
About This Quiz
Everyone knows that you don't retain everything you ever learned in school. Want an example? Try to define what a "dangling participle" is! Even so, most of us would love to think that we know more about physics than a fifth grader. After all, every adult must know more about the way that our universe works than the average eleven-year-old.
How well do you remember concepts like mass, velocity and volume? Can you recite Sir Isaac Newton's three laws of motion from memory, or are you a little bit rusty? Can you think both big and small, on macro and atomic levels, to better understand what makes up our world, as well as identify all of the moving parts of an infinitesimal atom? Do you know the rudimentary building blocks that the sharpest minds use to unlock the secrets of how our incredible universe works? If you should have had a least a cameo role on "The Big Bang Theory," it's time to show your stuff in this quiz that tests you on the basic principles and phenomena of physics and pits your mental might against that of your average fifth grader.
Are you up for the challenge? Let's get started.

One of the cornerstone concepts of physics is kinetic energy. The term is used to express the energy that an object in motion has. An object maintains kinetic energy until it changes speed.

A "force" refers to any interaction that will change the motion of something if left unopposed. It can alter an object from existing in a resting state to being in a state of motion.
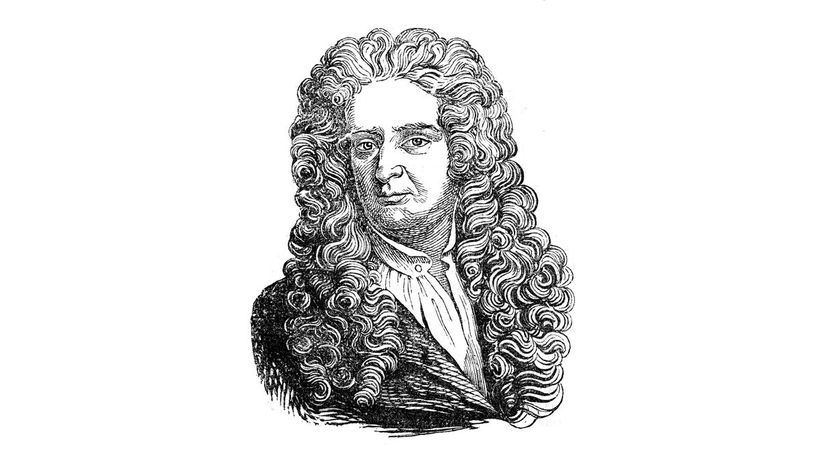

The notion that Sir Isaac Newton actually had the theory of gravity knocked into him by a falling fruit has been widely disputed, but it makes for a pretty incredible story about the origin of this theory. He published his famous work, "Principia," in 1687.
Advertisement
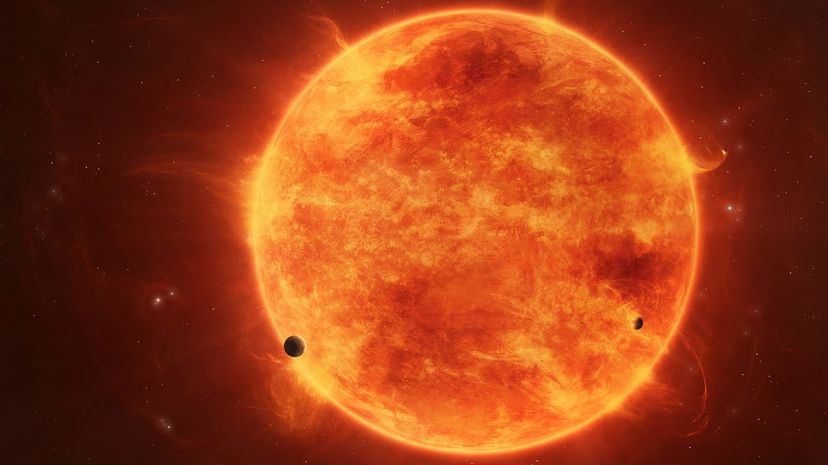

The sun's gravity keeps all of the planets in our solar system locked into their orbits, circling the sun. It's a good thing, too, because, without it, our planet would veer off into outer space.

