
About This Quiz
Knights, warfare and royal successions: there was plenty going on during the medieval times to make it a period worth studying for anyone interested in the history of Europe. Do you consider yourself an expert on what's been labeled the middle period between times when culture flourished? This quiz will test your knowledge on just that.Â
When discussing the medieval period, it's easy to dismiss it for what has traditionally been seen as a transition from one flourishing society to another, with the period in between deemed to be less worthy of study. That couldn't be further from the truth, however, as the medieval era had its own complex intricacies that influenced not only the future of European society but also the future of the world.Â
From the rise of the earliest kingdoms to the wars that ravaged Europe during the end of the period, will you be able to put all of your thoughts in order as you try to get a high score on this medieval history quiz? If we had to guess, the terminology questions will probably get the best of you.Â
When you're ready, dive in and see if you can catapult yourself to a high score.Â
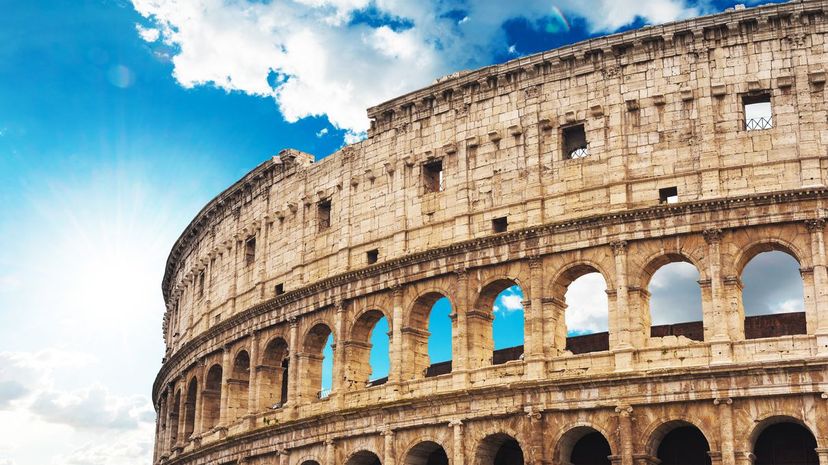

Prior to the fall of Rome, Germanic tribes were constantly pushing the Roman Empire along the northern borders. They twice sacked the city of Rome in the 5th century before the Germanic leader Odoacer overthrew Emperor Romulus Augustulus in 476 AD.
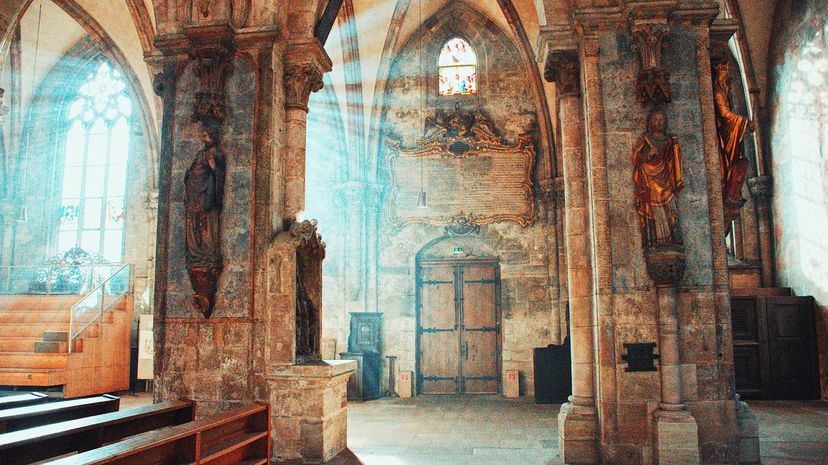

With the European landscape in shambles, the Catholic Church was able to take advantage of the chaos by providing a center of stability. It began this process by sending out missionaries like St. Augustine of Canterbury to spread the message of Christianity to "barbarians" living throughout Europe.
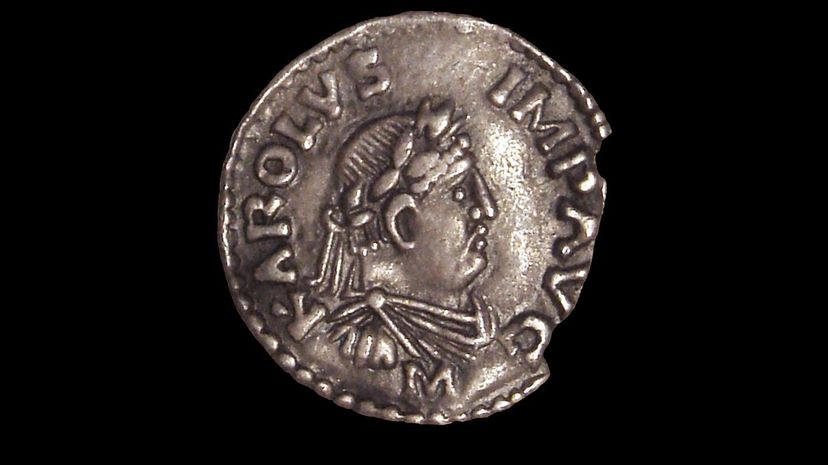

