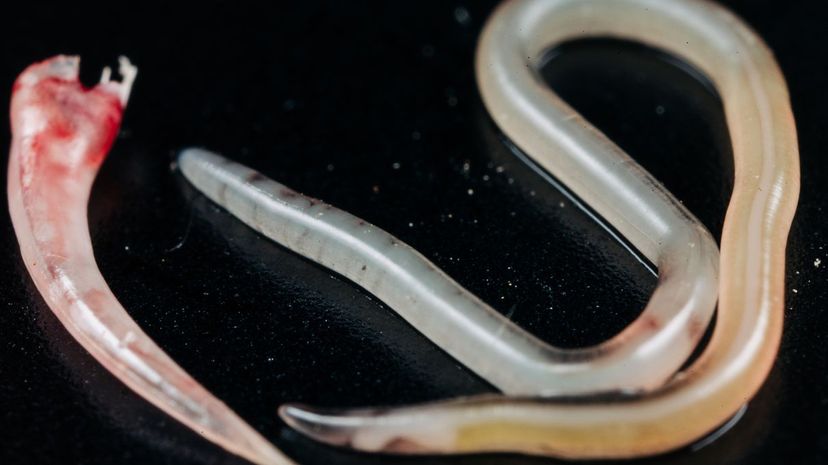
A parasitologist studies parasites and their hosts and how they interact. Parasitology is especially important to the field of medicine, because parasites can cause malaria, dysentery and other diseases.
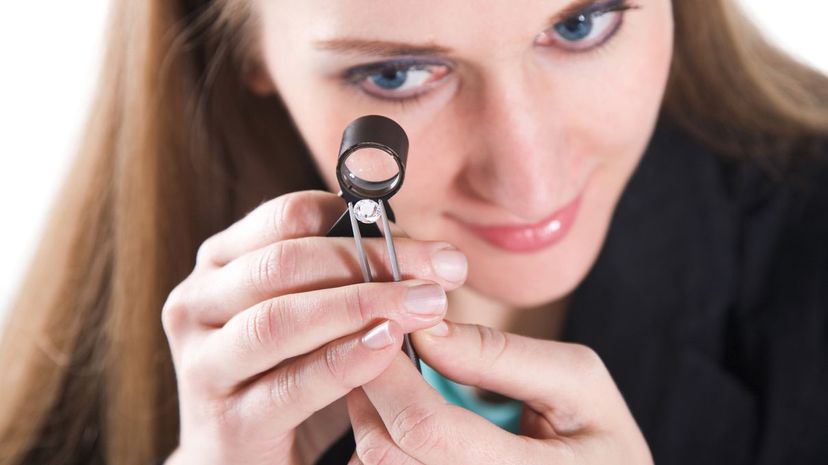

Gemology is a branch of mineralogy that focuses on gemstones. Many jewelers become gemologists so they can better evaluate the quality of gems. They use special tools, such as a refractometer, to examine gems.
Advertisement
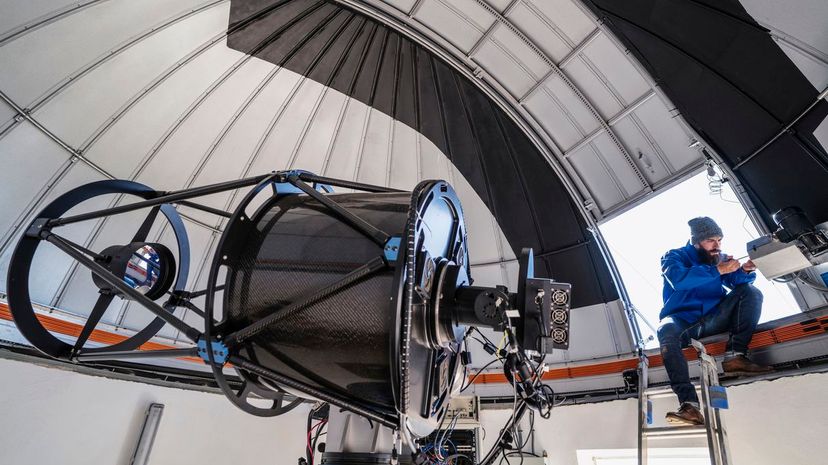

