
About This Quiz
From the beginning, Rome was one of the most violent civilizations of its time, utilizing brutal tactics and constant warfare to spread its influence throughout Italy and later Europe and Africa. This history of warfare would be a defining characteristic as Rome went from a monarchy to a republic and then to an extensive empire that spread from Britain to the Middle East.
Many of these Roman wars were against external threats, opposing empires trying to maintain their own base of power or even increase it. These threats came in many forms, from various regions with different levels of strength, which showed just how dynamic the Roman army was.Â
Of course, it wasn't always outside threats that the Romans had to worry about. Civil wars were common throughout Roman history, bringing about significant changes that affected the course of their civilization. These wars would also ultimately lead to Rome's downfall by the fifth century.Â
Are you prepared to march into this quiz to get a victory? The challenge will be immense as you face questions that would bring even the most knowledgable scholars to their knees.Â
When you're ready to make a charge, get started and see if you can get the win.
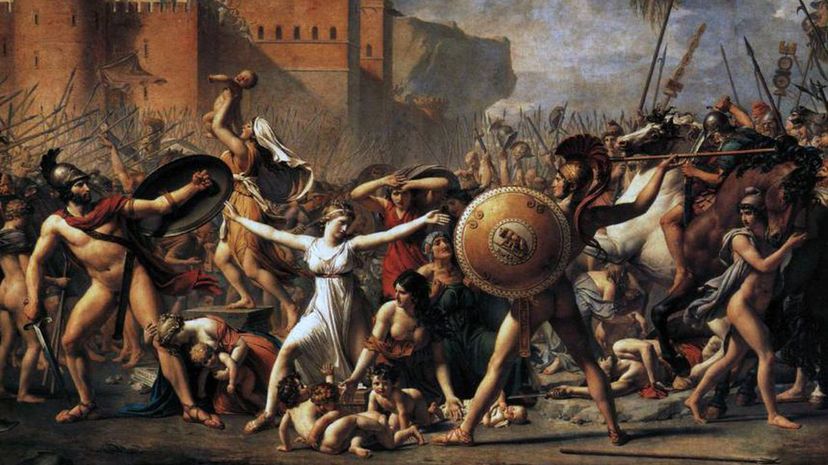

The abduction of the Sabine women took place in approximately 750 B.C. Jacques-Louis David, a French Neoclassical painter, represented a woman standing between the Romans and the Sabines in his work "The Intervention of the Sabine Women."

Located near each other on opposite sides of the Tiber, Rome and Veii had a history that saw them work both together and against one another at times. When a treaty between the two cities ended, Rome laid siege to Veii, which lasted 10 years before the Romans were able to penetrate the city.
Rome protected Campania against the Samnites, who lived in south-central Italy. Rome tried to make peace with the Latin states before war broke out, so they asked them to send representatives to Rome to present their demands. The Latin states did just that, requesting equal representation in the Senate, but this demand was refused. At that point, war was inevitable.
Advertisement

Strategically located in the Mediterranean, Carthage was an important trading center in the ancient world. Its role as a trading port made the city one of the richest and most powerful during its height.

The First Punic War started after Rome intervened in a dispute between two cities in Sicily: Syracuse and Messina. Sicily was controlled by Carthage at the time, and Carthage sided with Syracuse in the dispute. Rome took the other side, and the two powers went to war.

After his capture, Marcus Atilius Regulus was released to return to Rome, where he was supposed to negotiate a truce. He was then returned to his captors. Although reports differ, one account says that Marcus Atilius Regulus was tortured to death by the Carthaginians after he was returned.
Advertisement

Hannibal was the son of a renowned Carthaginian general named Hamilcar Barca, and he was trained from an early age to be a commander himself. Hannibal rose through the ranks and eventually came to command Carthage's Spanish empire.