The Frankish king Charles I, known better as Charlemagne, engaged in warfare with other Germanic tribes to unite them under the authority of Christianity. This new, united territory became known as the Holy Roman Empire.
Advertisement
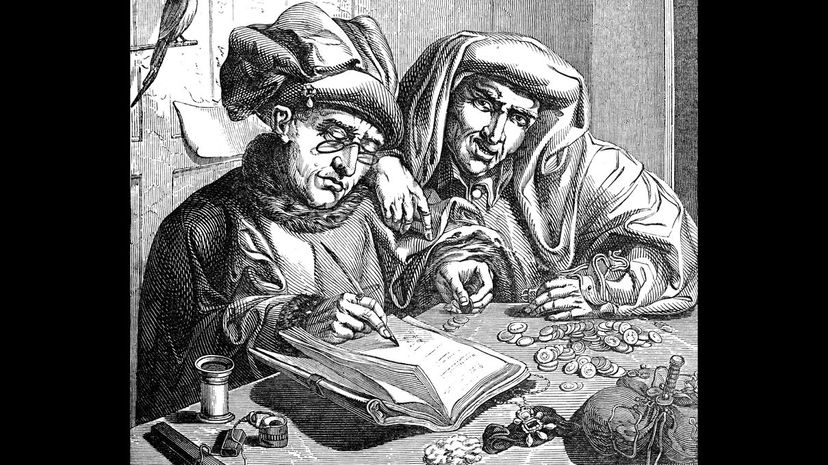

The Catholic Church established the 10 percent tithe to separate their income from the kings' taxes levied in individual kingdoms. Through this form of monetary acquisition, the Catholic Church was able to quickly establish itself as a major power during medieval times.
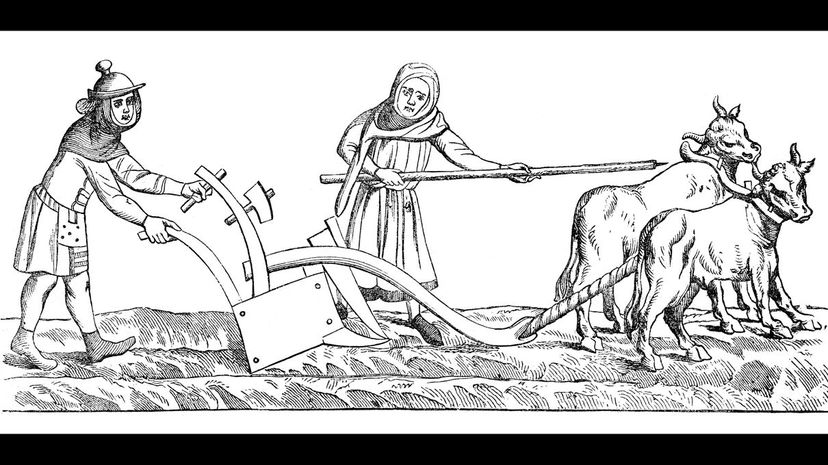

Serfs were the poorest of the peasant class, living in a way that's often considered slavery since they were required to remain on the land they worked. These serfs were owned by the lords they worked for and forced to not only grow food but also pay rent.
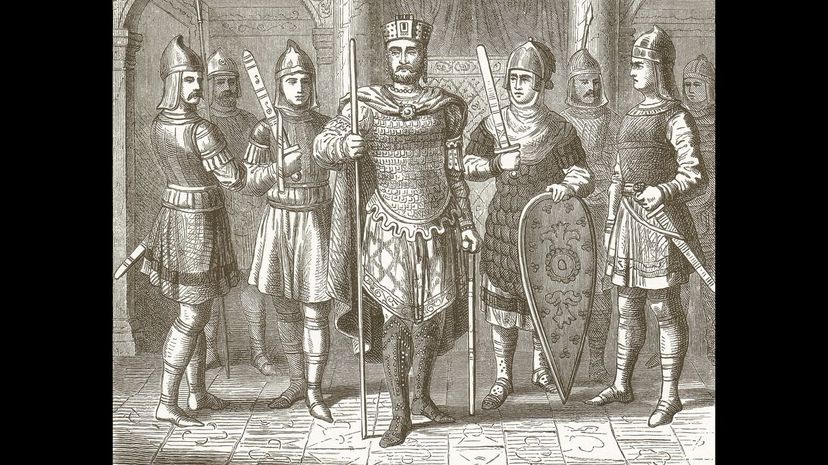

The Byzantine Empire split from the Catholic Church in 1054 AD in what became known as the East-West Schism. After the split, the church of the Byzantine Empire was called the Eastern Orthodox with their own authority figures and religious practices.
Advertisement
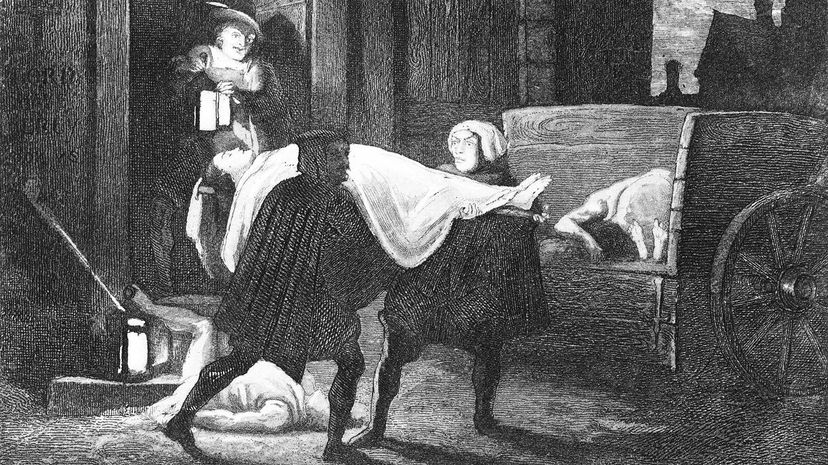

