
About This Quiz
Practically everyone has some degree of engine knowledge: whether all you know is that they make your car move or you rebuild LS2s for fun. Now it's time to find out which end of the spectrum you lie on.
A recent survey conducted by Cooper Tires found that nearly 50% of Americans aren't confident that they'd be able to change their vehicle's oil. The same study found that around a third of Americans couldn't even choose the right engine oil for their car. The problem isn't helped by the fact that 54% of people feel intimidated when dealing with mechanics. It's hardly surprising that nearly three-quarters of the vehicles on the road in the U.S. have at least one thing wrong with them.
Some research suggests that the decade you were born in can affect how mechanically knowledgable you are. When it comes to basic engine care, studies show that those aged 66 and older are the most competent age group. The same studies suggest that millennials are the least competent demographic, with just 51% feeling confident enough to drive a stick shift. Do you support this data or contradict it? Take our engine knowledge quiz and find out now!
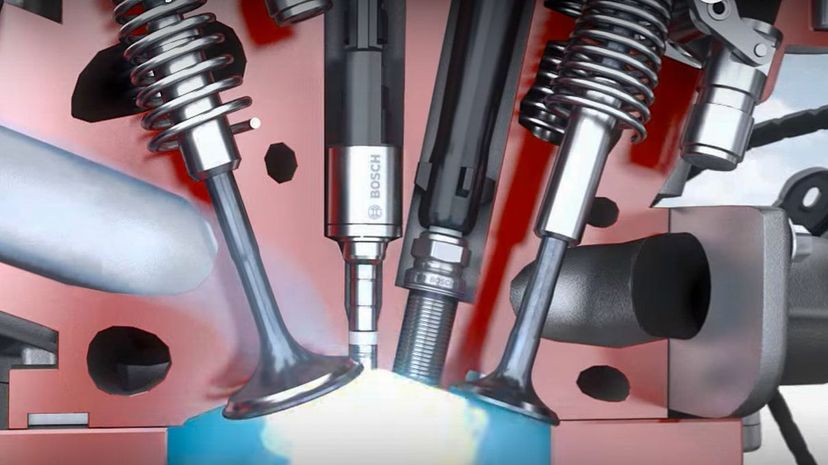

"FI" stands for fuel injection, which is the most common way of introducing fuel into a modern internal combustion engine. Nozzles inject fuel into the car's cylinders. How much fuel is injected and when it's injected is all determined by the car's ECU.
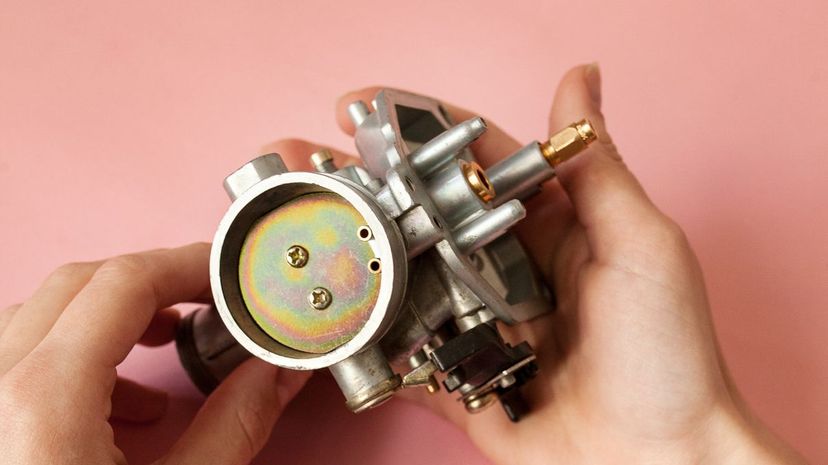

