
About This Quiz
The complexity of human anatomy has been studied for centuries. Over time, scientists have divided it into various parts and sections. As it stands right now, the human body consists of 11 different organ systems that allow your body to function in the way that it does. The major systems are the skeletal, lymphatic, nervous, respiratory, endocrine, urinary, digestive, reproductive, circulatory, muscular and integumentary systems.Â
Within each system, there are a number of organs working hard to keep you alive. Can you tell the difference between an appendix and a liver? What if a random, fake organ was placed in the question? It is one thing to know and recognize the seventy-eight organs that we house in our bodies, but it is another thing entirely when fake names are thrown into the mix. Do you know the human body well enough to discern between what is real and what is fake?Â
Whether you're a health care professional or simply relying on your freshman biology class from high school, we should all know what's in our bodies, right? Put your heart into this and prove your anatomical knowledge through the 35 questions in this quiz! It's time to see how much you know about your insides!
The pharynx is a very real organ. It plays a role in the digestive and respiratory systems. While it helps the body swallow in the digestive system, it helps inhale air through the nose in the respiratory system.
Despite its silly-sounding name, the jejunum is a real organ. It is the name given to the second part of the small intestine. The jejunum is used to absorb nutrients that have been digested by the organs before it,
Endogallum is a fake organ! The organ that actually aids in food transport through peristaltic contractions is the esophagus! Some of its more common names include gullet and food pipe.
Advertisement
The biliosack is a fake organ! The organ that actually stores bile is the gallbladder. The bile is then released into the small intestine to aid in digestion of fats. It is located under the liver.
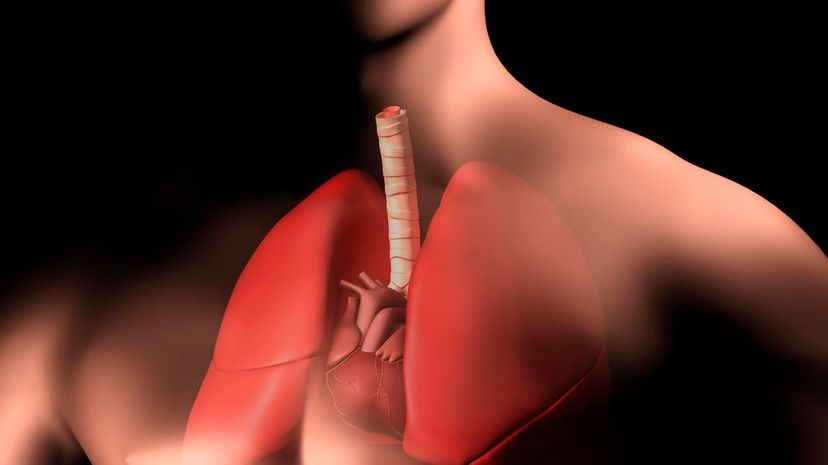
The trachea is a real organ! The trachea is responsible for connecting the pharynx and other parts of the respiratory system to the lungs. The trachea allows the body to inhale air.
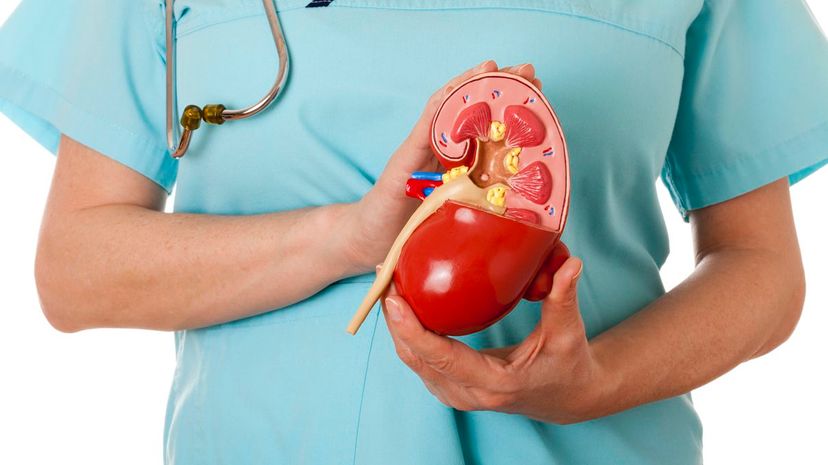
Renaltines are fake. The pair of organs that are being referred to here are the kidneys! The kidneys are responsible for filtering your blood and aiding in the production of urine.