The Black Death is thought to have been brought to Europe on ships sailing from Asia, where the disease first devastated communities. The disease was quickly recognized and the ships were sent away, but it wasn't quick enough to stop the disease from spreading.
After coming to power, it didn't take King John long to create enemies both inside and outside his kingdom. First, he lost favor with the Catholic Church over disputes with Pope Innocent III, and he later faced an internal rebellion after failing to maintain previous customs that were in place.
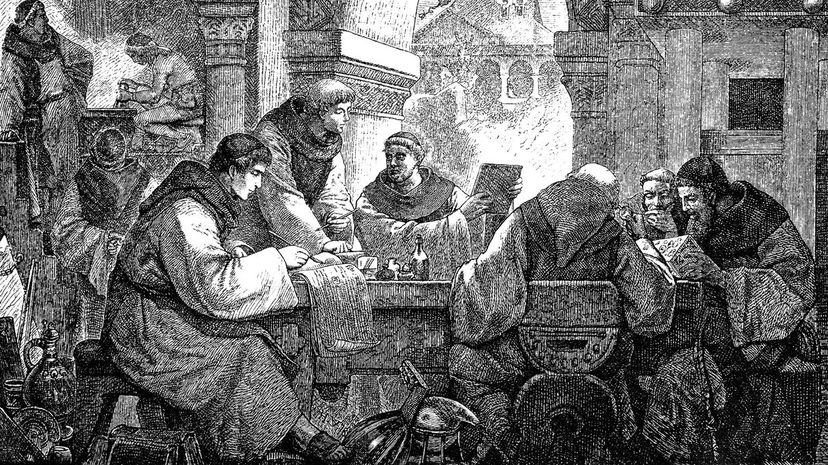

Monasteries in the Middle Ages were almost completely self-sufficient. The members of the monastery would both grow food and make clothes to keep from having contact with the outside world, as they wanted to put their full focus on God.
Advertisement
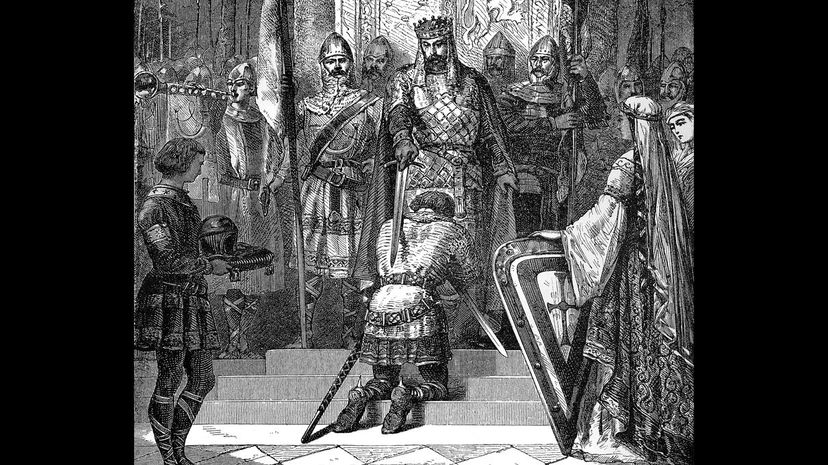

Violence and warfare were commonplace during medieval times, and knights, of course, were the ones engaging in this activity. Chivalry was established to give a knight ground rules on how to conduct themselves around those with less power than them.
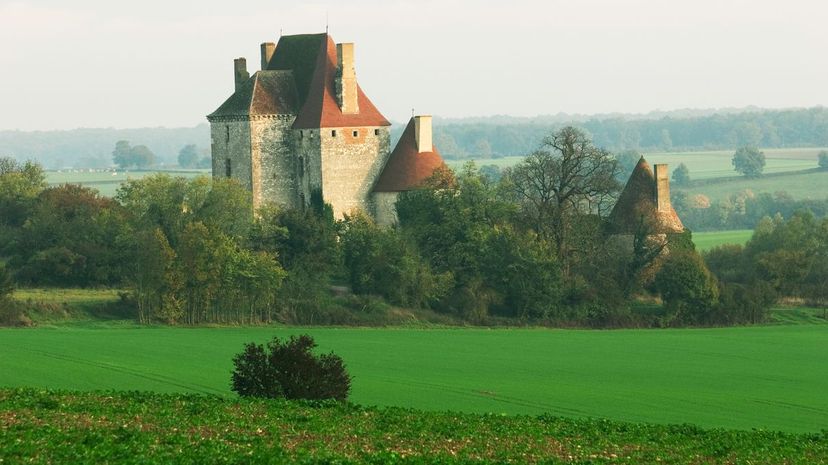