If it's your dream to observe galaxies, comets, planets and moons, then you should consider becoming an astronomer. These scientists study celestial objects to understand how they form and move.
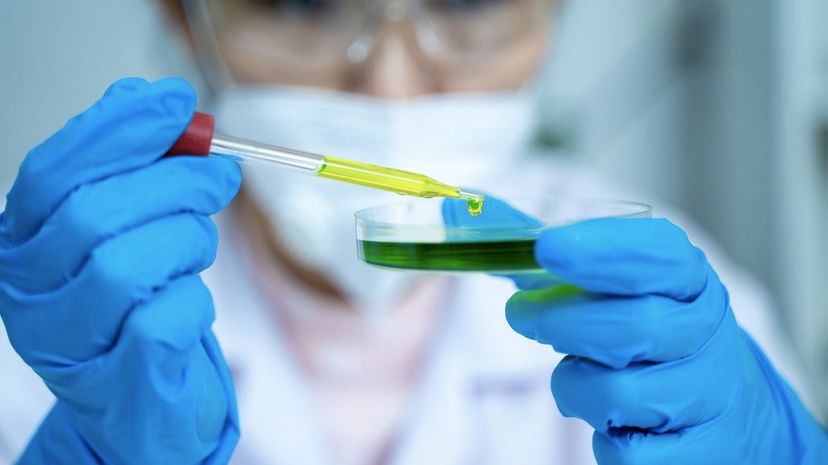

Doctors wouldn't be able to diagnose illnesses without the help of pathologists, who study the causes and effects of different diseases. Pathologists commonly analyze tissue or blood samples.

Mammalogy is a branch of zoology that focuses specifically on mammals, a diverse class of warm-blooded animals. According to mammalogists, over 6,000 mammal species have been identified thus far.
Advertisement

A branch of biology, pharmacology studies drugs and their effects on living organisms. Phamacologists try to discover the therapeutic benefits of chemicals, which is useful in the creation of drugs.

If you need an expert on solid, liquid and gaseous matter on Earth, a geologist is your best bet. These scientists also help find natural energy resources, like natural gas and petroleum.