The Fabian strategy involved avoiding open field combat. Instead, the goal was forcing the opposing army to chase the Roman army around or hiding out in a city while the chasing army depleted their resources.
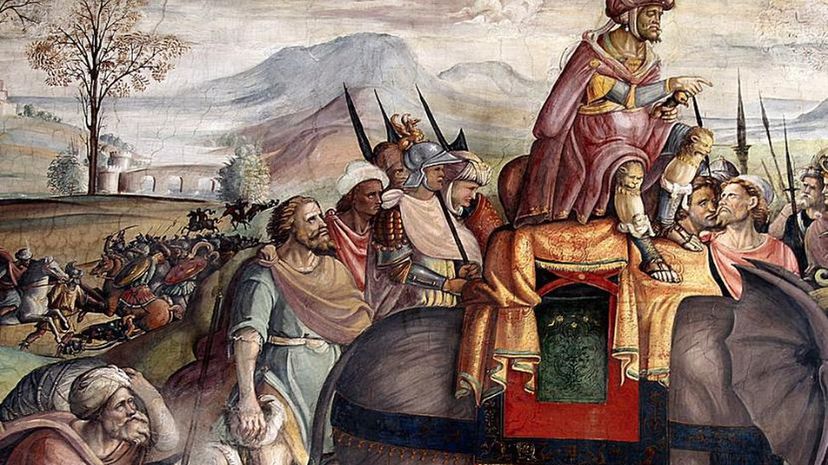

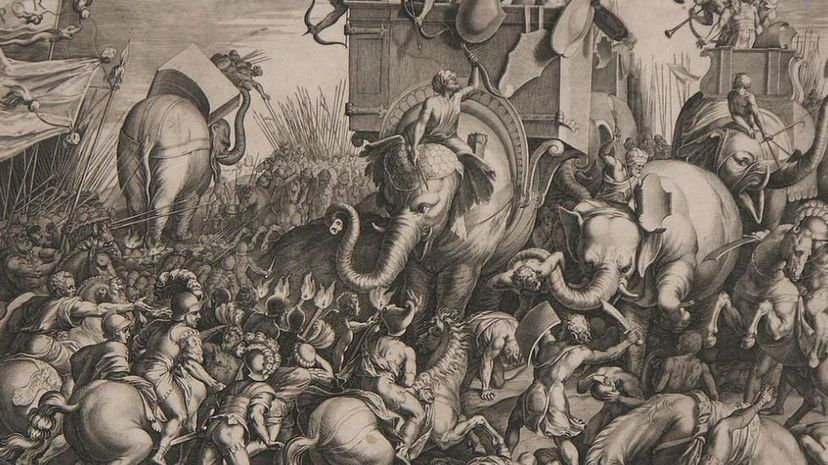
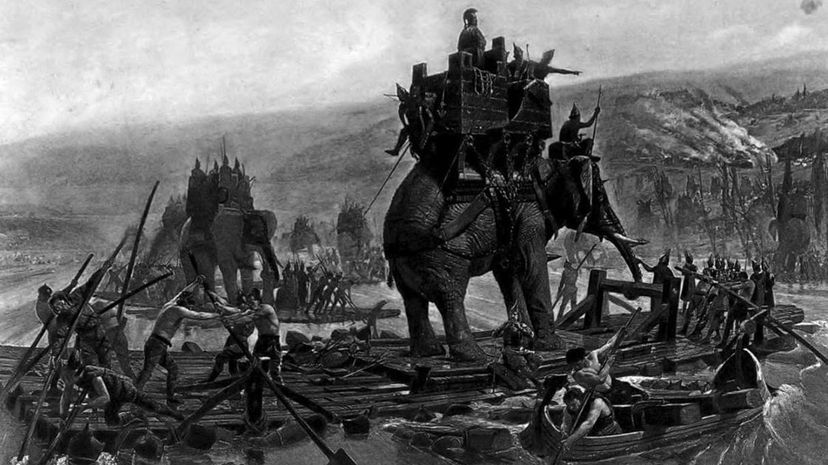
Hannibal invaded Italy through the Alps, which was viewed as an impossible task before he accomplished it. The fact that he brought along war elephants made the journey that much more astounding.
Advertisement
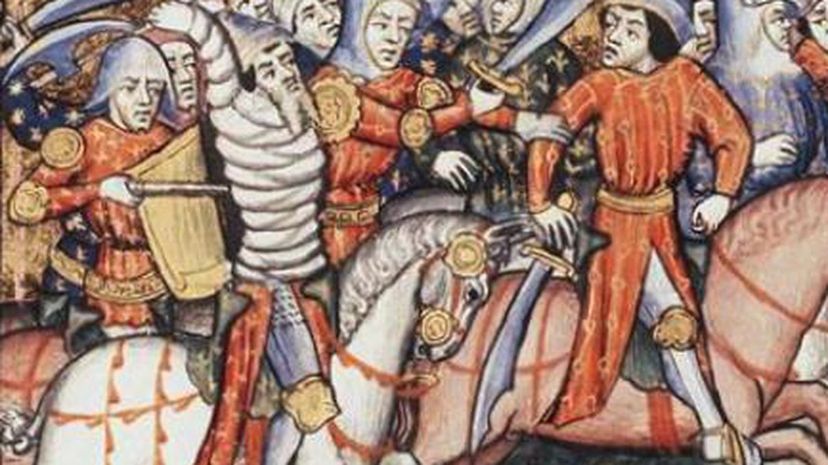