We use the word "friction" outside of the realm of physics, but scientifically it has a specific meaning. Kinetic friction refers to moving objects, and static friction refers to non-moving objects.
Displacement is a change in an object's location from its original position or a vector that covers the smallest distance between two points. It's determined by — what else — the displacement formula.
Advertisement
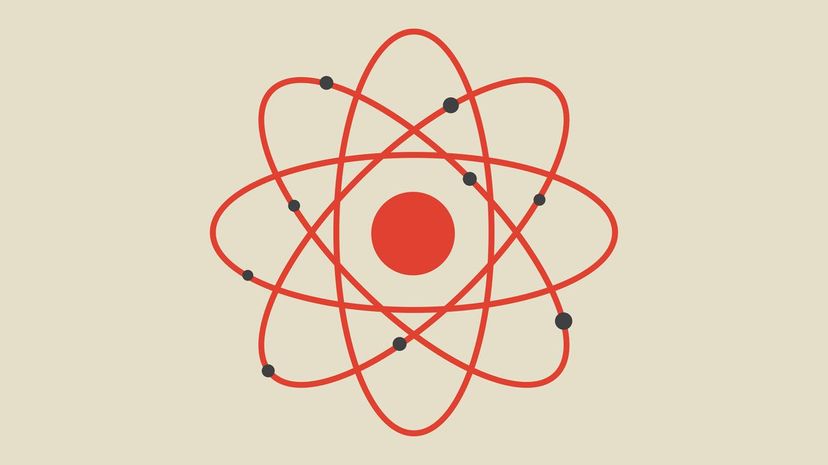
The middle of an atom is called the nucleus. The nucleus is made of subatomic particles — it's primarily comprised of protons and neutrons, with a very small number of electrons mixed in.

A "watt" is a standard unit used to measure power, equivalent to a single joule per second. A joule is a unit of energy. "Watt" is a common term, used to talk about electrical currents in our many devices.
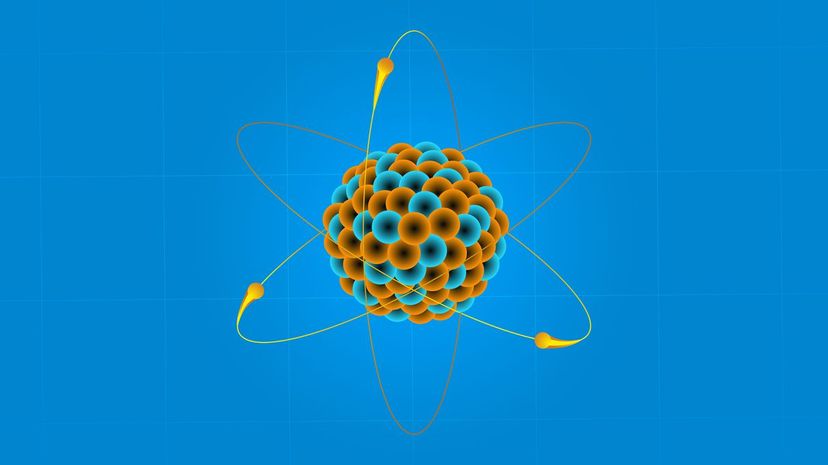
Radioactive decay, also called nuclear decay, refers to the disintegration of an unstable nucleus. When radioactive decay happens, the atom emits radioactive energy, which is, of course, dangerous.
Advertisement
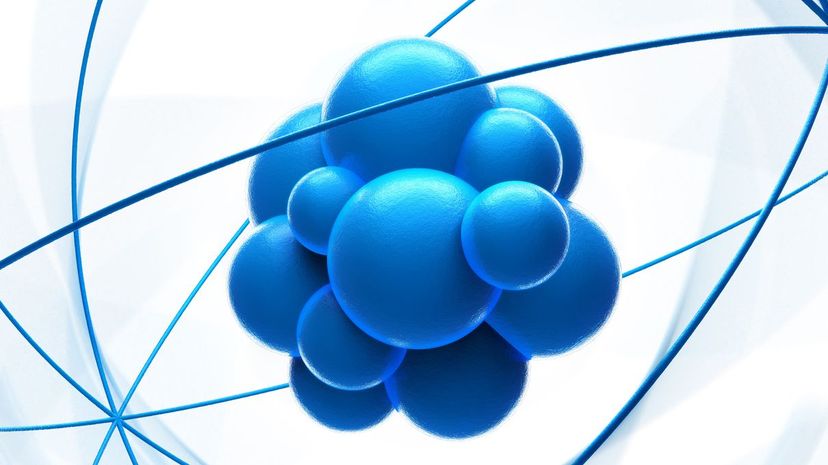
Electrons are negatively charged particles, whereas protons are positively charged ones. All atoms contain the same number of protons and electrons, so they effectively cancel each other out.