Before fuel injection systems, cars used carburetors. Air runs through carburetors once the throttle is opened, and this creates a vacuum that sucks gasoline in through a small fuel jet. This air/fuel mixture goes into the car's cylinders at the perfect ratio to create an explosion.
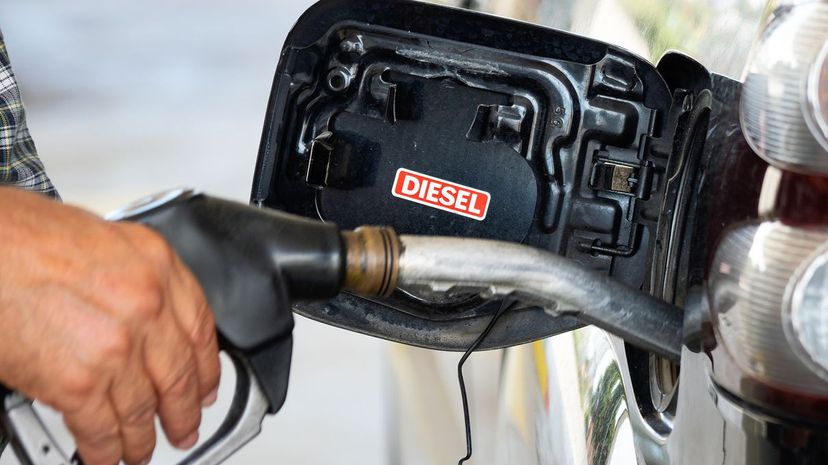

Whether you have a one- or 12-cylinder diesel engine, it doesn't matter, it won't have any spark plugs. This is because diesel isn't ignited the same way gasoline is. The diesel in a diesel engine is ignited by compressing the air/fuel mixture in the engine's cylinders.
Advertisement
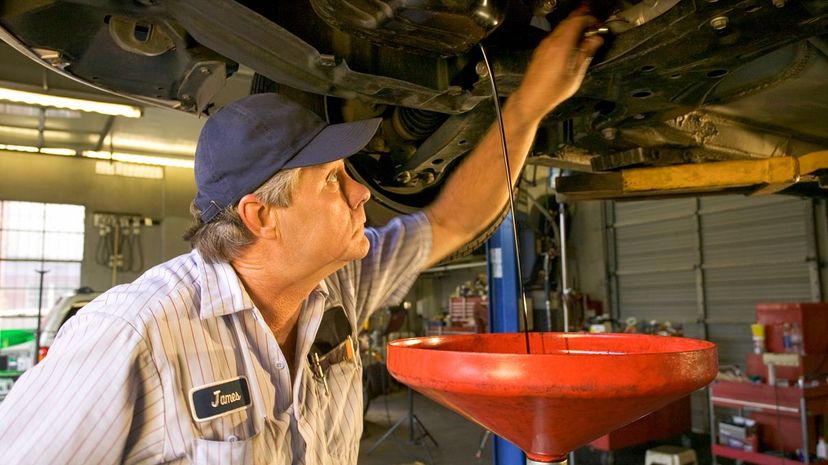

An engine's oil is pooled in a reservoir known as a sump. The sump is usually mounted below the engine. This oil is used to lubricate the engine's moving parts.
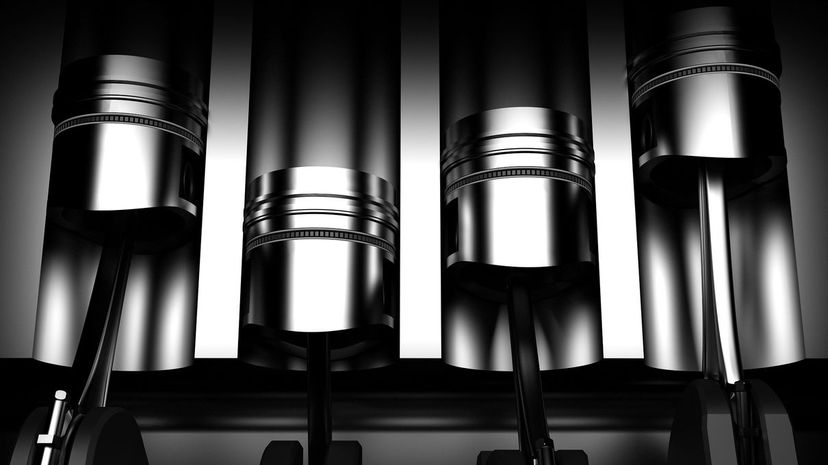

