
About This Quiz
"If the English language made any sense, lackadaisical would have something to do with the shortage of flowers."
While this quote by columnist Doug Larson is certainly humorous, it hits on just how complicated and interesting the English language can be. Words often don't mean as they sound, and certain rules are applied at seemingly arbitrary times. That's because English is an amalgam of languages and root sources, and takes a lot of its foundation grammar, spelling, and language rules from two uniquely different sources: Germanic and Latin.
Because of these two different but equally important influences, as well as the introduction of words from languages around the world as communication and travel became easier, English can be particularly challenging to learn, and even more difficult to understand. As it is, many native language speakers know instinctively when and how to apply the rules of grammar, without even knowing what they are.
How well do you think you know the roots and origins of these English rules of grammar? Put your knowledge of Germanic and Latin origins—as well as other important language influences—to the test by taking this quiz. See if you can correctly apply the rules—and even understand why they're there in the first place. Good luck!

When we place an adverb (a word ending in "ing") between the word "to" and the following verb, we have split an infinitive. In the Latin language, infinitives cannot be split, so the rule carried over to English, though it currently faces debate.

Classic compounds are words that combine two forms from classic Greek or Latin vocabulary to create another word. They appear often in the medical fields and might look like "bio" and "graphy" coming together for "biography" or the study and recording of life.

Travel lovers will be familiar with the word "wanderlust" which indicates a desire or pleasure to explore the world. While this is a romantic theme, the word wanderlust is Germanic in origin.
Advertisement

While some English words are taken directly from languages where they still exist, there are others two that remain the only current use of those words. Concealer is a commonly used word in English, but no longer exists in French, from where it originated.

A great many of our words, particularly our prefixes and suffixes, come from the Latin language. When we add the Latin prefix "circum" to the front of a word, we get options like "circumvent," "circumference," and "circumnavigate."

The word "human" plays by both sets of rules, which means everything is a little bit chaotic. If the word were entirely Latin, it would be "humens," but because "mann" or "man" comes from Germanic root, we have "mans" instead.
Advertisement

When Latin and Germanic words appear in the English language, there is often a related version. In this case, the word "brotherly" come from Germanic and the Latin equivalent would be "fraternal."

Anyone who has studied languages has come across a "false friend" or two in their time. It often happens when the second language keeps the word of the first and the first language changes its meaning. In French, an example would be "egre" which means "sour" but sounds like "eager."

Oftentimes, English ends up with several different words that mean the same thing but have different origins. Royal is Latin, regal comes from Old French, and kingly is Germanic in root. Vulpine means "foxlike."
Advertisement

Cobalt is a word that seems so at home in the English language, it's hard to believe there was ever a point when it didn't belong. In this case, the word cobalt is Germanic in origin.

Dutch has many similar words to English and, in fact, has directly contributed many of the words in the English lexicon. Bluff comes from "bluffen" (to brag, boast) or "verbluffen" (to baffle, mislead).

A loan word is a word taken directly from the source language and incorporated without translation. The word "cafe" which in English means a coffee shop comes directly from the word "cafe," which means "coffee" in French.
Advertisement

A portmanteau is created by the blending of words, parts of words, or their sounds. The word itself is French is origin. An example of a portmanteau would be "motel" made up of "motor" and "hotel."

Germanic/Latin doublets are words that appear in science that have similar meanings in both Germanic and Latin. In Germanic, the words are nouns—bird. In Latin, the words are adjectives—avian.

If it seems like there are many words in English that have the same meaning, that's because there are. "Ancient" is a word that has Latin origins, and the related Germanic word is "old."
Advertisement

While it's difficult to trace the origins of specific English rules, the whom vs. who rule can relate directly to the words "whom" and "who," which are the product of Germanic root words.

The English language has begged, borrowed and stolen many words from French. A gallicism can be one of several things: a French idiom, a French mode or custom, a loan word or a loan phrase borrowed from the French.