Advertisement
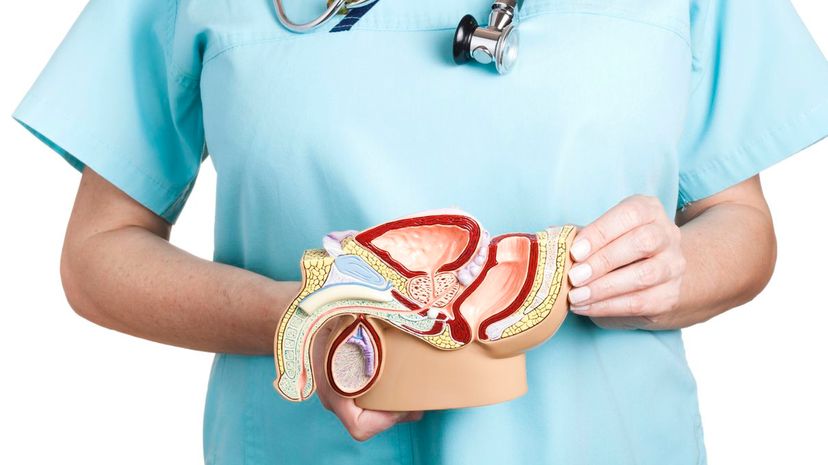
The epididymis is a real organ. Its primary function is to connect the testicles to the vas deferens. It is tightly packed in adult males, but the organ itself can be 20 to 23 feet long!
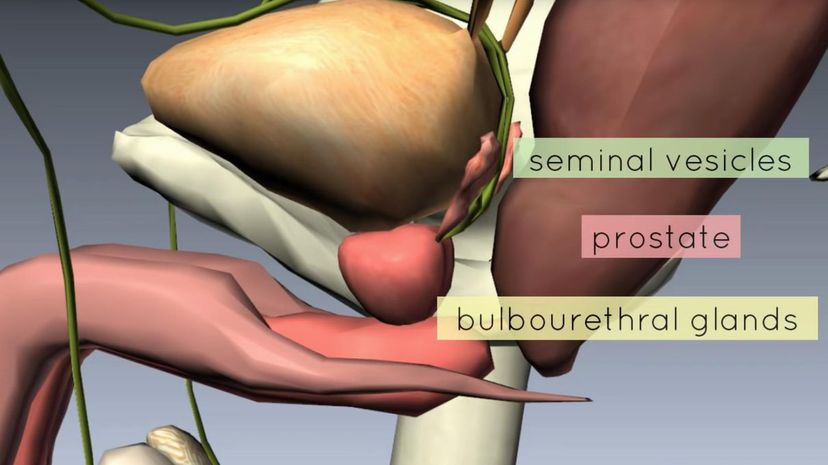
The bulbourethral gland is real! Within the male body, it is roughly the size of a pea. The female equivalent of this organ would be Bartholin's glands. They are common in most male mammals.
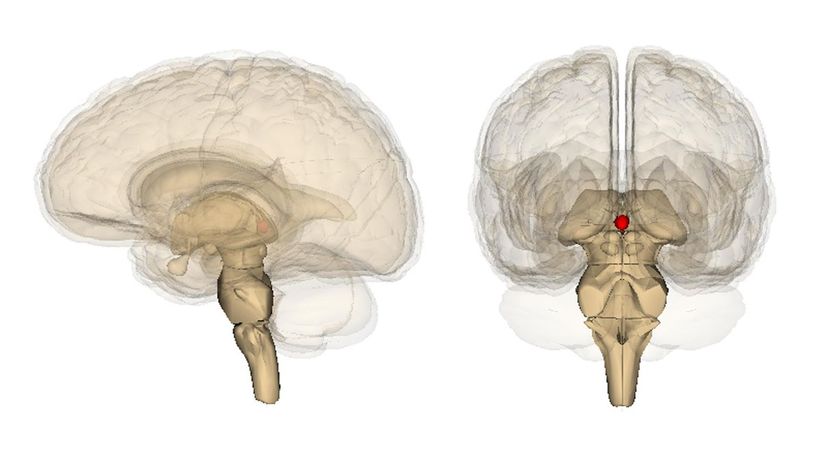
The pelotineal gland is not real. The gland that is responsible for serotonin production is the pineal gland. This gland is part of the endocrine system and can be found within the brain.
Advertisement
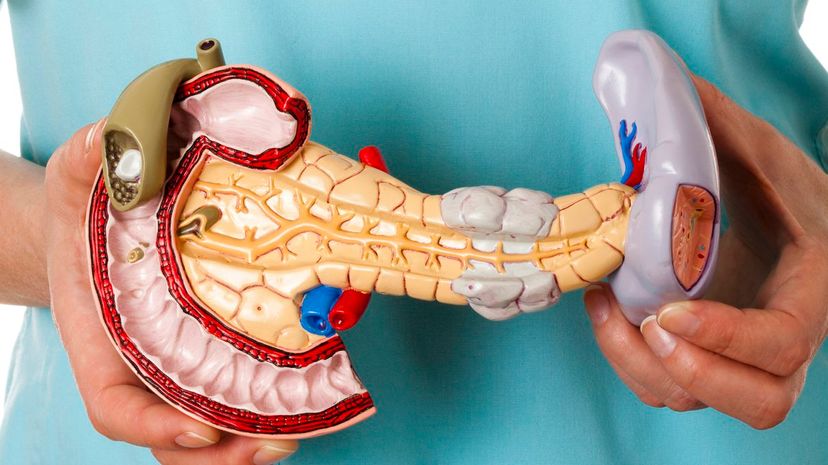
There is no such thing as a panneal! The organ responsible for regulating blood sugar in the body is the pancreas. It is also used for distributing insulin and somatostatin to the body.