In piston engines, the "bore" refers to the diameter of each cylinder. The bore of each cylinder is one of the elements considered when determining an engine's capacity.
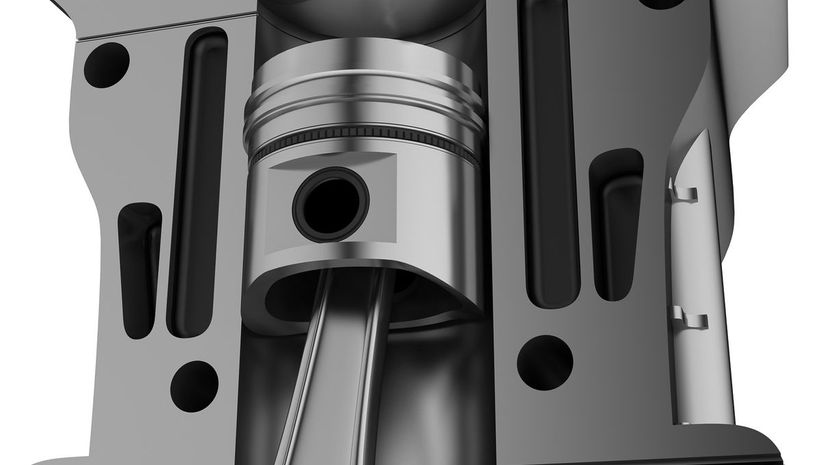

During an engine's intake cycle, its piston moves down. Once the piston moves down, air and fuel flood the cylinder. Then the combustion happens and the car moves!
Advertisement
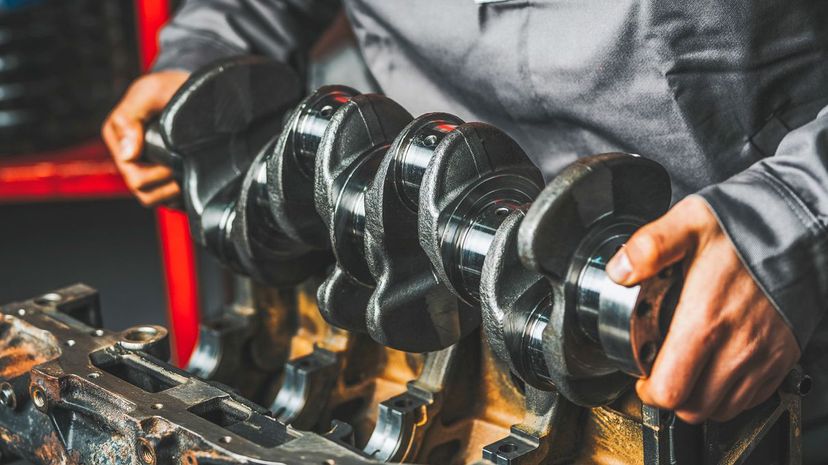

The linear energy created by your vehicle's pistons runs through a connecting rod to the crankshaft. Connecting rods can snap and, if yours does, you can be sure that your crankshaft won't move.
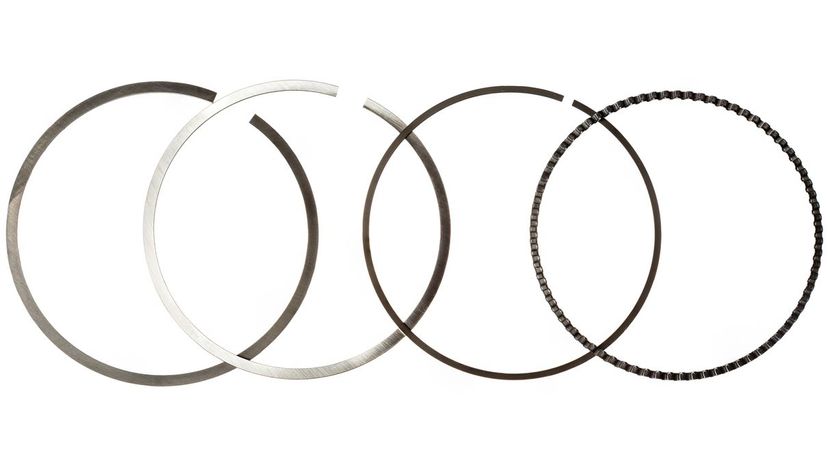
Your car's piston rings control engine oil consumption and oil pressure. So, when they wear out, there could be a range of problems. Worn piston rings can be misdiagnosed as other problems that revolve around low compression, so it's best to get your car checked by a mechanic if you notice it has any of the issues mentioned above.
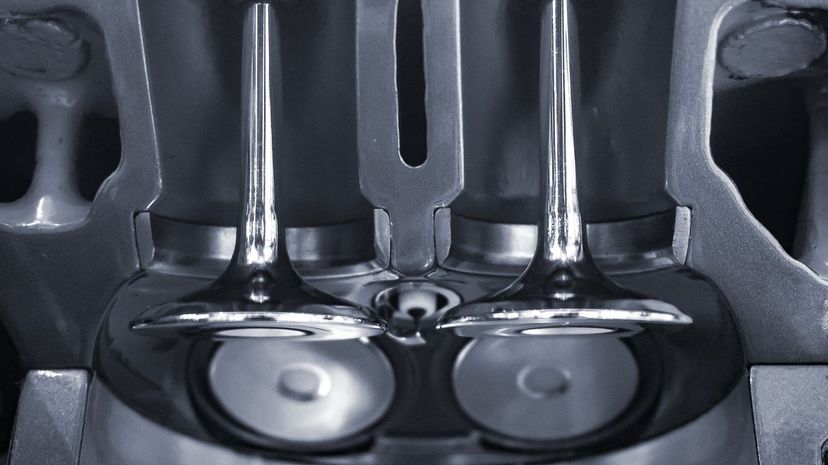