A fief, an estate of land, was provided to a free man from a lord in exchange for services and loyalty. The main service provided was a military allegiance in the event that war broke out and the lord needed to raise an army.
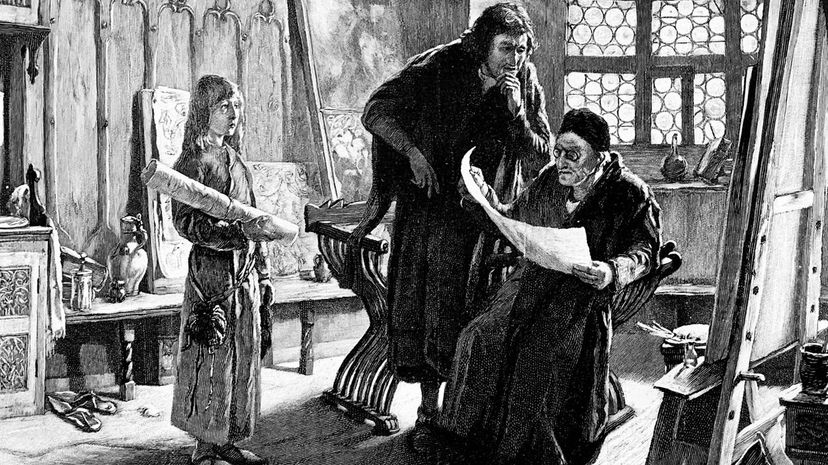

An apprentice in the Middle Ages could became a journeyman after three to four years of practice at a craft, which they often started as young as 10 years old. As a journeyman, they were still training to become an expert, but they could start working within the marketplace.
Advertisement
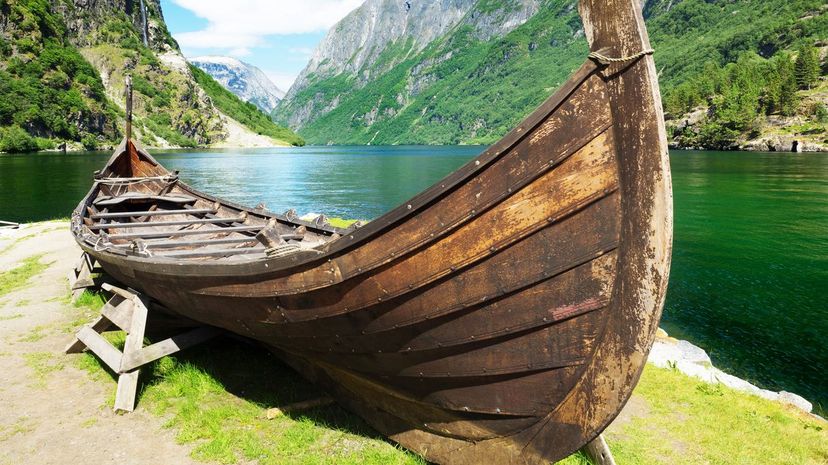

The Vikings had a very complex political, social and religious life living in Scandinavia. They carried many of these customs across the sea with them as they raided distant lands while also merging with local cultures as they settled these new areas.

Typically, vassals were either knights or barons, though occasionally members of the nobility became trusted vassals as well. The concept of a vassal is believed to have originated in England where all land was considered to be in possession of the king.
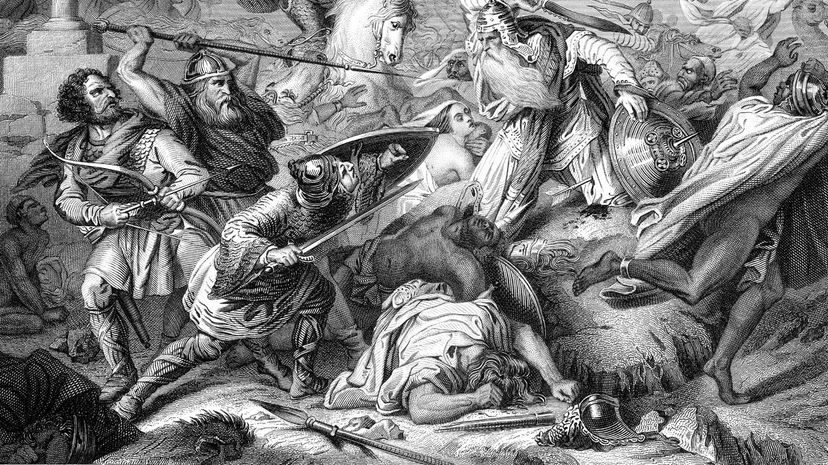

Charles Martel led Frankish forces against Abdul Rahman Al Ghafiqi and the Umayyad Caliphate, who had been expanding Muslim influence in Europe for decades. The Frankish victory was the beginning of a dynasty that dominated Europe for centuries to come.
Advertisement

