About This Quiz
Given that people started tinkering around with the idea of internal combustion engines all the way back in the 1700s and that there are more than 268 million cars in America alone, you'd think more people would know what's going on in a car's engine. But like a TV or a computer, most people are happy to let it do its job without really getting into the literal nuts and bolts of why and how it runs. So when it comes to being able to diagnose that weird rattling noise, or figuring out why the heater doesn't work, many of us are left out in the cold figuratively and literally.
Luckily, some people do take the time to learn the ins and outs of an engine. They know the timing of a camshaft and the precise air/fuel ratio to make that engine purr like a jungle cat. They can change an oil filter as easily as an air filter and point out the crankcase like it was something they've known their whole lives. If you fancy yourself a bit of an engine expert, maybe you'd like to take a look and see if you can ID all fo these engine parts based on just a picture. Give the quiz a try and see!
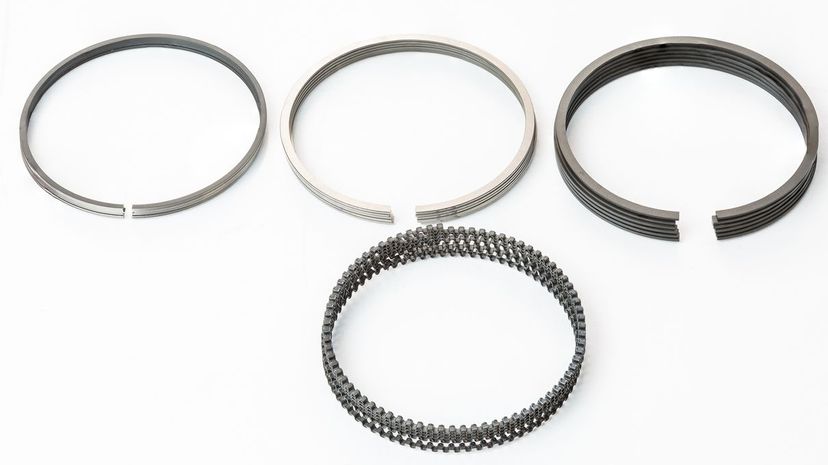

A piston ring is split, meaning it's not a complete circle, and it fits into a groove to maintain gas compression between the piston and the cylinder wall. It prevents the combustion gas from leaking out so that the engine can function properly.
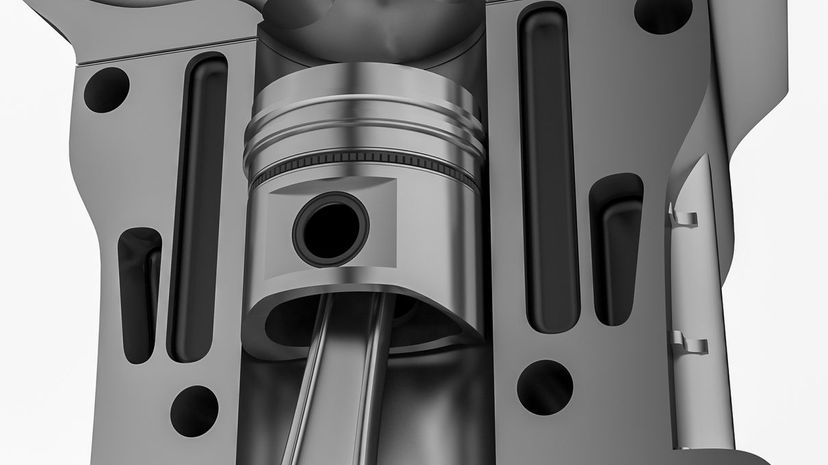
Engine pistons pump up and down inside the engine cylinders which are covered by the cylinder head. Engines have cylinders arranged side by side in an engine block, generally anywhere from four up to 12. Six or eight tend to be more common in most North American vehicles.
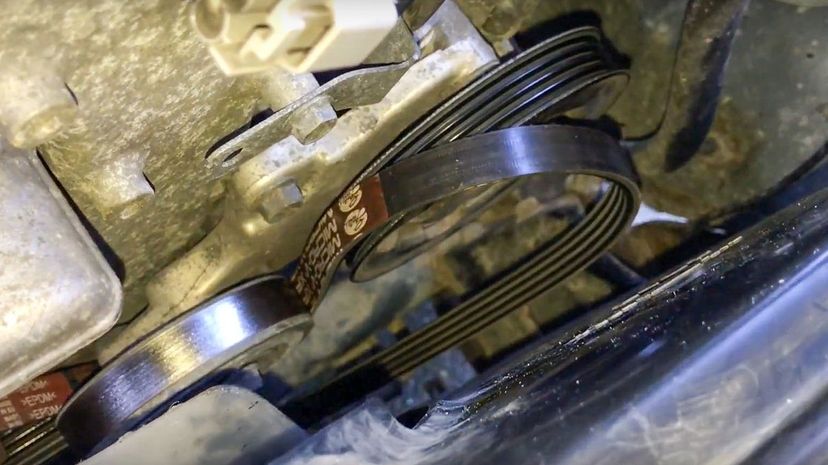