The Battle of Cannae was fought with brains over manpower. Knowing his army was outnumbered, Hannibal decided to lure the Roman army into a trap where he drew back his center as they advanced, only to then surround the Romans on all sides.
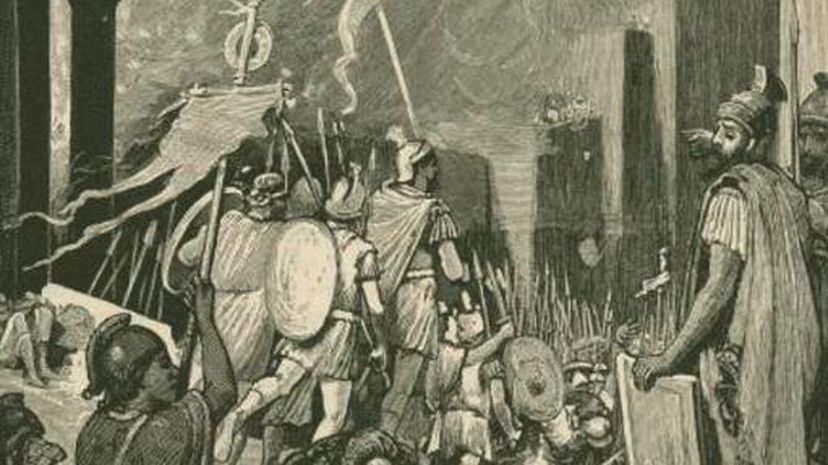

Romans used slaves for a variety of purposes, from household chores to working in the fields and on construction jobs. Across the empire, around one-fifth of the population was enslaved.
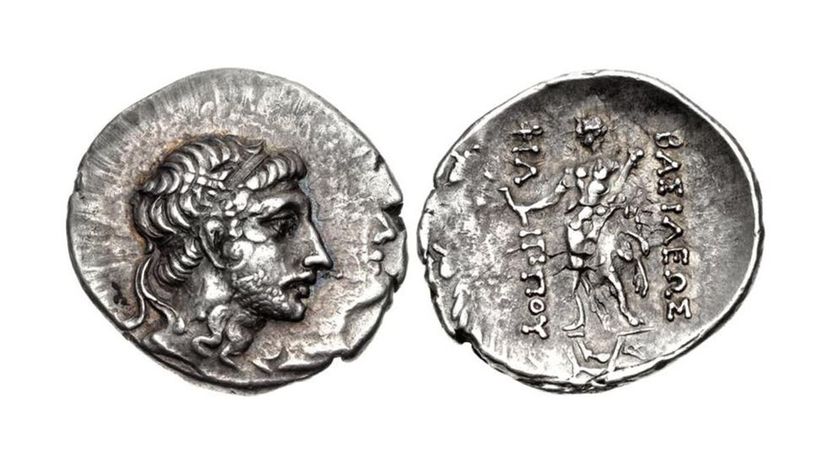

Claiming to be the son of Perseus, the former king of Macedonia, Andriscus was actually a pretender when he gained the throne. His reign didn't last long before he was defeated by Rome, which made him the last king of Macedonia.
Advertisement

The Laconian War was fought on Sparta's side under King Nabis, who sought to rebuild Sparta's army and secure Spartan dominance. However, Nabis ruled through bloodshed, executing Spartan royalty on his way to the top. His allies eventually assassinated him.

Corinth took the brunt of the force unleashed by Rome during the Achaean War. As the war came to a close, the city was completely annihilated by the Romans, who killed all of the men and sold the women and children into slavery.

There was no higher elected office in the Roman Republic than that of consul, two of which were elected yearly by the citizens of Rome. When Rome went to war, the consuls served as the commanders of the Roman legions, where they had almost unlimited power.
Advertisement

Throughout his life in the Roman military, Gaius Marius made changes that put more power in the hands of the Roman consuls, as the military's loyalty aligned more with the general than with the Senate. Sulla, on the other hand, supported the Senate and used his power to ensure the body was preserved.