The word "geography" comes from the Greek for "Earth description," and that's what geographers provide: a comprehensive description of the land, physical features and phenomena of the planet.
Advertisement
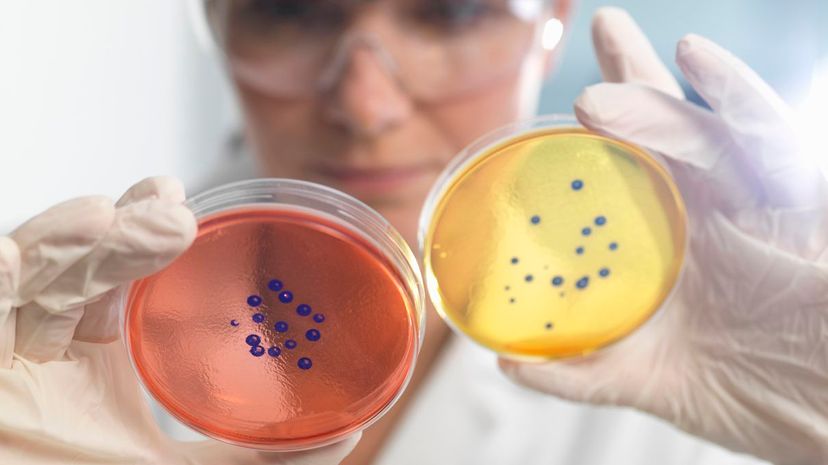
Lucky for us, bacteriologists study bacteria and how they impact medicine. For example, these scientists explore how certain bacteria cause diseases, which helps them develop antibiotics.
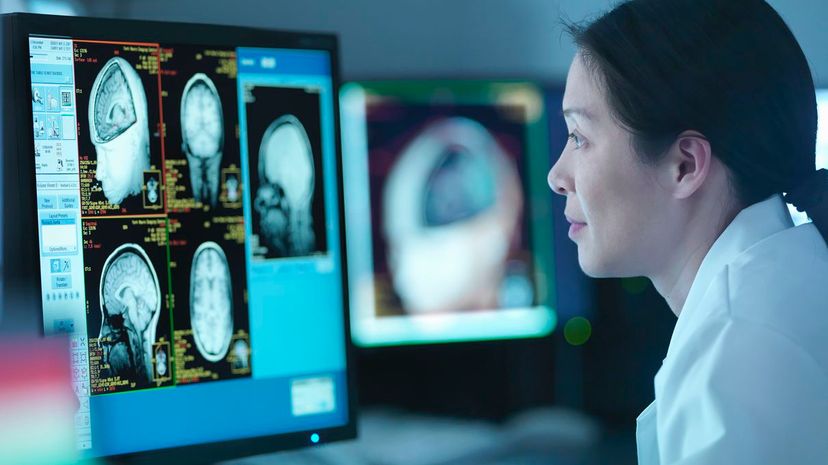
If anyone knows all about the nervous system and its impact on learning and behavior, it's neuroscientists! They study the brain, spinal cord and nerves to better understand diseases like multiple sclerosis.
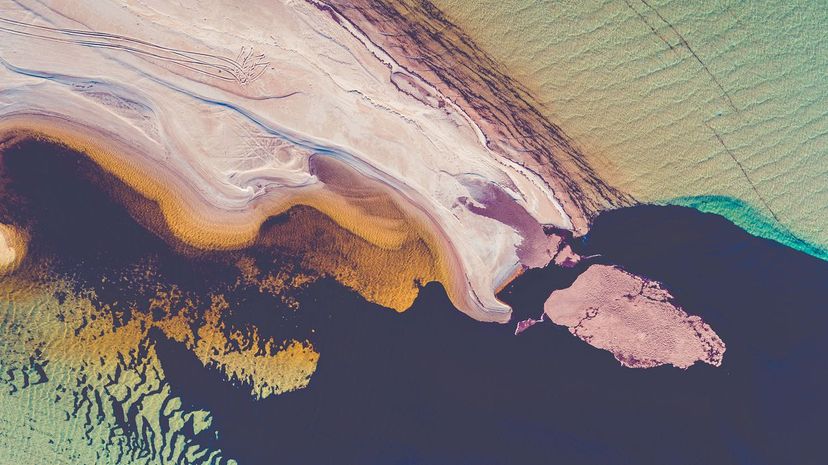

Climatologists are concerned with climate changes. By analyzing atmospheric conditions over an indefinite period of time, they can make predictions about future climate conditions.
Advertisement
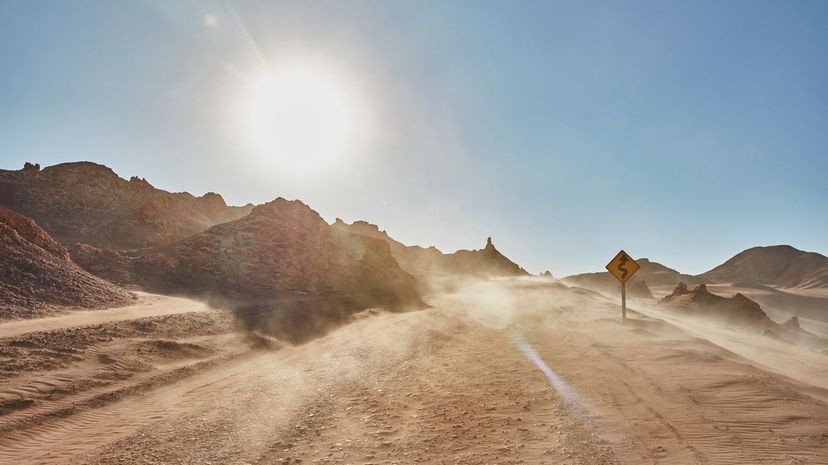