Early engines used leather belts that wore out and needed to be replaced quickly. Modern fan belts are made of longer-lasting rubber though they still require regular maintenance.
Advertisement
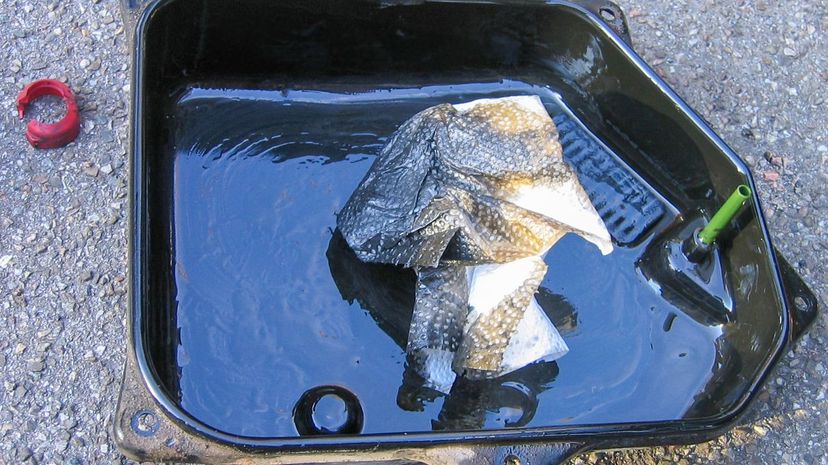

The sump is a metal dish that covers the bottom of the engine block. As its alternate name oil pan suggests, it exists to hold the oil when it's not circulating throughout the engine.
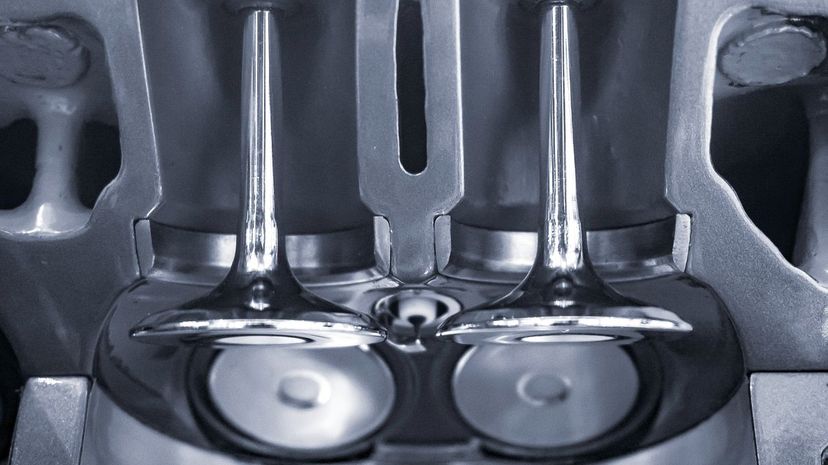