The Norman conquest of England brought major changes to the kingdom other than new rule under the House of Normandy. One major change resulting from William's conquest was the elimination of slavery in England, a practice that could be traced back to the Romans.
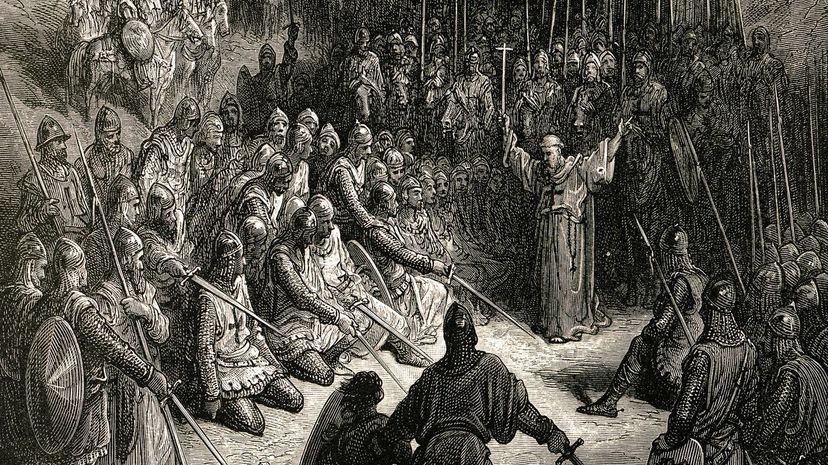

When Pope Urban II made a call for a force of crusaders to take back Jerusalem from unfriendly Muslim forces occupying the city, Peter the Hermit took note and made it his mission to lead the charge. He immediately traveled across Europe seeking members to join his People's Crusade.
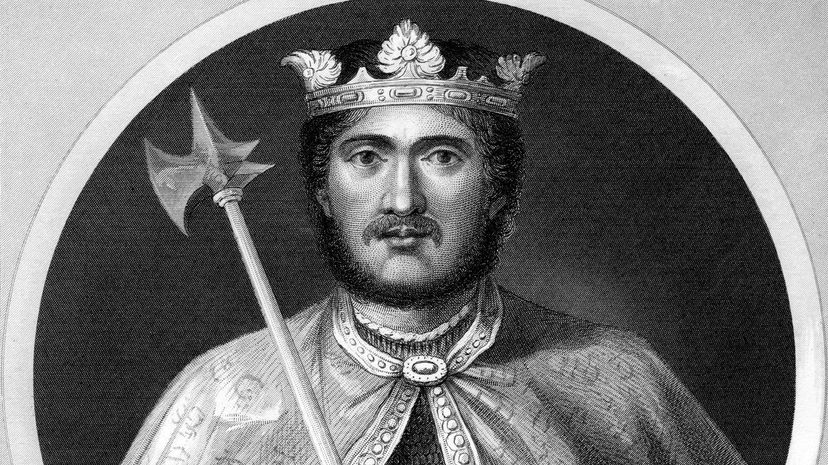

The Third Crusade was the result of Saladin, who ruled as the Ayyubid sultan, conquering Jerusalem during his conquest of the Holy Land. Forces from England, France and Germany united on this journey and achieved major victories, but they weren't able to recapture Jerusalem.
Advertisement

Rollo is depicted as a character in the show "Vikings" that premiered on the History Channel in 2013. In the show, he's the brother of the Viking legend Ragnar Lothbrok, but eventually he betrays his brother to become the Duke of Normandy.

Uniting England, Denmark and Norway, Cnut the Great formed a vast territory under his rule known as the North Sea Empire. However, the empire did not survive long and began to crumble near his death before fully collapsing after he passed.

By the end of the 9th century, the Vikings had made their presence known across Britain by winning major territory in the north and east parts of the country. These invaders managed to force Alfred the Great to go into hiding before he raised forces and launched a counterattack at the Battle of Edington.
Advertisement

After the Umayyad Dynasty conquered much of Iberia in the 8th century, Muslims maintained at least some control in the region until the end of the Middle Ages. During this period, Muslim, Christian and Jewish cultures merged as these groups were forced to live aside one another.
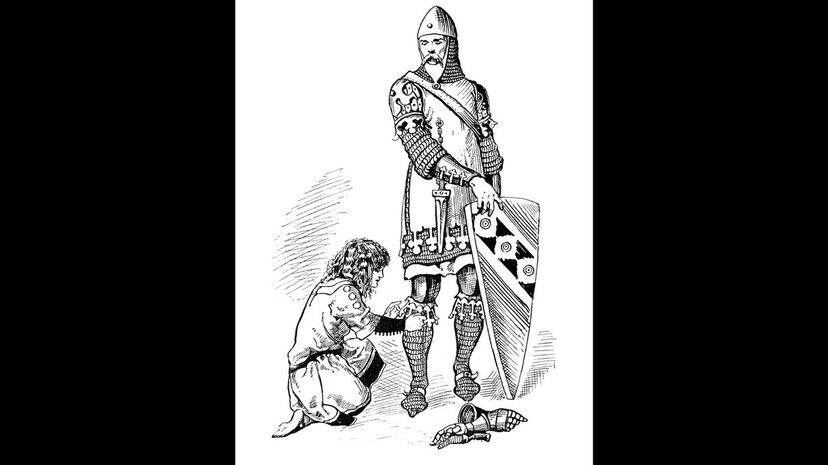