Under constant threat of being attacked by the Gallic tribes, Roman leaders saw that the only way to secure their border was to go to war and bring Gaul under Roman influence. Julius Caesar saw this as an opportunity to increase his status in Rome while also obtaining wealth, so he decided to lead the charge.
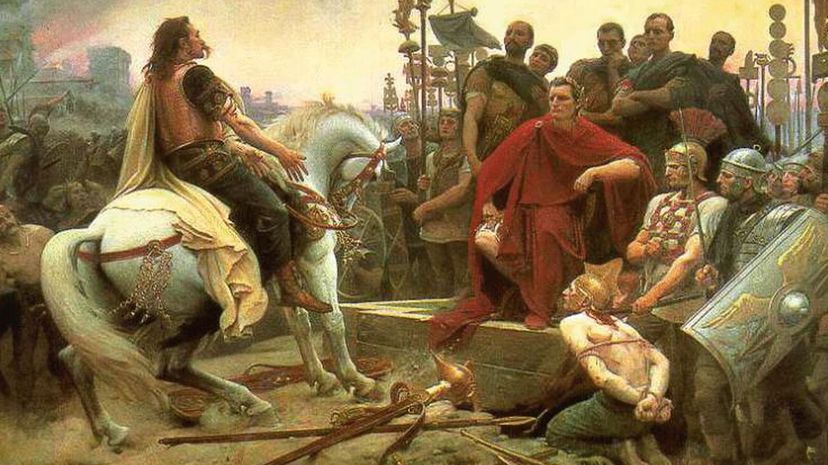

In his campaign against Gaul, Julius Caesar was able to defeat many of the Gallic tribes because they were not united into a single force. By the time the chieftain Vercingetorix united the tribes for the Battle of Alesia, they were too weak to defeat Caesar's army.
Advertisement
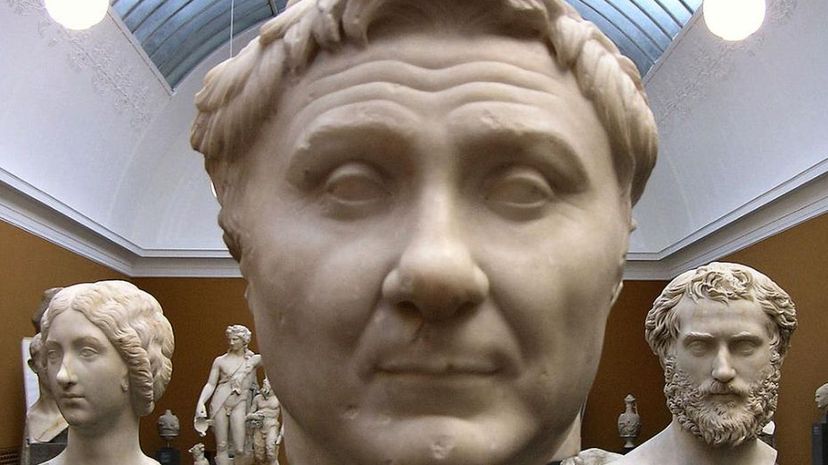

Pompey, one of the great generals in the First Triumvirate, had many triumphs as a military leader in Rome. His military career included battles in Africa and Spain, as well as helping end the slave revolt led by Spartacus.
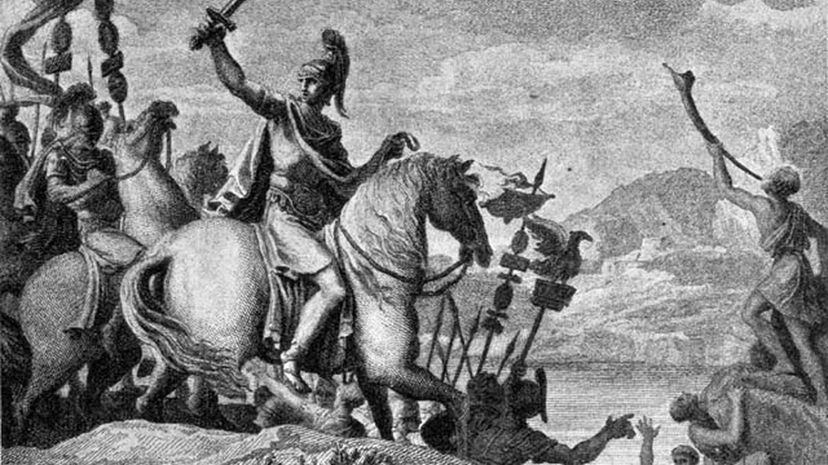