Most vacuums have no matter in them, and those that do have so little that it hardly even registers. They have very low pressure and are considered to be inhospitable environments.

Atomic energy is created through nuclear fission or nuclear decay. It is a powerful but sometimes unmanageable form of energy that can be dangerous if it is mishandled.
Advertisement
A sonic boom is the loud noise that shock waves make when an object travels faster than the speed of sound. Chuck Yeager was the first pilot to break the sound barrier, back in 1947.

Oceanic tides are primarily caused by the moon's gravity. For many years, these tides were considered one of the more mysterious phenomena on the planet, but now we understand why they happen.
Back in 2006, Pluto was stripped of its planethood by scientists who decided that it just didn't meet all of the criteria — specifically, clearing its neighborhood of "other objects" near its size.
Advertisement

It's very hard to wrap your mind around the speed of light, which moves at an astonishing 186,282 miles per second. Light is by far the fastest-moving thing in our entire known universe.

Who doesn't love a little guilty pleasure inertia once in a while? Anyone who has ever binged on Netflix knows that staying in a state of rest until forcibly moved is an underrated talent.

When an object rounds out like a sphere, it's considered to be convex. When light passes through a convex lens, it tends to bunch together rather than split apart on the other side.
Advertisement

Gravity, in its simplest form, means that objects with mass tend to be attracted to each other. Since virtually everything on our planet has mass, we are firmly rooted to the Earth.

Let's talk about Albert Einstein's famous theory of relativity! This varsity level concept basically states that our perception of gravity is based on the curvature of space and time.

Actually, the opposite is true. The universe is expanding, and it seems to be expanding at a much higher rate than it has in the past. Don't worry — this doesn't have any real effect for us humans.
Advertisement

Current generally flows from positive points to negative points. This term refers to the way an electrical force flows through a conductor. Metal is an exceptionally good conductor.

Since electricity always prefers to travel through the path of least resistance, it tends to avoid messing with rubber. Rubber is highly resistant and can stop an electrical current.
Fahrenheit, Celsius and Kelvin are all valid measurements of temperature. Kelvin is rarely used outside of scientific scenarios, but Fahrenheit and Celsius certainly are. Fahrenheit is generally used in the United States.
Advertisement

You can thank Sir Isaac Newton and fellow scientist Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz for your killer hard 10th-grade calculus class — the two men came up with calculus independently. Newton's three laws of motion are the building blocks of physics — he came up with those on his own.

For an object to qualify as a prism, it has to have a few specific qualities. The ends must be identical and have flat faces. Of course, it must be clear so that light can pass through it.
Antimatter might sound like a sci-fi term, but it's actually a useful component of medical imaging, specifically, Positron Emission Tomography (PET). Also, antimatter occurs in cosmic rays, and it's studied for its unique properties.
Advertisement

Acceleration can mean a number of different things, even just increasing speed while driving a car. In physics, acceleration is the rate of change of velocity in a certain amount of time.