Sedimentologists look at sedimentary structures to get a better idea of the Earth's geologic history. In particular, they study how sediments form, erode, change and move over time.
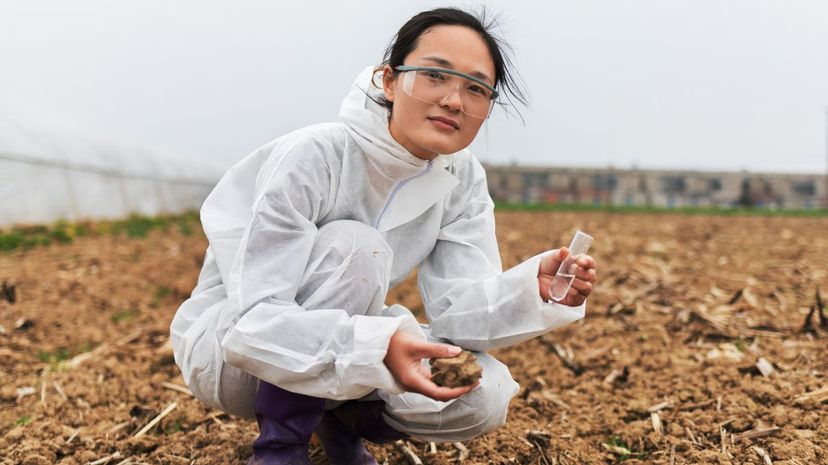

Edaphology is a type of soil science that explores how soil affects plant life. Understandably, edaphologists are invaluable scientists in agriculture because they can measure soil fertility.
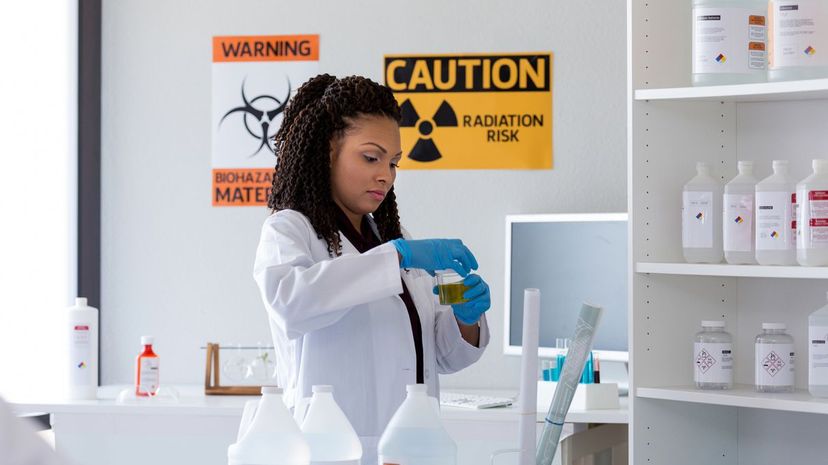

Radiobiologists study the impact on living beings of ionizing radiation. While radiation has useful purposes, such as for treating cancer, too much of it can have adverse health effects.
Advertisement
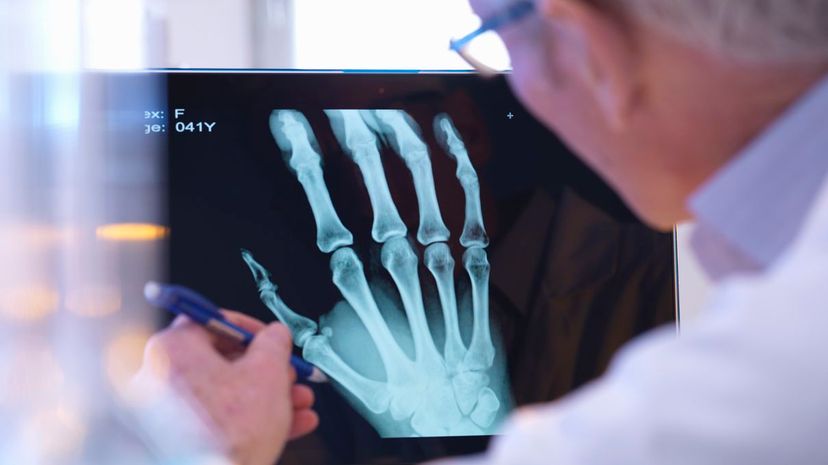
Osteology is a branch of science that focuses on bones, their structure, how they grow and their diseases. An osteologist may, for example, be able to determine the age and sex of a human skeleton.