As the servant of a knight, squires had various responsibilities that they were required to perform in service of their lord. They often carried around supplies and attended to horses, but some squires even followed knights into battle.
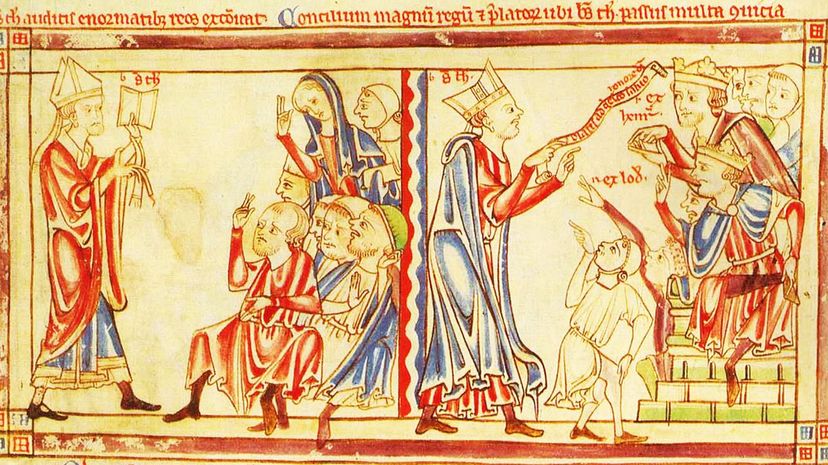

The Catholic Church wasn't afraid to excommunicate a king who went against their wishes. However, they didn't limit excommunication to royalty, as members of the clergy, vassals and common people all faced being cut off from the influence of the Papal power.
Advertisement
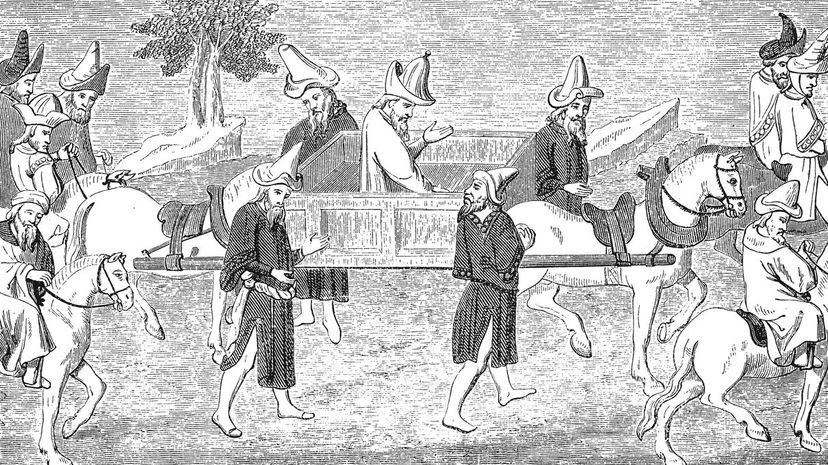

During medieval times, Marco Polo used the Silk Road to travel between Europe and Asia, where he made contact as far as China. Though he wasn't the first European to embark on this journey, he was the first one to write a book about his adventures, giving Europeans a glimpse of what Asia was like.

To better control England, William the Conqueror had the Domesday Book recorded in order to get a better gauge on where power lay within the kingdom. He was able to use this knowledge when he redistributed land to the followers who were loyal during the conquest.
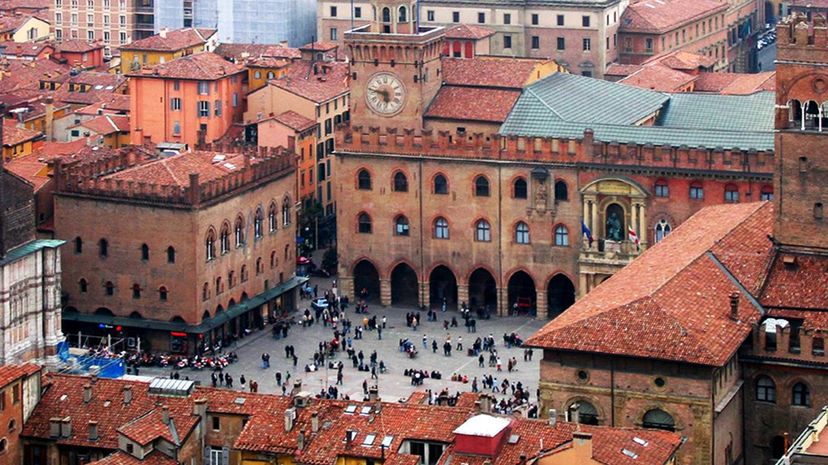

Founded in 1088 AD, the University of Bologna was established as a center of study in law for students across Europe. The earliest students went on to fill positions within either the Catholic Church or the state.
Advertisement
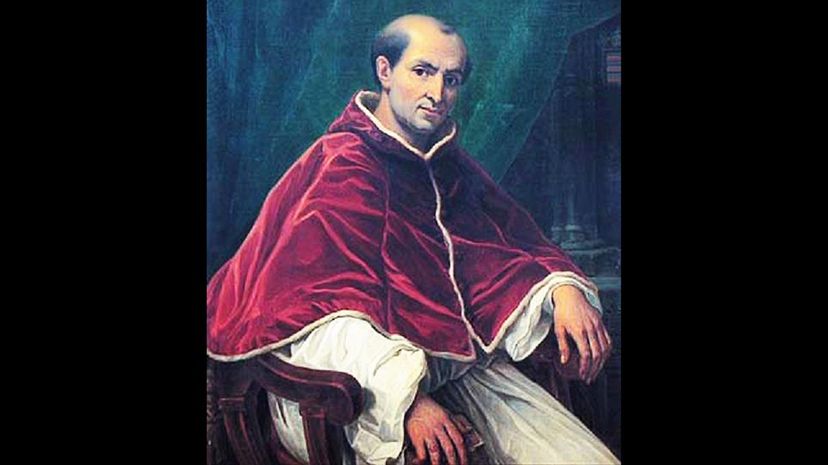

Pope Clement V became a close ally of King Philip IV of France, who he allowed to imprison and torture members of the Knights Templar into giving confessions of heresy. Philip encouraged the pope to provide him with this authority because he wanted to eliminate debts France owed to the Templar.