A typical combustion engine has both intake valves and exhaust valves. While the exhaust valve lets air out of the engine in the form of exhaust, the intake valves do the opposite by pulling air in. These have to open and close in a precisely timed sequence to maximize efficiency.
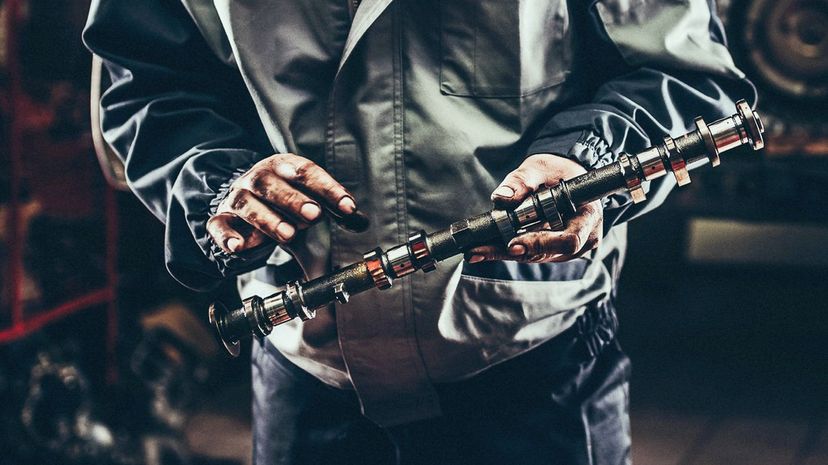

The camshaft is connected to the crankshaft. As the shaft rotates, the cams move up and down, opening and closing inlet and exhaust valves. The precise timing of this allows for control of the air/fuel mix through the engine.
Advertisement
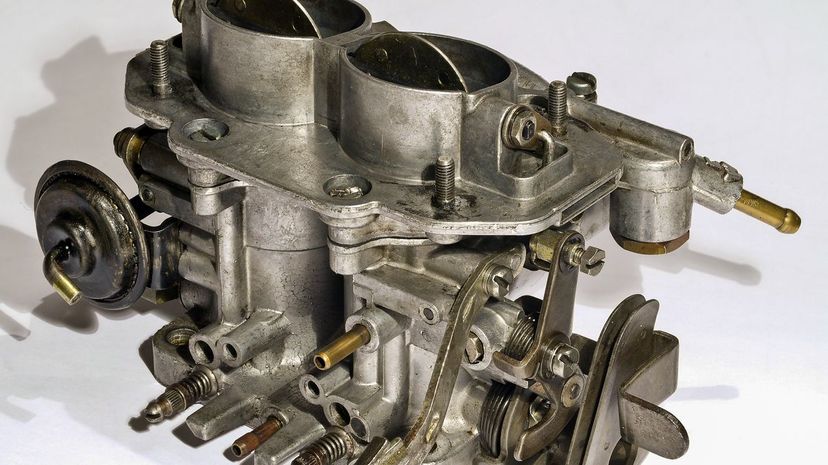

Carburetors maintain the air/fuel ratio and are actually fairly uncommon these days in most modern cars as fuel-injection has mostly taken over. That said, you can still find carburetors in small engines.
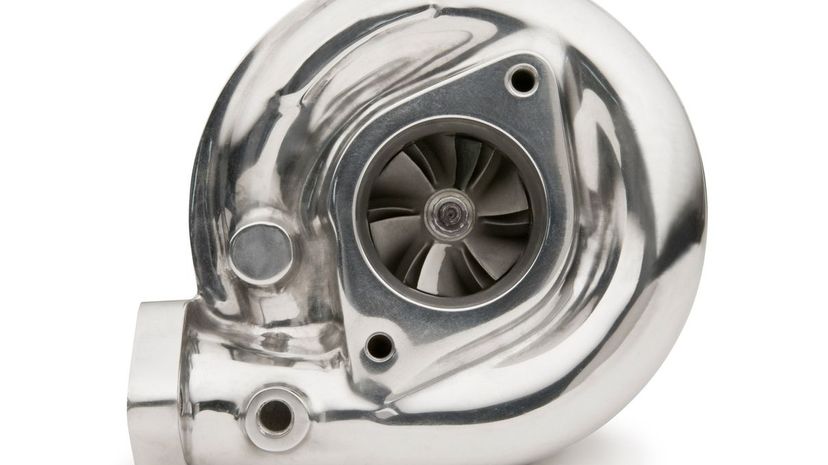