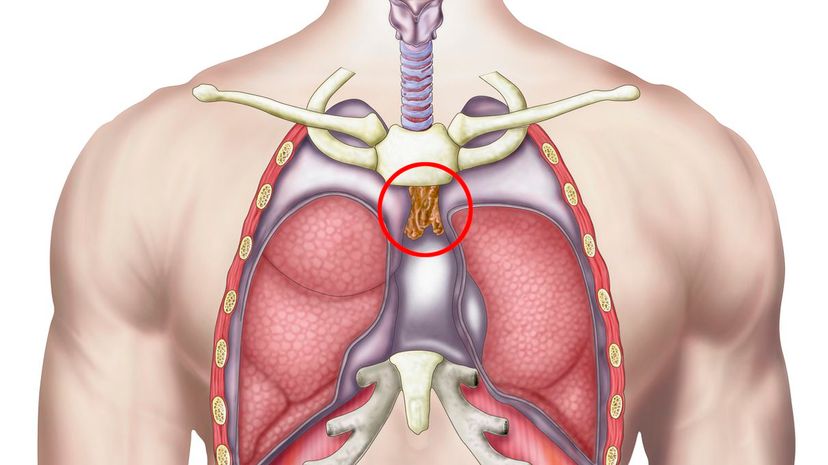
The thilio is not real. The organ that aids our immune system is the thymus. The thymus is responsible for aiding in the maturity of T cells. T cells are needed to adapt to bodily threats.
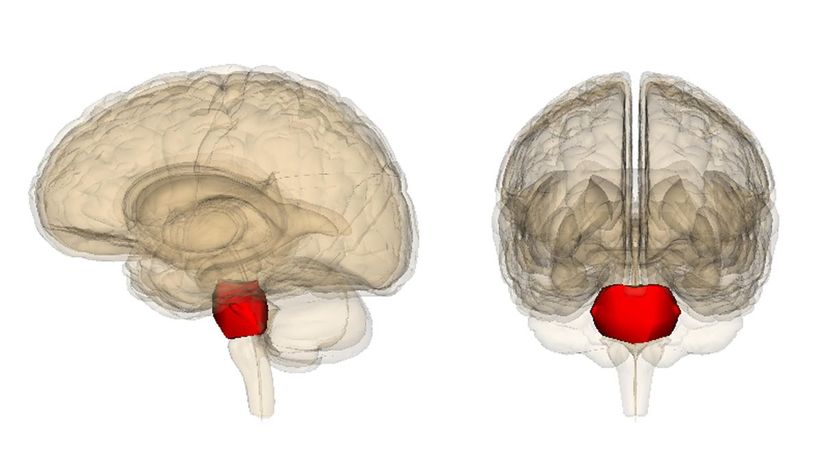
Despite its short and simple name, the function of the pons is rather complex. The pons is the part of the brainstem that transmits information from the brain to the cerebellum and medulla.
Advertisement
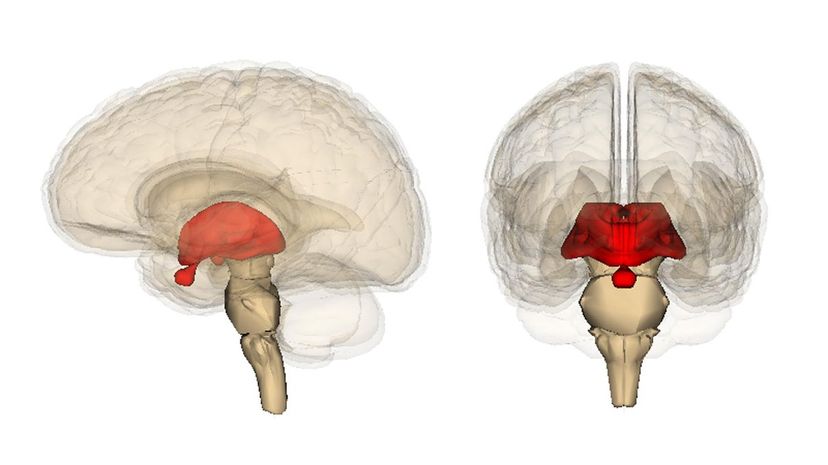
The diencephalon is a real organ. In addition to connecting two systems, it also connects to the optic nerve. The diencephalon is also able to create and organize memories and emotions.