A vehicle's exhaust valve releases burned gases from the cylinder. This needs to take place before another combustion cycle can begin. Most modern engines have two exhaust valves per cylinder.
Advertisement
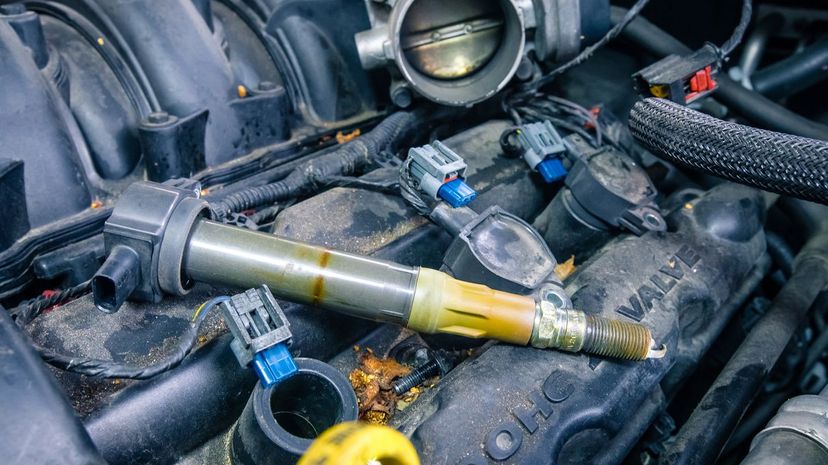

An ignition coil (also known as a spark coil), connects an engine's spark plugs to its battery. The ignition coil transforms the low voltage from the battery to the thousands of volts needed to create a spark from a spark plug.
Your car's engine control unit (ECU) is also known as an engine control module (ECM). It monitors and optimizes the performance of your vehicle's engine.
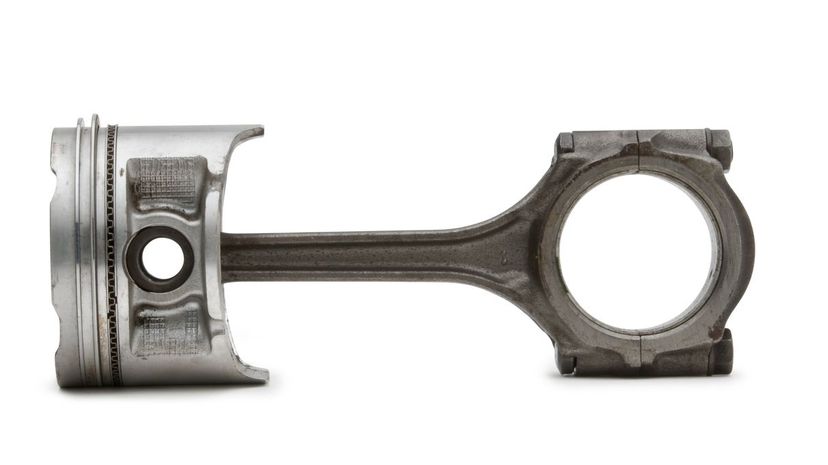