The turbocharger runs by engine exhaust spinning a compressor that draws in more air to then force it into the combustion chamber, which will increase the overall power and performance of the engine. In short, it makes the car more powerful.
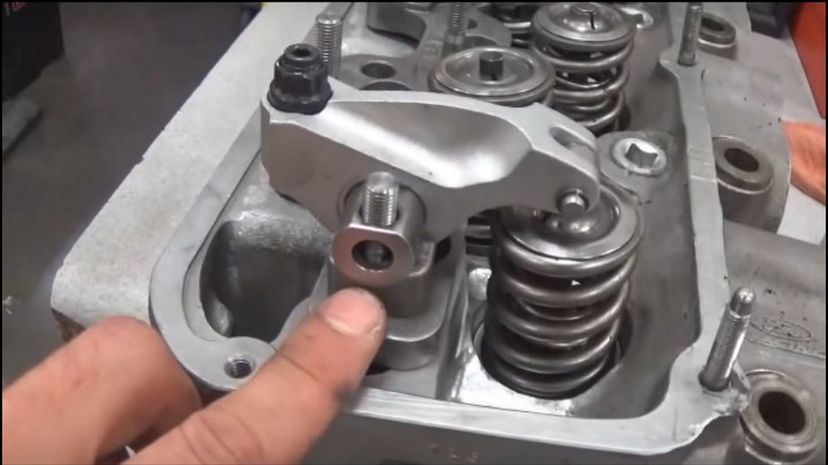

The rocker arm in your engine takes the rotational movement in the overhead camshaft and turns it into the up and down motion required to open and close the valves in the engine.
Advertisement
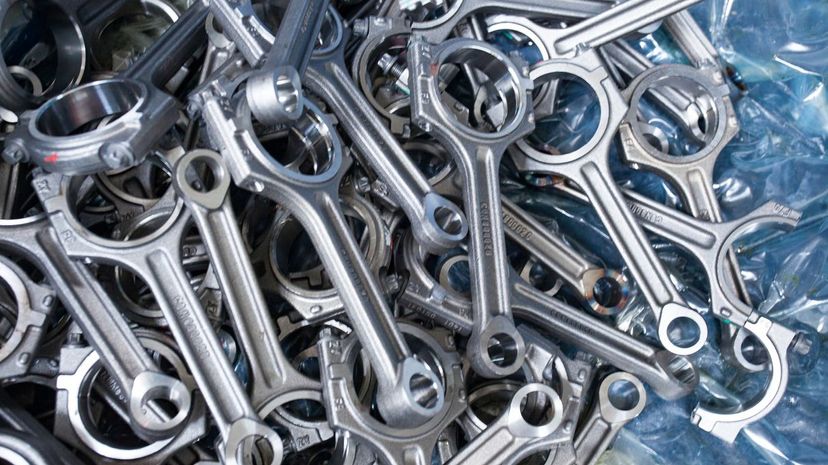