The pleurisis is not a real organ. The organ being referenced here is the spleen. The spleen gets rid of old red blood cells. It can also hold a supply of blood on reserve and helps the body get rid of bacteria.
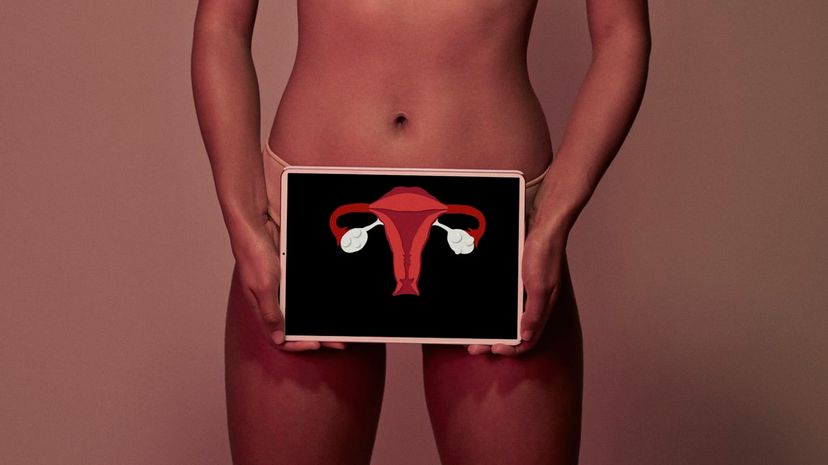
It is the ovary that does this, not the ovalian. In addition, the ovary also helps control the menstrual cycle through the hormones it releases. Each female is typically born with two ovaries.
Advertisement
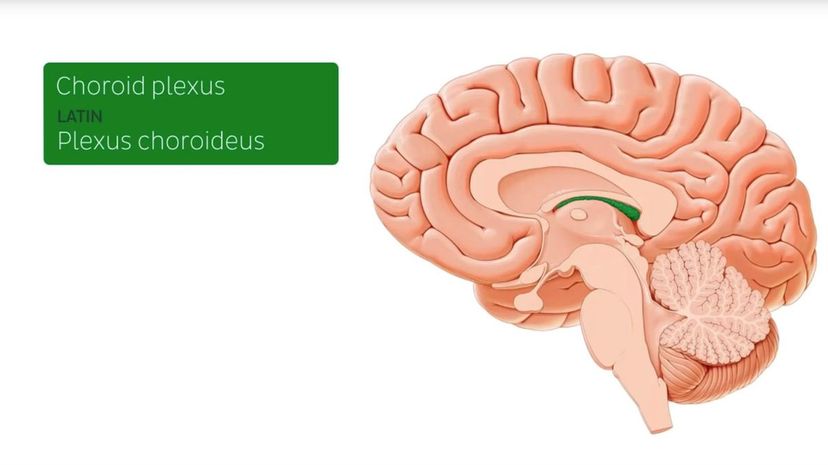
The choroid plexus is a real organ! It is located in the brain and is the fourth ventricle. The fourth ventricle lies under the cerebellum. The choroid plexus also helps balance iron levels in the brain.
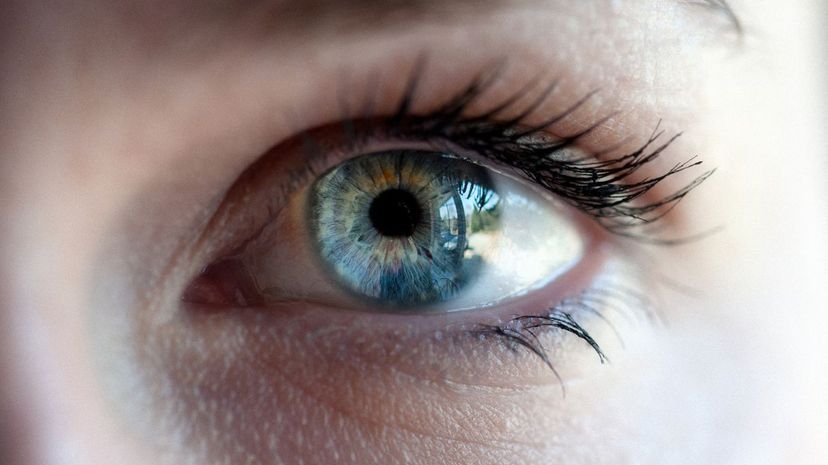
It is the iris that controls the light amount, not the interior illia. The iris also determines a person's eye color and controls the diameter of the eye, functioning much like an aperture in a camera.