"The Canterbury Tales" was written as a series of stories following pilgrims as the embark on a journey from London to the Canterbury Cathedral. These pilgrims were encouraged to tell a story that would be rewarded with a free supper if their story was deemed the best.

After a long war, both England and Scotland sought peace to end the bitter conflict, which had turned in the Scottish favor. The Treaty of Edinburgh-Northampton was finally reached with the agreement that King Edward II's daughter would marry the son of Robert the Bruce.
Advertisement

The death of Charles IV of France left the French kingdom without a ruler as he died without an heir. King Edward III of England was his closest male relative, but the nobility in France refused to accept an English ruler, leading to war when Edward tried to claim the throne.

The Peasants' Revolt in England came in the middle of the bitter Hundred Years' War, which had already taken its toll on the English crown. The revolt was the result of taxes levied on the people of England to fund English campaigns in France.

Holding vast territory across France due to an invasion in 1415, England seemed to have the upper hand in the Hundred Years' War. When French forces led by Joan of Arc broke the Siege of Orleans, it was a major turning point for the French, who would go on to win several more battles in the coming year.
Advertisement

After the split with the Eastern Christian Church, the Western churches were able to maintain a uniform canon law throughout the medieval period. However, the Protestant Reformation in the 16th century changed not only canon law but also the future of religion in Europe.
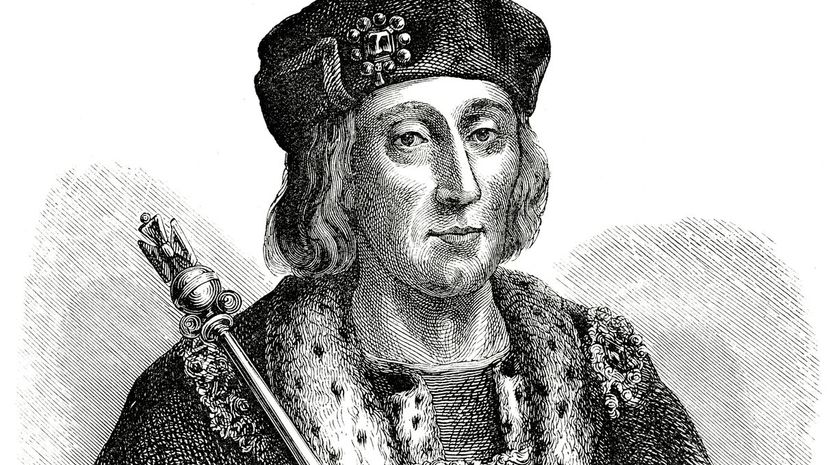

The House of Tudor began with the ascension of Henry VII and wouldn't end until the death of Elizabeth I, who died without an heir. With the death of Elizabeth, James VI of Scotland came to power, beginning the House of Stuart.
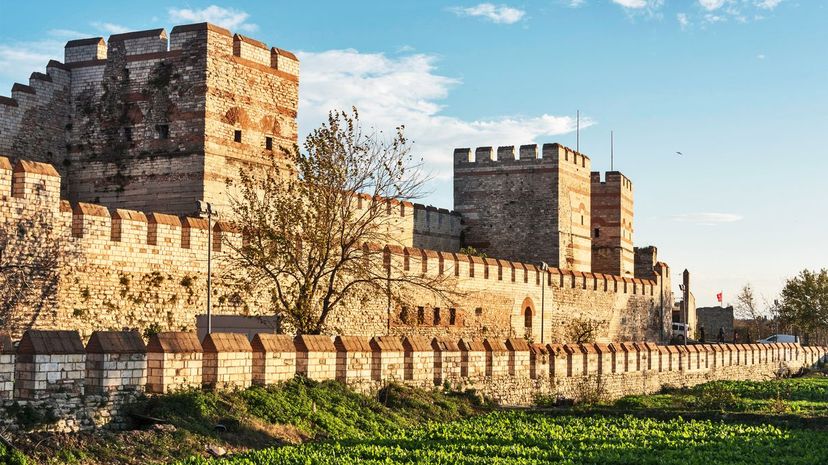

Despite numerous sieges, Constantinople managed to survive as the capital of the Byzantine Empire for over 1,000 years. Its longevity can be credited to a series of walls built around the city throughout the 5th century.
Advertisement
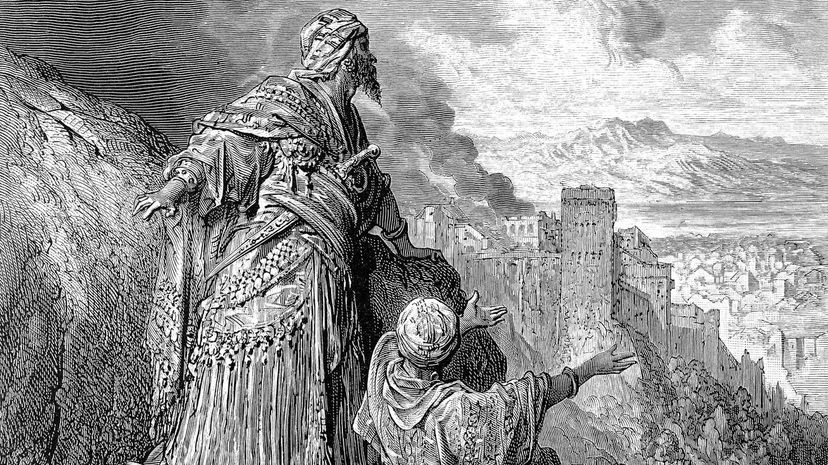