The pistons are connected to the crankshaft by the appropriately named connecting rod. It transfers motion from the pistons to the crankshaft in a way that transforms it from reciprocal to rotational energy.
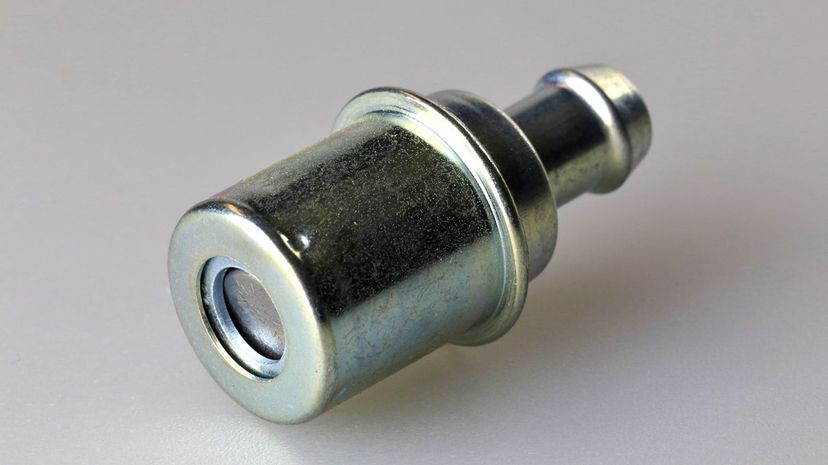

PCV stands for positive crankcase ventilation, which helps recycle engine gases to the intake manifold to be pumped back into the engine for combustion rather than just venting them freely as was done in older models.
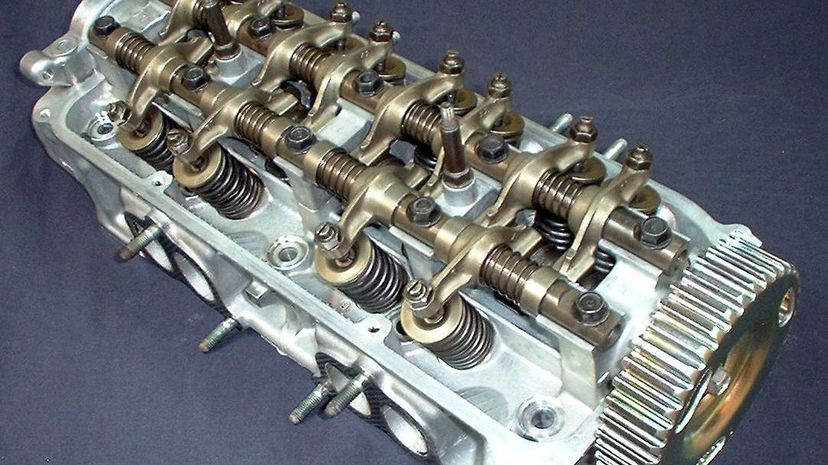

The cylinder head sits over the cylinders in the engine block, sealing them so that proper combustion can take place thus allowing the engine to function properly and making the whole car actually go when you try to drive it. No cylinder heads means no combustion can take place.
Advertisement
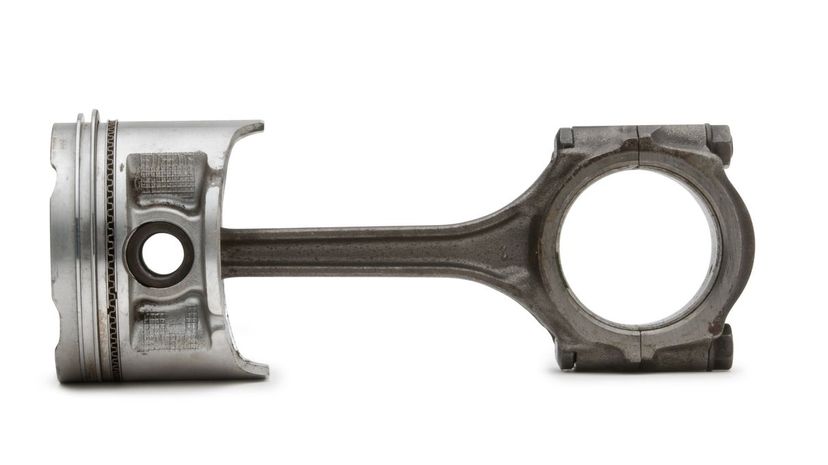

In a reciprocating internal combustion engine, the piston pushes up inside a cylinder compressing the fuel and air into a small space where it's ignited by the spark plug. That's the combustion part of the combustion engine, which in turn helps force the piston back down, expelling exhaust.