As tough as it is to fully grasp, it's entirely possible — and even very likely — that some of the stars we gaze at in the night sky are not there any longer, thanks to the speed at which light travels.

Heliocentric universes — including ours — revolve around a star or sun. The idea that we live in a heliocentric universe was first envisioned by Copernicus, but it didn't catch on for centuries.
Advertisement

The term "impulse" refers to a sudden change in momentum — either an increase or a decrease. This can occur when an object either moves from a state of inertia or has a change in momentum.

Sir Isaac Newton's third law of motion states that "For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction." This is one of the governing laws of physics and holds true for everything.
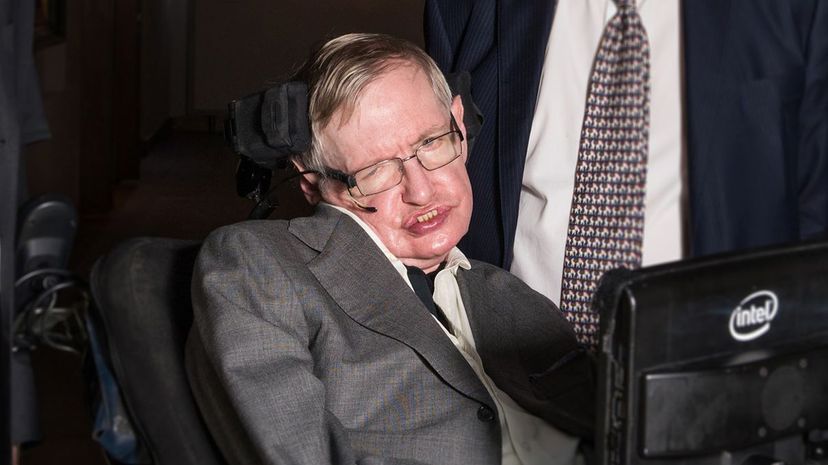

Stephen Hawking was one of the most brilliant physicists who ever lived. His books, specifically "A Brief History of Time," made physics accessible and understandable to nearly everyone.
Advertisement
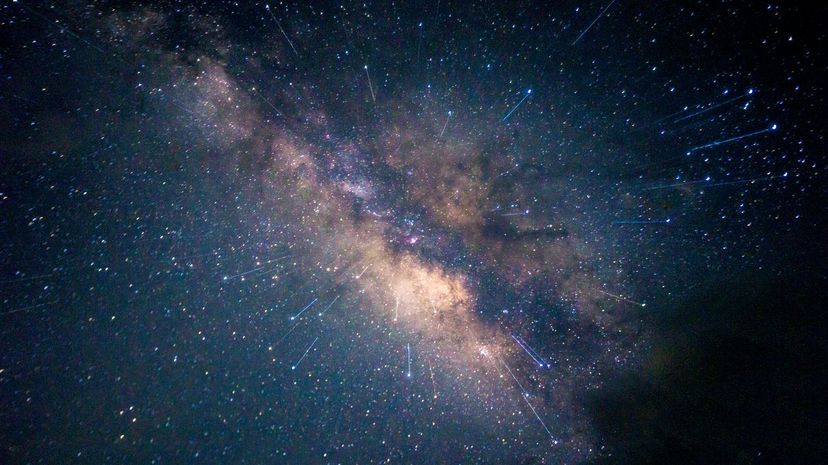

The Milky Way, a spiral shaped galaxy, is our home. Specifically, our planet is located in the Orion Arm of the galaxy. The Milky Way disk measures as much as 120,000 light-years in diameter.
In physics, the term "mass" is simply the measure of how much matter is in something. The mass of an object doesn't change, even if external forces are acting upon the object.