The pistons in a vehicle's engine are usually made from cast aluminum alloy. This material is used because it's lightweight while still maintaining high structural integrity. Cast aluminum alloy also has low manufacturing costs.
Advertisement
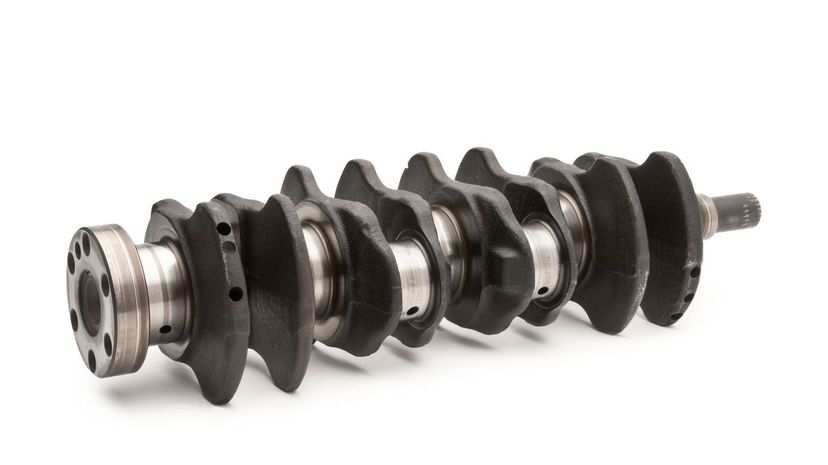

All the pistons in a car's engine are connected to its crankshaft. The liner energy created by the pistons is converted to rotational energy through the crankshaft. This will ultimately cause the vehicle's wheels to rotate.
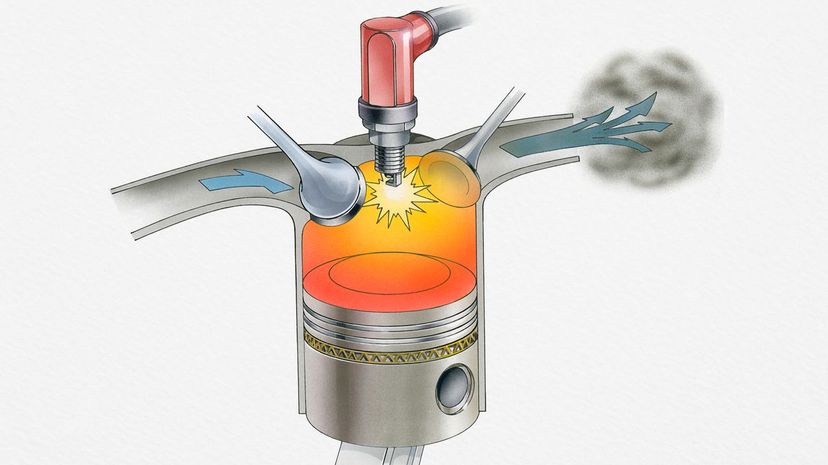
As an engine's piston moves up through its cylinder, it pushes the air/fuel mixture into a smaller space. Once this mixture is ignited, the fact that it's in a smaller space will result in a more powerful explosion.

There are several factors that result in diesel engines producing more torque than gas engines. One of the main reasons is that they have a higher compression ratio, which results in higher peak pressure in the combustion chamber. This results in more pressure being applied to the crankshaft.
Advertisement
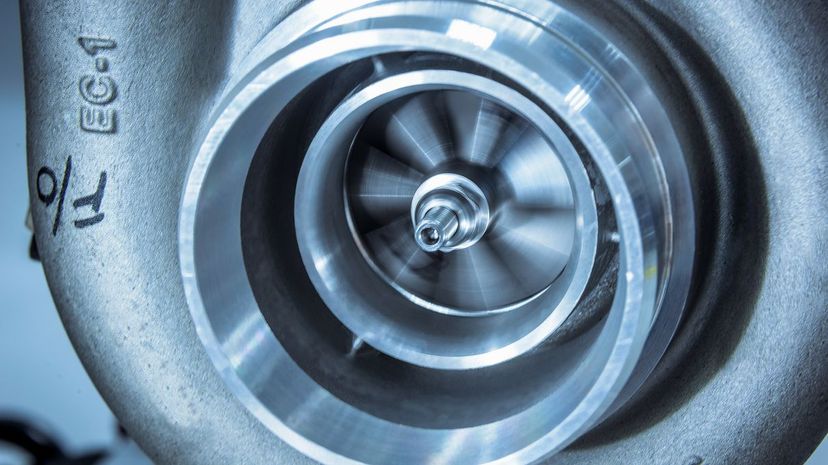