The word "barbarism" once referred specifically to the mixing of the Greek and Latin languages, but it expanded—as language often does—to include any error in language that was considered unpolished or rude, specifically in morphology.
Advertisement

The word "educate" comes from the latin root word "educare." As there are many different words with similar meanings in English, the word with Germanic roots that has a similar meaning is "teach."

If it seems like many hybrid words are easy to define—even if you've never seen them before—that's because they have a lot of similar prefixes and suffixes from Latin and Greek origins. While other hybrids exist, this is the most common combination.

English has a tricky relationship with translations. In some cases, words are adapted without being translated. In other cases, they are loosely translated. When it comes to "calques," the word is translated word-for-word.
Advertisement

It would surprise few that Germanic pronunciation is often bold and definitive. This antique shift toward stressing the first syllable ultimately led to many single-syllable words in English.

If you have studied the romance languages, then you'll know there are a great many tenses to remember and conjugate. The Germanic language influence on English means we have far fewer tenses.

Numerus may come from the Latin, but with the exception of a small shift in spelling, it appears in the English language as "numerous." This word shows up in many mathematical terms.
Advertisement

If you thought of the word "memory" or "memorabilia" or "memorial," you're on the right track. "Memor is a Latin prefix related to memory and mindfulness that appears in many English words."

If you've ever heard someone's speech referred to as "sibilant," this is why. Fricatives and sibilants are used to described the movement of air during the pronunciation of certain words.

Many words that appears in biology or in the scientific world are derived from Latin roots. The word "genus" itself is Latin in origin, as are many of the defining names that are colloquially adapted into English.
Advertisement

Poltergeist, a word for a type of ghost, looks and sounds like a lot of German words, and that's because it's Germanic in origin. That also explains why it fits so well into the English language.

It might seem like "blanc" for "blank" or "white" has been around forever, but there is a beginning story to every word and in the case of this one, it dates back to Germanic roots.

As explained in an earlier question, a double, known also as an etymological twin, is a word with the same roots comprised from two different languages. There can also be triplets or more.
Advertisement
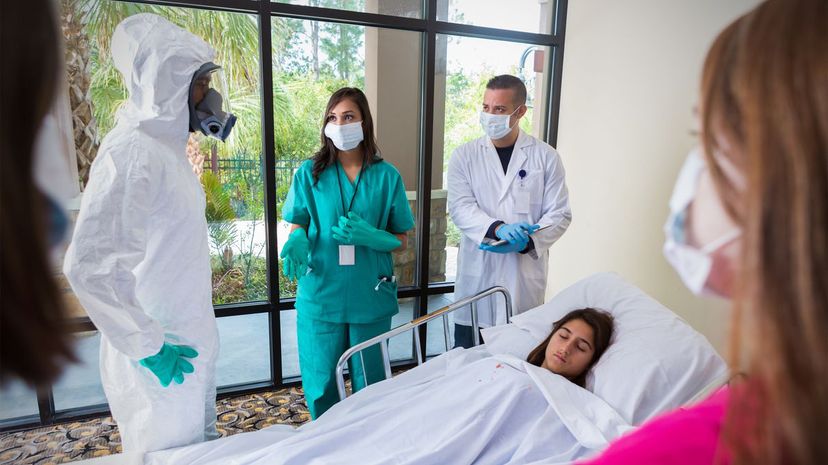
If you've studied romance languages, you'd be tempted to see the word "quarantine" as relating to "40" in some way—and it does. The word refers to how long people suspected of disease were kept away from civilization—40 days.

If the word "schizophrenia" had followed one of the traditional paths of language adaptation—likely through French, Greek, or Latin—it would be pronounced like "skyzo," rather than "skitso."

The Germanic weak verbs are the most commonly appearing verbs in the Germanic languages, and often referred to as regular verbs. This does not necessarily mean they are the most important or historic.
Advertisement

A strong verb is not necessarily the opposite of a weak verb. You get a strong verb when the conjugation of the verb to fit the subject of the sentence or the tense changes: I sing, I sang, I sung.

Persona has an incredible number of uses in the English language, including as a standalone word, persona. It can be used in many words — often related to self or person — and it comes from Latin.