The rocker cover is the covering that is bolted over the rocker arms in an engine. Most people call them valve covers and in some engines it would be entirely inappropriate to call them rocker covers since not all engines actually have rocker arms.
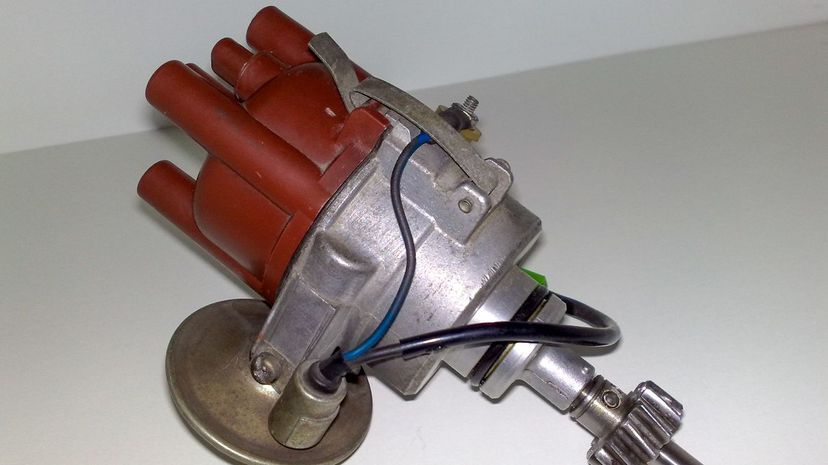
The distributor is powered by the camshaft and distributes high voltage current from the ignition coil to the spark plugs. As it's moved by the camshaft it allows for precise firing of the spark plugs to keep the combustion process moving in the engine.
Advertisement

If you want combustion to take place, you need fuel and air mixed together which is why the air intake manifold is there. It mixes the air with the fuel in the proper amounts to make combustion as efficient as it can be to maximize performance.

The crank pulley or crankshaft pulley is located at the end of the crankshaft. It turns the drive belt that operates engine accessories. Basically it's connected to the air conditioner compressor and the alternator and other parts.
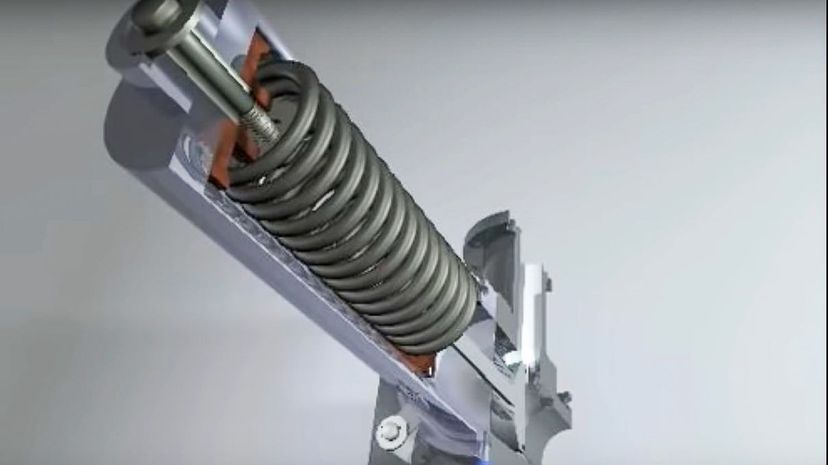