A naturally aspirated, sometimes referred to as a normally aspirated, engine only relies on atmospheric pressure for its oxygen intake. This means it doesn't use any kind of forced induction, such as a turbocharger or supercharger.
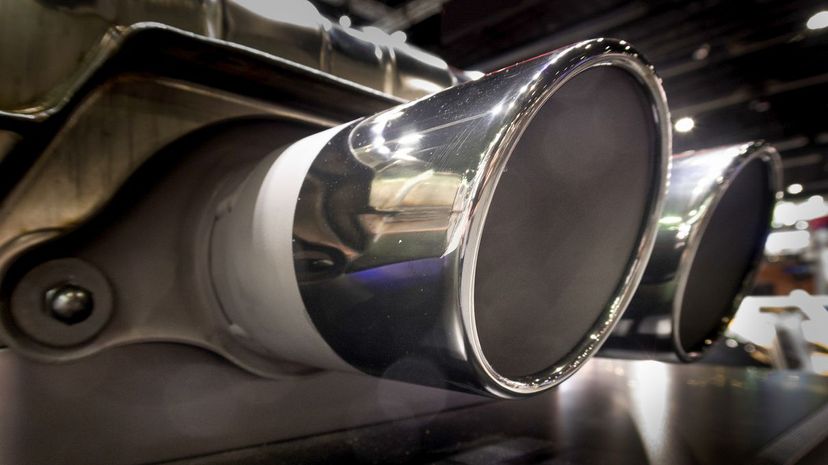

Dual exhausts can get the gases out of your cylinders faster than a single exhaust. This means the next engine cycle can start quicker than if you had a single exhaust system. The more used gases your engine can get out, the more it can suck in: this will give you more horsepower. Dual exhausts make a much more noticeable difference in a turbocharged vehicle, as there is forced induction.

Four-stroke internal combustion engines complete four strokes in one operating cycle. The four strokes take place in this order: intake stroke, compression stroke, power stroke and exhaust stroke.
Advertisement

For a two-stroke engine to operate correctly, oil must be mixed with the fuel as it's sucked into the combustion chamber. This oil serves as a lubricant for the internal components: without it the engine would seize.

The most common cause of a seized engine is oil starvation. When there's insufficient oil to lubricate an engine, it causes it to overheat. When an engine overheats, its parts begin to melt and, eventually, amalgamate.

During an engine's combustion cycle, a spark ignites the air/fuel mixture in the cylinder. Although the piston is up when the combustion starts, the resulting explosion forces the piston back down.
Advertisement

It's not possible to bump start a car with an automatic transmission. In order to bump start a car, you must build up momentum in the car, put it into gear and pop the clutch. Since cars with automatic transmissions don't have manual clutches, it's not possible to manually engage them.

"ICE" stands for "internal combustion engine." These engines generate power by burning fuel with air inside the engine and using the hot gases produced to drive a piston. The term "ICE" has become more popular with the rise of electric vehicles, as the need to differentiate between the two is greater than ever.