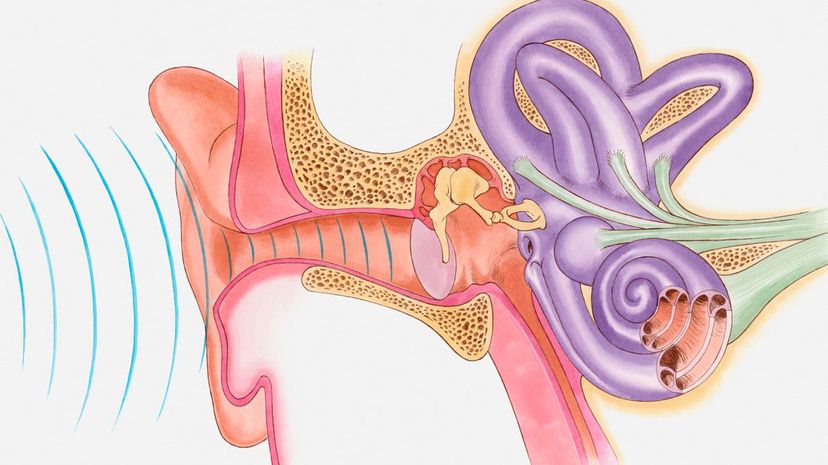
The cochlea is real! This spiral-shaped space in our ear makes it possible to hear. Its appearance resembles that of a nautilus shell and it has three chambers within it. These chambers are the vestibular duct, tympanic duct and the cochlear duct.
Advertisement
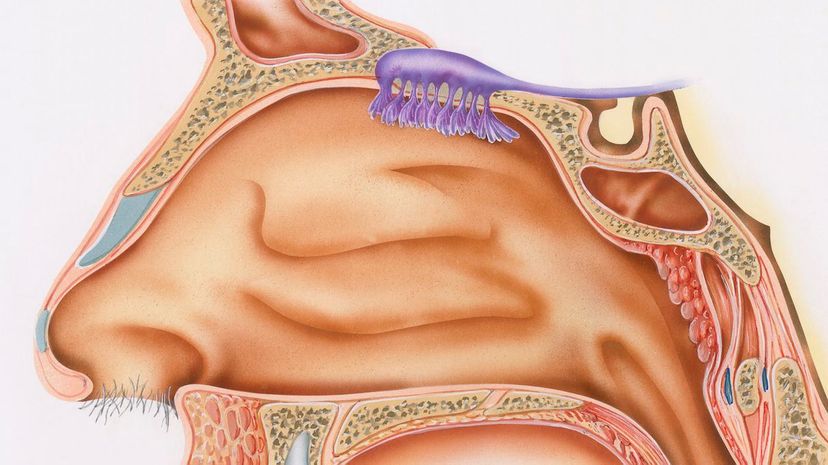
The olfactory epithelium is a type of special tissue that allows us to smell! There are four types of cells within the epithelium which make it function properly: olfactory sensory neurons, supporting cells, brush cells and basal cells.
The spinal cord is very real! It connects the brain to the rest of the central nervous system. The spinal cord is how your brain talks to the rest of your body, which allows it to move.
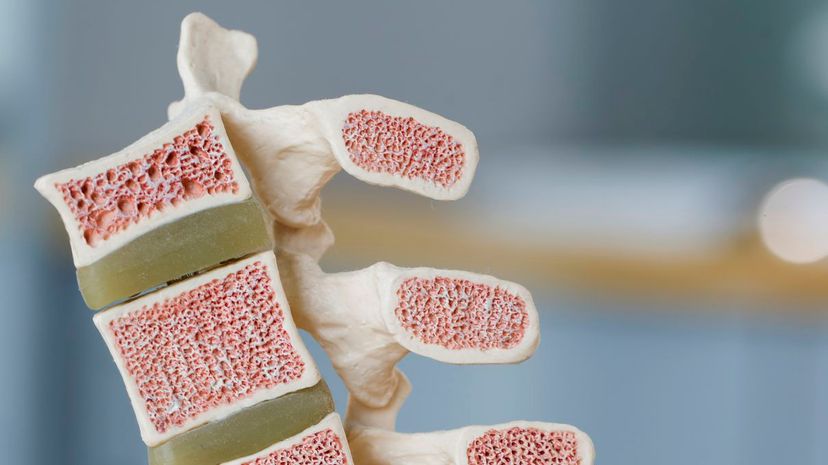
The organ that is being described here is bone marrow. For adults, the majority of our bone marrow is found in our pelvis, sternum, ribs and vertebrae. Bone marrow typically makes up 4% of a human's mass.