The crossing of the Rubicon has become a famous reference in Western culture. Whenever someone mentions the event as a metaphor, they mean that they have reached a point of no return, similar to Julius Caesar when he crossed the river in 49 B.C.
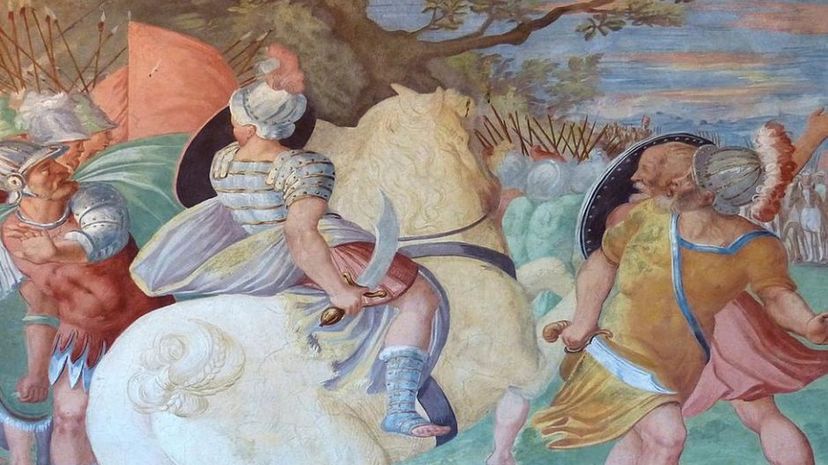

Despite strategic victories against Julius Caesar in their bitter civil war, Pompey wasn't able to finish off his rival for good. Eventually, Caesar routed Pompey's larger army near Pharsalus, forcing Pompey to retreat to Egypt, where he was assassinated.
Advertisement
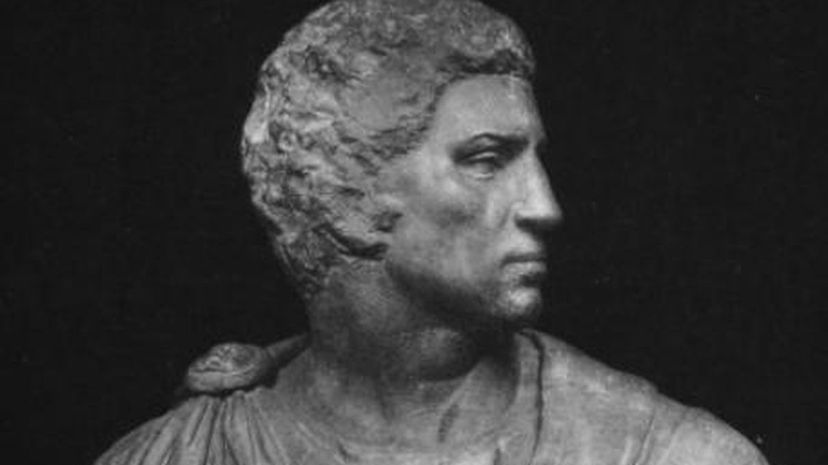

When William Shakespeare wrote his play "Julius Caesar," he depicted Marcus Junius Brutus as a close friend of Julius Caesar who only killed him to preserve the Roman Republic. Perhaps there was some truth to this, but Brutus also stood against Caesar prior to his assassination when he fought with Pompey at Pharsalus.
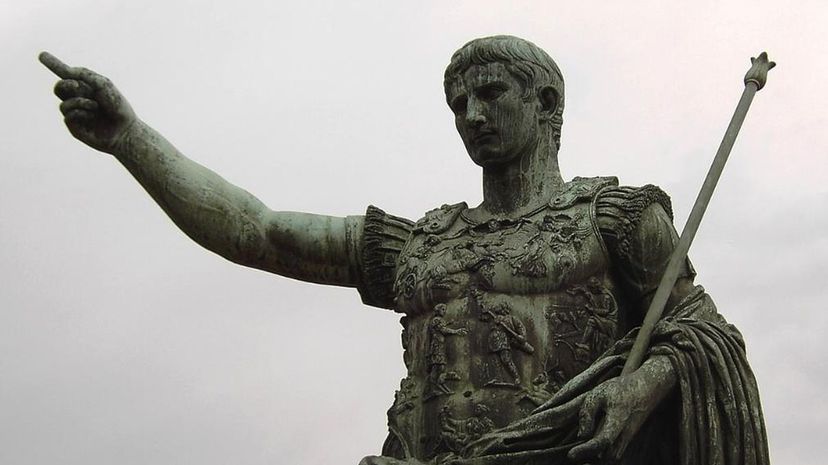