Older cars that used carburetors usually had a choke valve. The choke restricts the flow of air which enriches the fuel-air mixture: this makes it easier to start the engine. You'll still find these on some lawnmowers and other yard equipment.
Advertisement

Rotary engines use oil injectors to input small amounts of oil during the combustion cycle. This is mixed with the fuel in order to lubricate the engine's seals. More oil is burned this way than with a piston engine.
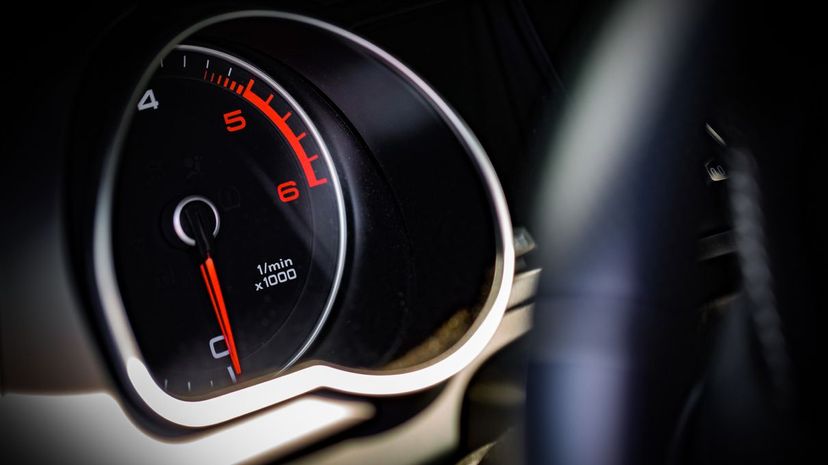

Your vehicle's RPM gauge, also known as a tachometer, measures how many times your engine's crankshaft makes one full rotation every minute. The number you see on your tachometer is usually multiplied by 1,000. So, if you see a four, your crankshaft is turning 4,000 times per minute.
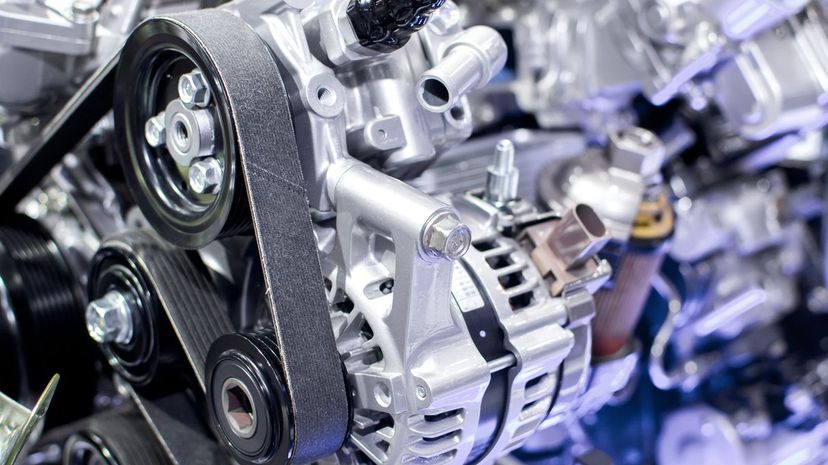

An engine's timing belt, also known as a timing chain or cambelt, synchronizes the rotation of its crankshaft and camshaft(s). This synchronization ensures that the engine's valves open and close at the correct times.
Advertisement
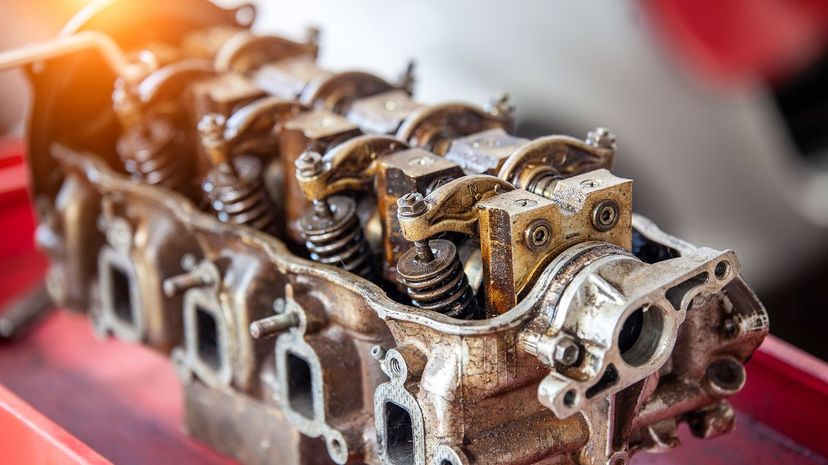