Advertisement
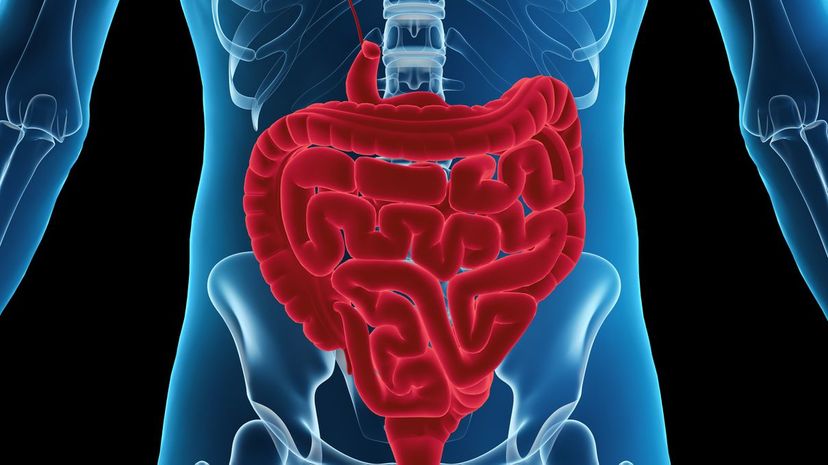
GALT, which stands for gut-associated lymphoid tissue, is the permeable membrane that lines the intestines. It helps the body absorb food with its finger-like appendages, called villi.
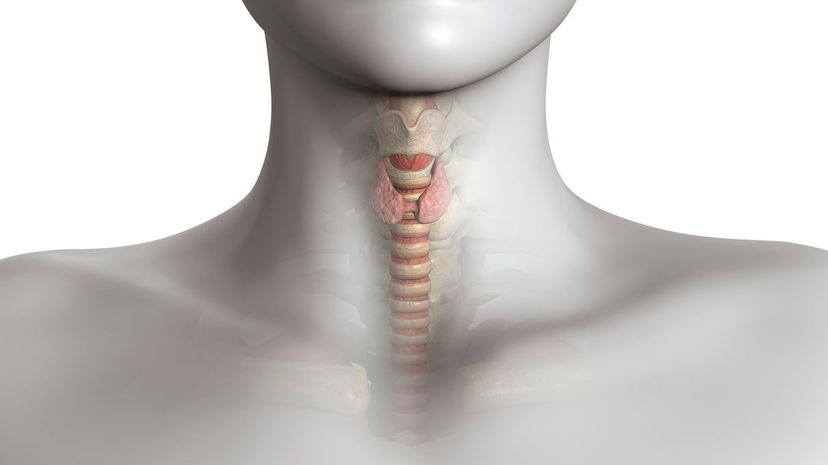
The gland located in the neck is the thyroid. The primary function of the thyroid is to control our metabolic rate. This is controlled by the amount of thyroid-stimulating hormone that is released by the body.
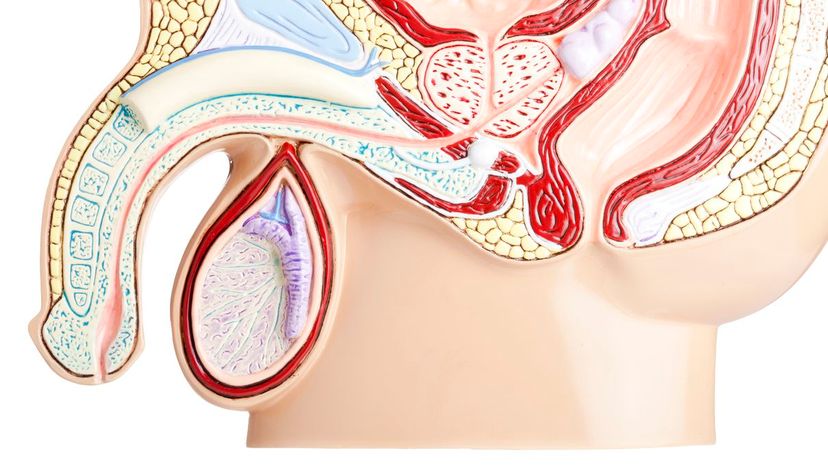
The scrotum is what's found beneath the penis. It is made up of skin and muscle, and encases the testes. In females, the body part that is comparable to the scrotum is the labia majora.
Advertisement
The area that is being referred to here is the vulva! The vulva includes a variety of female reproductive parts, like the clitoris, labia majora and the mons pubis. The vaginal opening is also included.
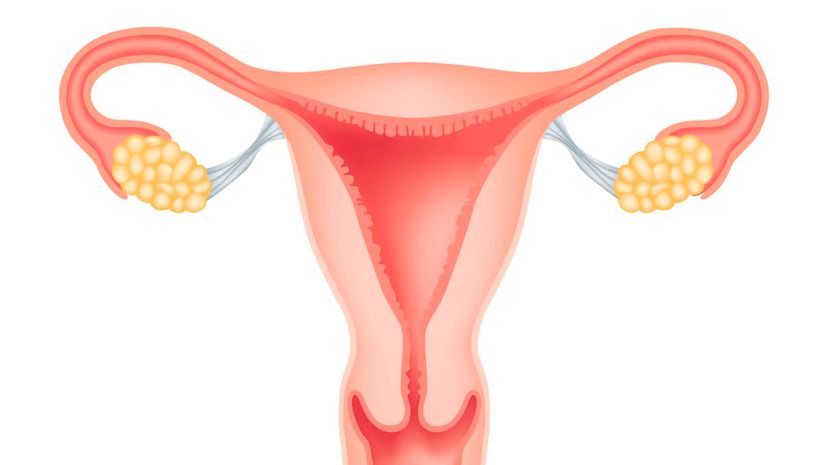
Salpinges are very real! They are more commonly called fallopian tubes, and they serve as the passageway for the egg from the ovary to the uterus. The tube itself is made up of four layers.

