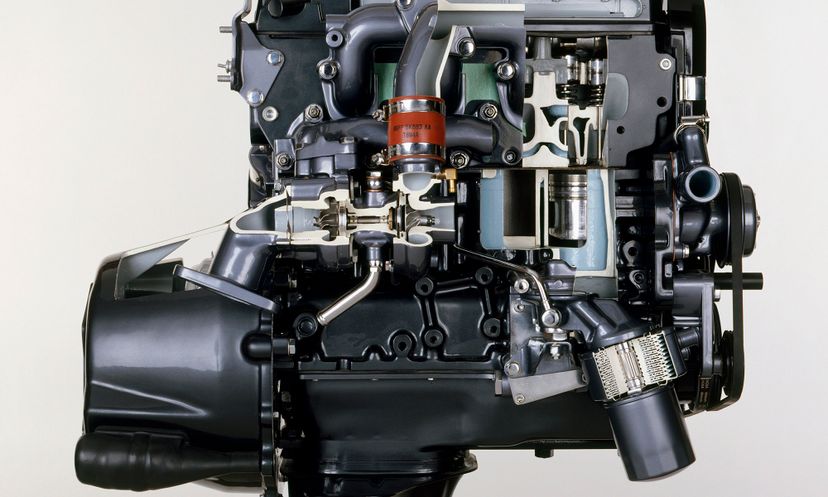
About This Quiz
Know what makes diesel engines run? Take this quiz to test your knowledge!
Not so very long ago, diesel fuel was less expensive than what most of us put in our cars. Additionally, some auto manufacturers are designing Sports Utility Vehicles that run on diesel. Diesel has become a way to run clean, fuel-efficient engines. But what's the hype all about?
The diesel engine was named after its inventor, Rudolf Diesel, a German engineer. Originally used in submarines and ships, diesel engines became a long haul vehicle and large equipment staple. Now, diesel engines are in use just about everywhere, with about half of all consumer vehicles sold in Europe being of the diesel engine type. The hype is based on the fact that diesel engines are simply more fuel efficient than standard combustion engines. And, now that the cost of diesel fuel is in reach for just about everyone and engine enhancements have made diesel far less dangerous to the environment than it once was, diesel engines are making headway in the engine market. Of course, even if diesel fuel itself is slightly less expensive than regular gasoline, the increase in efficiency makes it worth it.
So, if you think you can handle the speed of this quiz, let's get started.
Rudolph Diesel created, developed and patented the first diesel engines.
It is the heat of the compressed air that ignites the fuel-air mixture, which is why diesel engines are considered compression ignition rather than spark ignition engines.
The RTA96-C generates 107, 390 hp using 14 massive cylinders.
Advertisement
While high oil viscosity can be a problem, the primary reason cold diesels are tough to start is heat absorption during the compression stroke.
A glowplug is a small electric heating element that helps ignite the fuel-air mixture when a diesel engine first starts.
Diesel-electric engines work well in locomotives both because a mechanical transmission would wear out quickly under such massive loads and because electric motors provide superior torque for pulling across the power band.
Advertisement
The TEP80 hit an unverified top speed of 168 mph in 1993 while traveling between St. Petersburg and Moscow.
The ECM in a modern diesel can make numerous tiny adjustments to the timing of fuel injection to compensate for cold temperatures.
Rudolf Diesel obtained a patent for a "combustion power engine" -- what we now call the diesel engine -- in 1892.
Advertisement
Disturbed by the inefficiency of gasoline and steam engines, Diesel decided to devote his time to developing one with higher efficiency.
As opposed to gasoline engines, diesel engines work by first compressing the air and then injecting the fuel.
Indirect injection helps to evenly distribute fuel vapor, and moves the injector out of the cylinder, where it doesn't have to endure such high pressure.
Advertisement
Higher compression ratios lead to higher efficiency and more power. While gasoline engines have compression ratios of 10-to-1, diesel engines compress at a ratio as high as 25-to-1.
Some indirect injection engines, such as some versions of the Austin BMC B-series, can be manufactured in conventional gasoline engine and diesel engine versions by changing little more than the cylinder head and ignition/injection systems.
Responsible for the shipment of about 94 percent of freight, diesel is an integral part of the economy.
Advertisement
Diesel fuel has more carbon atoms in longer chains than gasoline does, making it heavier and causing it to slowly evaporate.
CRT particulate filters and catalytic converters burn soot and reduce particulate matter, carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons by as much as 90 percent.
Biodiesel is an alternative or additive to diesel fuel that can be used in diesel engines with little to no modifications to the engines themselves. It's not made from petroleum -- instead it comes from plant oils or animal fats that have been chemically altered.
Advertisement
Dave Evans drove a Cummins diesel-powered car in the 1931 Indy 500, finishing the race on one tank of fuel and finishing 13th.
For most of the 20th century, submarines were powered by diesel engines that charged batteries while on the surface, then shut down when submerged, leaving battery power to run the electric drive motors.
A 2-stroke engine can produce more power than a 4-stroke engine of the same size in certain applications, typically generators or large ship engines.
Advertisement
The pickup truck was powered by a Cummins diesel engine and towed its own support trailer to the track.
Diesel engines don't rely on an electrical ignition system, so wet conditions don't affect engine performance.
A common rail system uses a single pressurized fuel line instead of a separate line for each injector.
Advertisement
A BMW 320d won the 24 Hours Nürburgring race in 1998 powered by a diesel engine, the first diesel win in a major 24-hour endurance race.
Cold diesel fuel is prone to "gelling," which can be prevented with special additives.
Although diesel engines have some advantages for use in aircraft, they were replaced by gasoline engines and turboprops (and eventually jet engines).
Advertisement
The sulfur in diesel fuel not only pollutes the environment, it reduces the efficiency of the engine. Low sulfur fuels and biodiesel are possible alternatives.
Gasoline engines suffer drastically reduced efficiency at idle, while diesel engines remain efficient at idle. This is why diesel generators and truck engines can be left running for hours while burning minimal fuel.
A gasoline engine can only handle a limited amount of boost because too much leads to premature ignition and engine knock. A diesel engine can take much more boost, up to the point when the cylinder head fails.
Advertisement