Once we know the bore and stroke length of a cylinder, we can determine what size it is. Since multiple cylinders make up an engine, we need to know how many there are. Once you know how many cylinders an engine has, you can multiply this number by the displacement of one cylinder to give you the engine's total displacement.
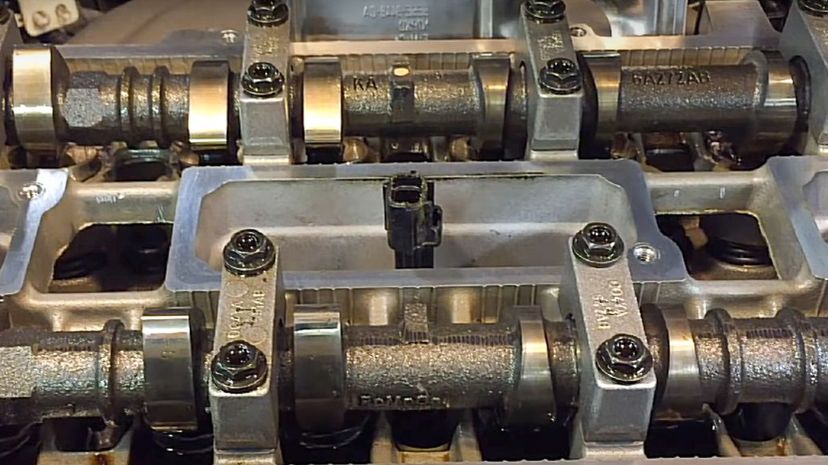

The i4 DOHC is an extremely popular inline four-cylinder engine found in may Fords. "DOHC" stands for "double overhead camshafts," meaning the vehicle has two camshafts.

A supercharger increases the pressure or density of the air supplied to an engine. This means there's more oxygen for the fuel to react with during each intake cycle, which increases the horsepower.
Advertisement

During the last part of an engine's cycle, the exhaust stroke, waste gas from the explosion is removed. This gas then goes to the catalytic converter to be cleaned. After this, it will reach the muffler before it exits through the tailpipe.
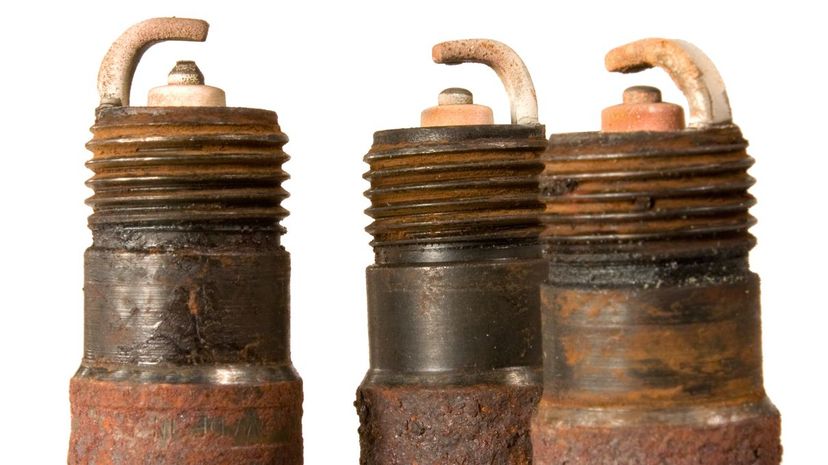

An engine's spark plugs breathe life into your vehicle by igniting its air/fuel mixture time and time again. When they start to go bad, they don't emit sparks as they should. This can lead to a range of problems from slow acceleration to making the vehicle hard to start, and everything in between.

Engines rely on oil pumps to keep them lubricated. If an engine's oil pump fails, then the lack of lubrication will cause excessive friction between its moving parts. Eventually, this friction will cause the engine to seize.
Advertisement
Engines come in all shapes, sizes, and configurations. Certain engines are more likely to be seen in certain vehicles, like a V-Twin in a motorcycle or a V8 in a muscle car. But one engine configuration you'll never see in any vehicle is a lateral eight, because it doesn't exist (yet).

Hybrid cars can boast a range of benefits over conventional internal combustion engines. The instant torque provided by electric motors improves acceleration, while the motor's assistance also improves mileage and reduces emissions.