Bronchus, or bronchi for more than one, are responsible for passing air into the respiratory system by way of the lungs. It's important to note that the exchange of gas does not happen in the bronchi, but in the lungs.
Advertisement
The organ that actually detoxifies the body is the liver! It is located beneath the diaphragm. It is the liver that produces the body's bile, which is then held by the gall bladder.
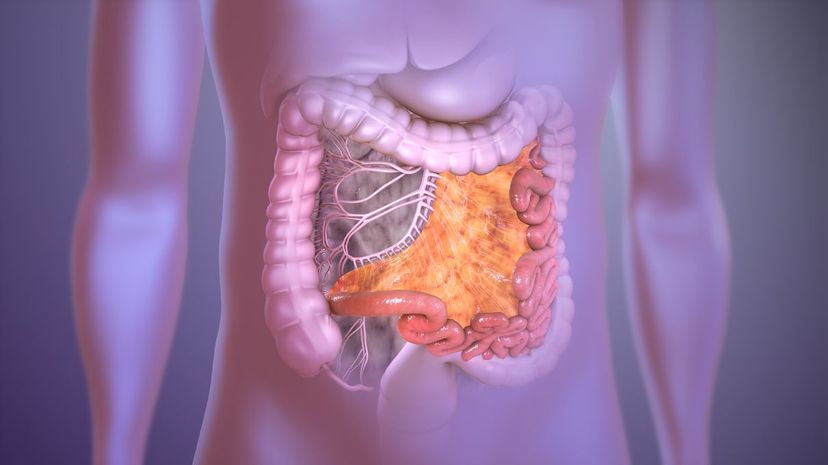
The mesentery is a very real collection of tissues that keeps our intestines where they should be! This internal organ also helps store fat and provide blood and other necessities to the intestines.
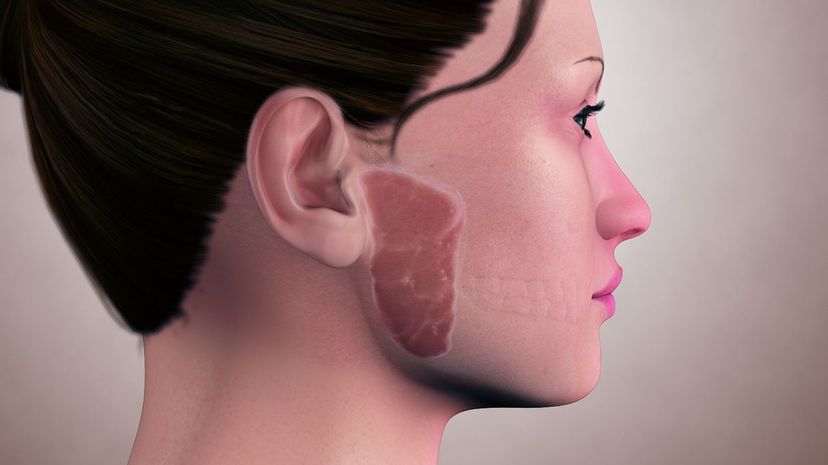
The parotid glands are very real! They are located on each side of the mouth, just before the ears. If someone contracts mumps, it is likely that both of the parotid glands will swell.
Advertisement
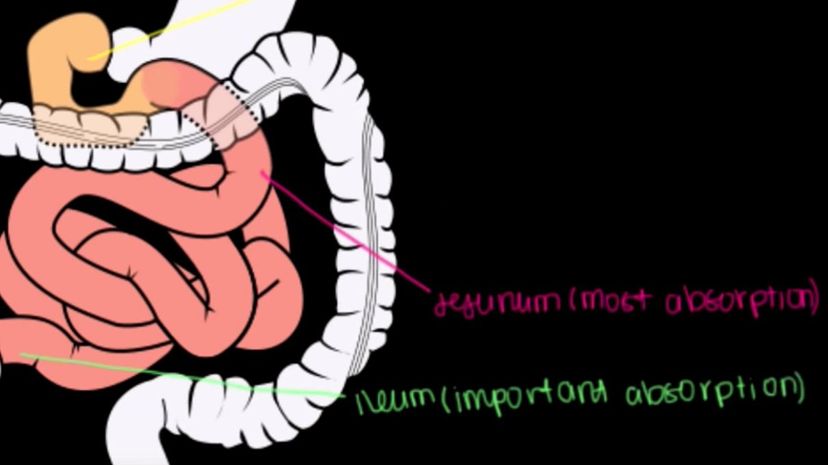
The ileum is real! It follows the duodenum and the jejunum. Its primary purpose is to absorb whatever nutrients were not grabbed by the earlier parts of the small intestine. One such nutrient is bile salts.