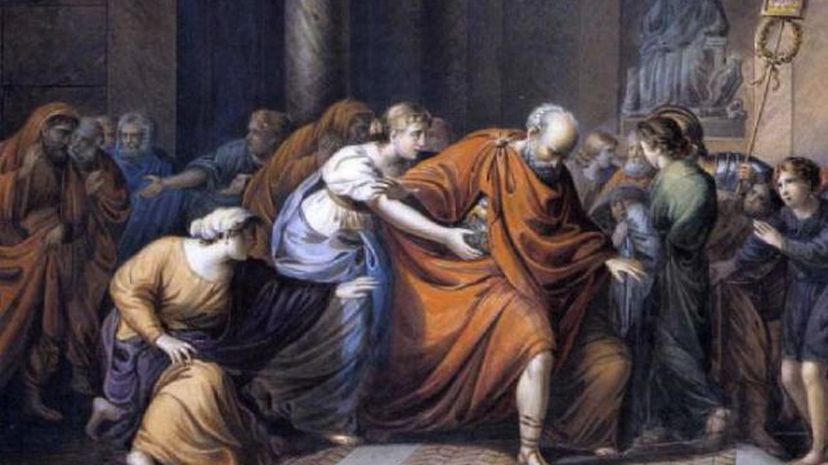
After the rise and fall of Julius Caesar, Rome was in a state of turmoil, and its territories were on the verge of collapse. To secure Roman dominion, Octavian eliminated his rivals and consolidated all power for himself, which brought an end to the Roman Republic.
The pilum, a 7-foot-long javelin, was primarily used by Roman armies as a throwing spear, though it was occasionally used at close range as well. Those who were most experienced with the pilum could throw it up to 100 feet.
Advertisement
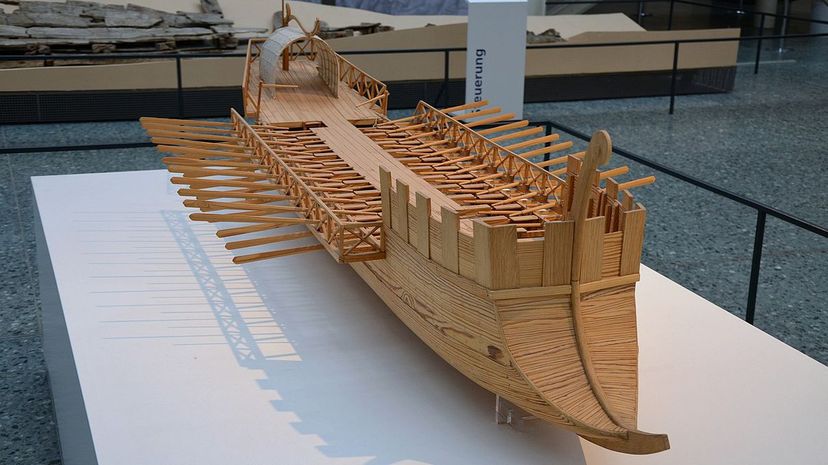

Around the time that Augustus came to power in Rome, the Roman navy went from a single fleet to multiple regional fleets who controlled the waters for the Roman Empire. The Classis Britannica was one such fleet, created when Emperor Claudius ordered the invasion of Britain.
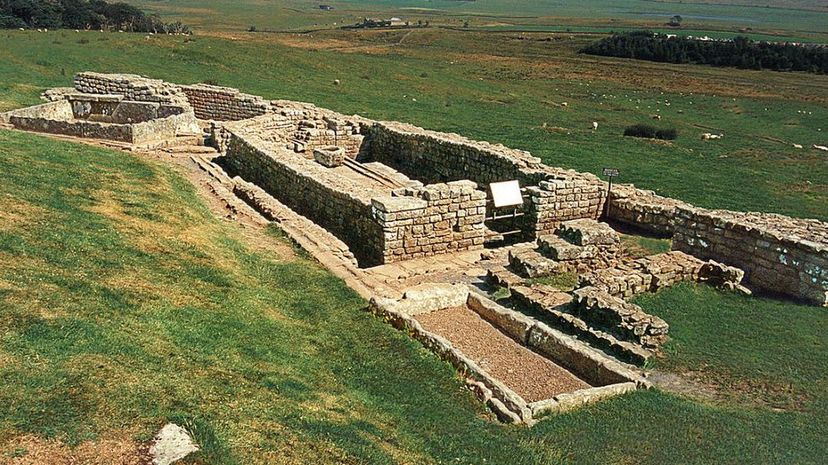

Hadrian's Wall, named after Emperor Hadrian, stretched from British coast to British coast, running 73 miles. Built by Roman soldiers, the wall consisted of 14 to 17 forts, which were manned by those soldiers.