The Reconquista was one of the final events that marked the end of the medieval period in Europe. Spain and Portugal became the leaders of the new era to rise, the Age of Exploration.
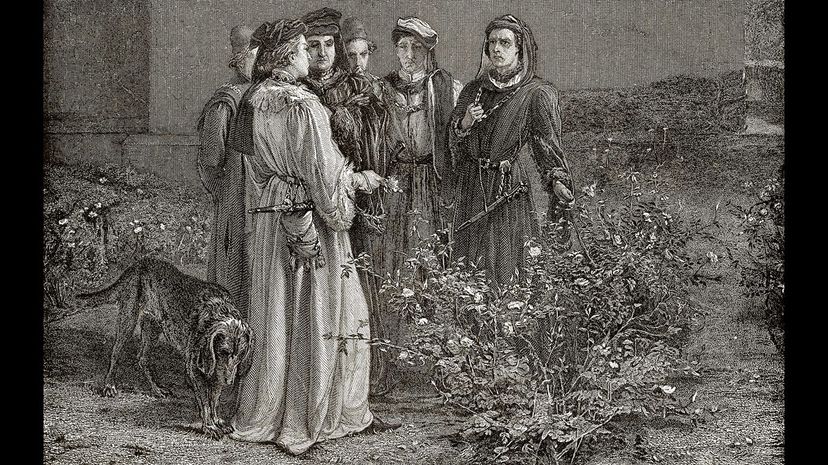

The conflict between the Duke of York and the Duke of Somerset started after Henry VI's mental breakdown that left him unable to rule. The two dukes vied for the right to serve as the Lord Protector, a position that was awarded to the Duke of York until Henry recovered.
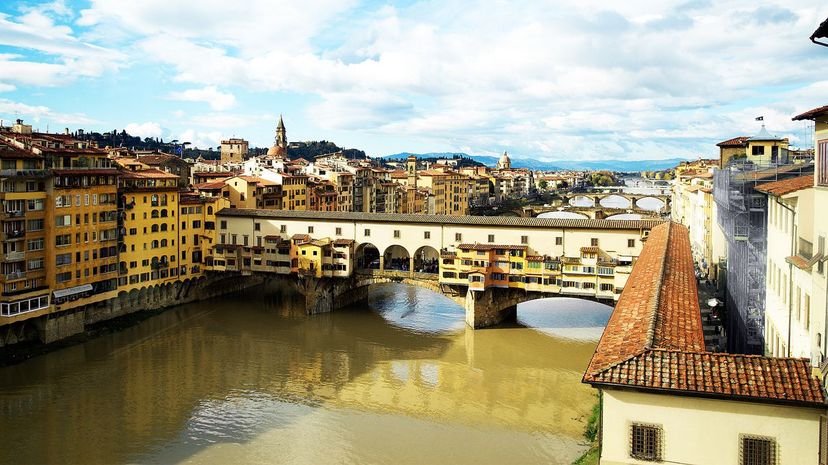

Stationed in Florence, the Medici family was one of the richest families in Europe. They used their wealth to inspire arts and humanism across the continent, helping usher in the Renaissance.
Advertisement
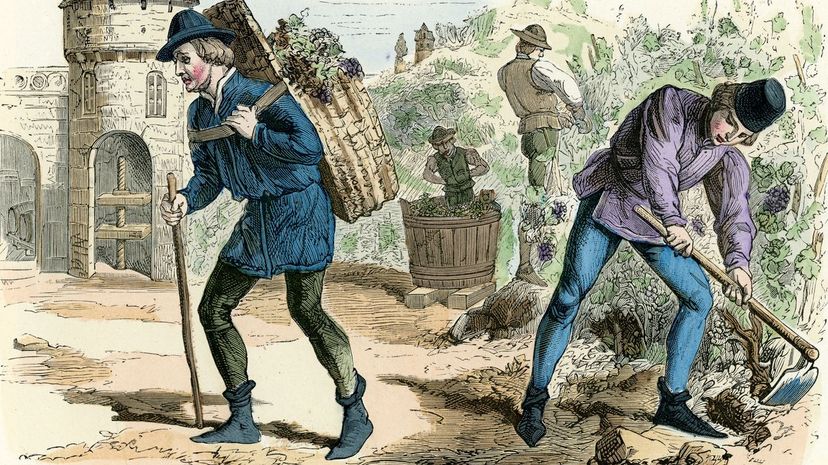

Considering 90 percent of the population worked as peasants, feudalism clearly showed an imbalance of power. A peasant's life in medieval Europe was quite difficult and relatively short, as most died before the age of 30.