The organ that is being talked about here is the tongue! It helps the body swallow and manipulate the food around one's mouth so that it is adequately chewed. It is the primary organ of taste.
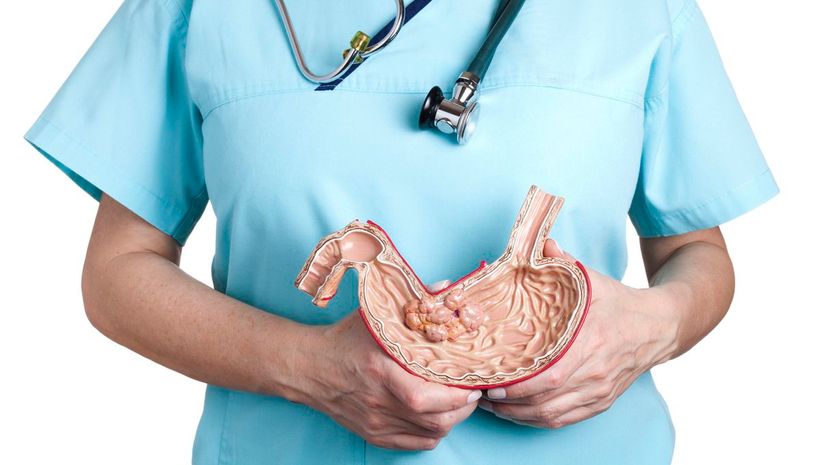
There's no such thing as a cardial sack! It's the stomach that collects food and begins the second part of digestion. The stomach uses acid to break down food after the body has chewed it.
Advertisement
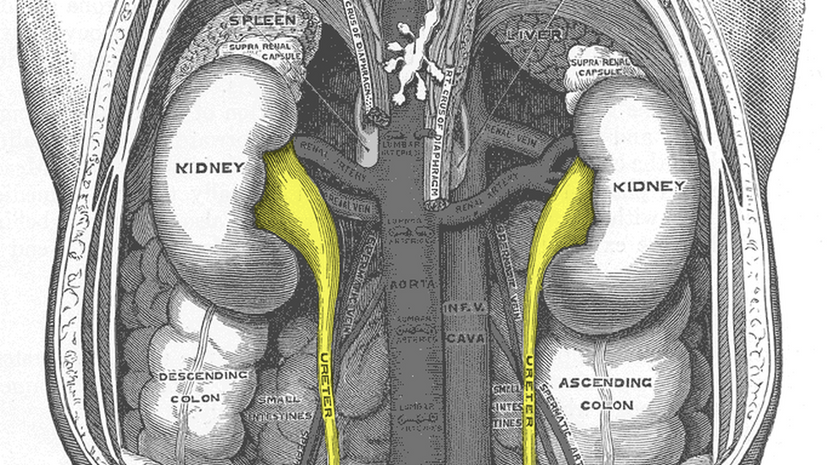
The ureters are very real! Each body has two that connect to each kidney. They then transport urine into a singular bladder. The primary material that makes up the ureters is smooth muscle.
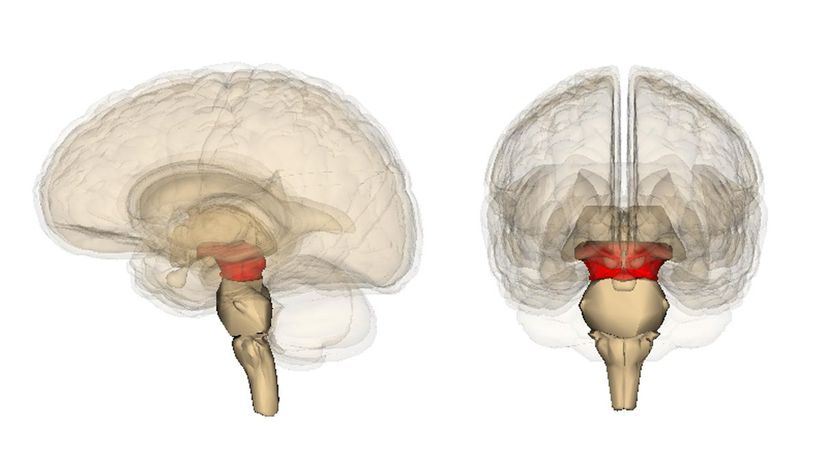
The olfacephalon is fake! The organ in question here is the midbrain, or mesencephalon. It helps the body with things like temperature regulation, as well as hearing, vision and arousal.