Rome looked at Armenia as a buffer state between the Roman Empire and the Parthian Empire, which meant they couldn't allow a Parthian ruler to sit on the throne. When Tiridates I took the throne at the request of the Parthian king, Rome's only option was to go to war.
Advertisement

The Second Temple, an important place of Jewish worship, was completed around 515 B.C. to serve as a replacement for Solomon's Temple. At the end of the Great Revolt, the temple was destroyed in retaliation for the uprising.
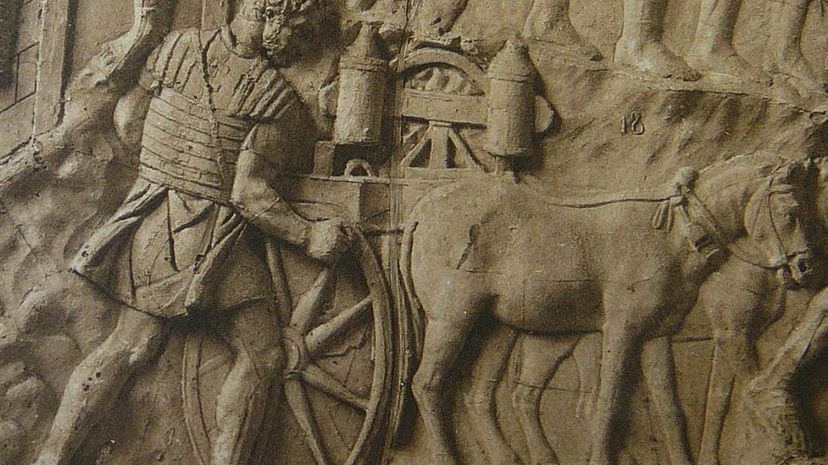

To honor Trajan and his victories in the Dacian Wars, Rome constructed Trajan's Column. It stands over 100 feet, including its pedestal, inside Trajan's Forum. A statue of Trajan was placed on the top of the column, but it was later replaced with a statue of St. Peter.

One of the most significant influences in Sassanid culture was Zoroastrianism, which became the state religion. Though the Sassanids were relatively tolerant of other faiths, Zoroastrian priests were some of the most powerful people in their society.
Advertisement
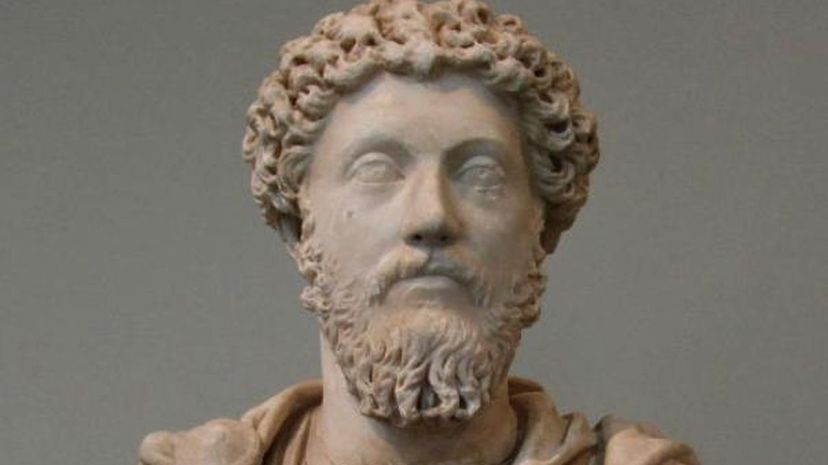

"Meditations" is a series of notes written by Marcus Aurelius, who was considered one of the Five Good Emperors of Rome. The notes were meant to serve as self guidance and explore his belief in Stoic philosophy.
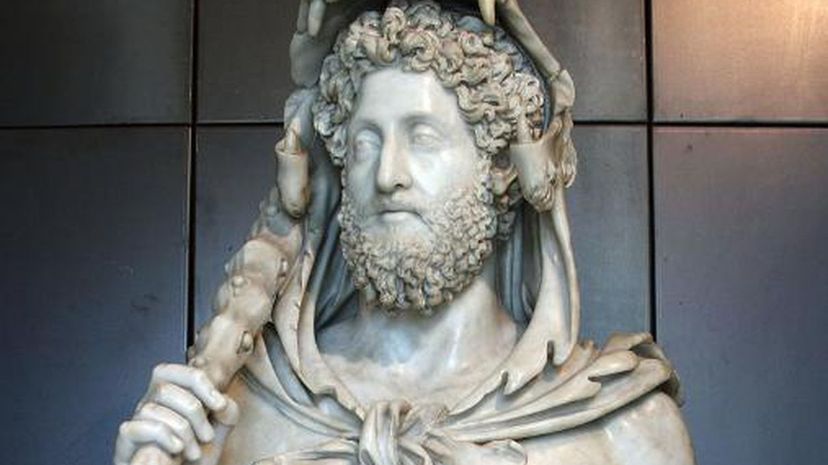

The Year of the Five Emperors was a violent affair in 193 A.D. that came about after the assassination of Emperor Commodus. By the end of the year, two of the five emperors were dead, and the others were engaged in a war for power.

With the Edict of Milan, issued in 313 A.D., Christians were allowed to worship openly without fear of persecution. However, the edict did not make Christianity the state religion within the Roman Empire.
Advertisement
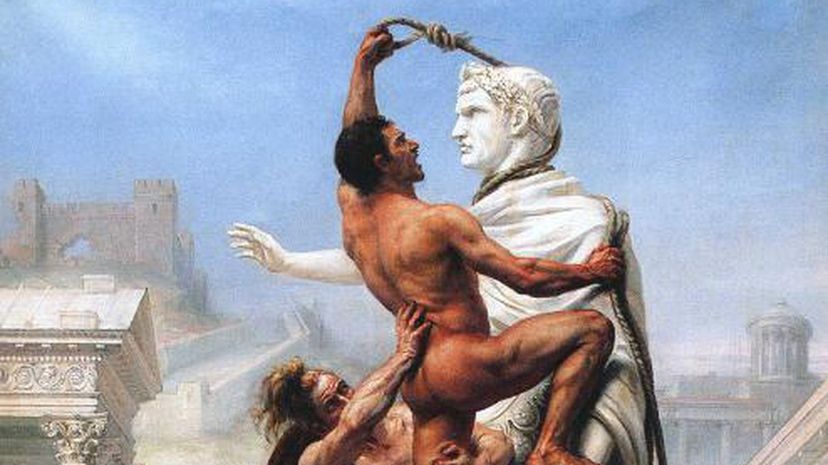

The Visigoths were a western tribe of Goths who warred with Rome for centuries before landing a major defeat at the Battle of Adrianople in 378 A.D. During this time, the Visigoths were able to establish their own kingdom, which extended from Iberia to Eastern Europe.
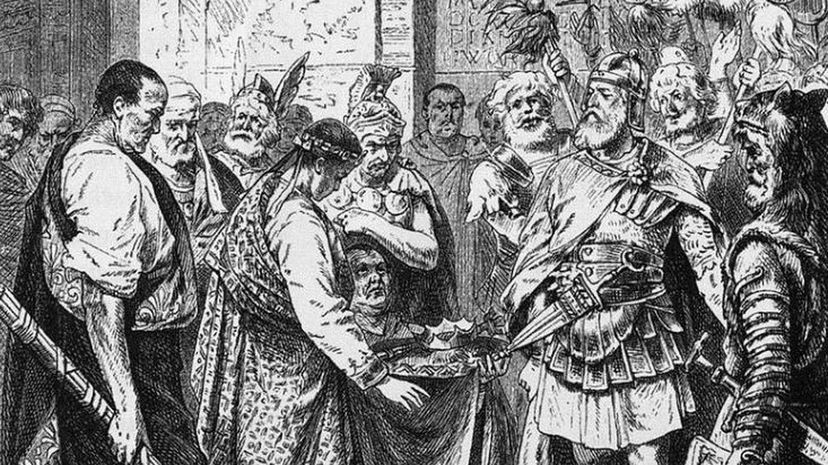

By the time Romulus Augustulus came to power in 475 A.D., the Roman Empire was already split between the West and the East. Even after the Western Roman Empire collapsed, the Eastern Roman Empire continued on in some form until Constantinople was sacked in 1453.