The poppet valves are employed in an engine to open and close the air intake and exhaust in the cylinder head. The cams push on the valves to force them to open and close, allowing air in and out.
Advertisement
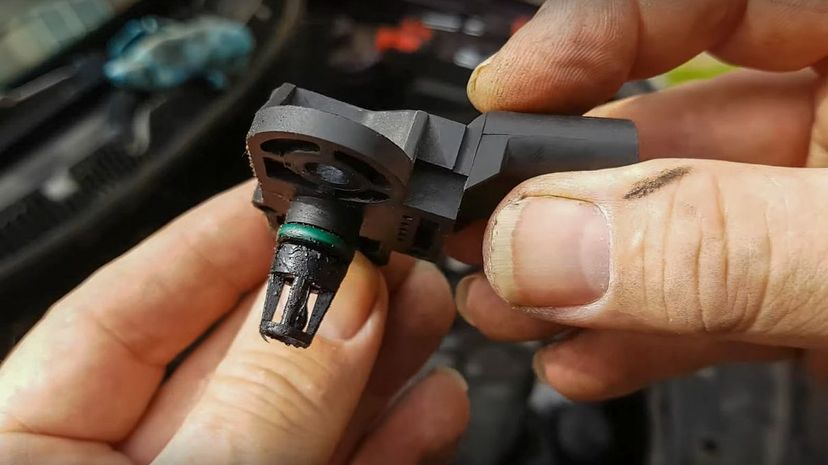

The MAP sensor, or manifold absolute pressure sensor, is a part of modern fuel-injected engines that electronically monitors your engine's airflow. It allows the computer to adjust the amount of fuel to add to the combustion chamber.
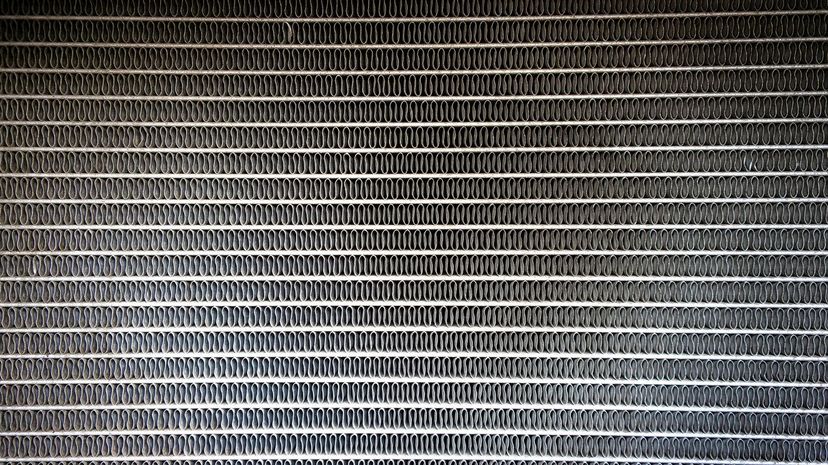

The radiator in your car moves coolant to maintain the temperature of your engine and prevent it from overheating. The coolant gets hot in the engine, then loses heat again as it passes through the radiator before being cycled back to start the process over again.
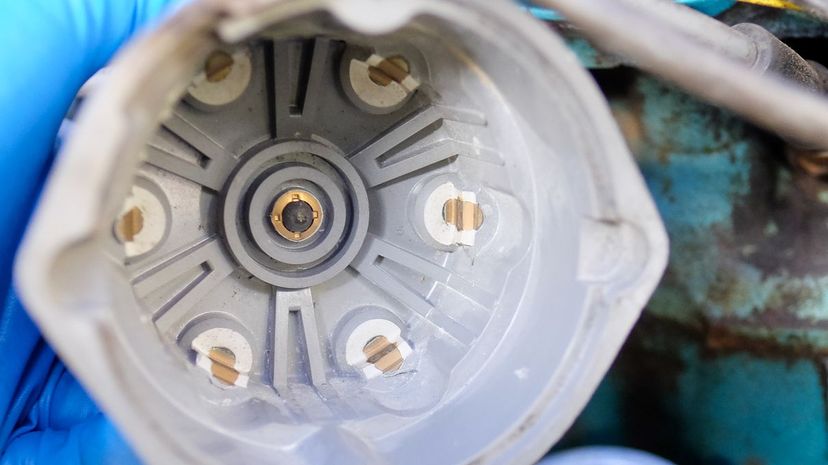
The distributor cap covers the distributor. It's one of the parts of an engine that requires close maintenance as the heat, vibration and current it experiences will cause it to wear out more frequently than many other parts.
Advertisement
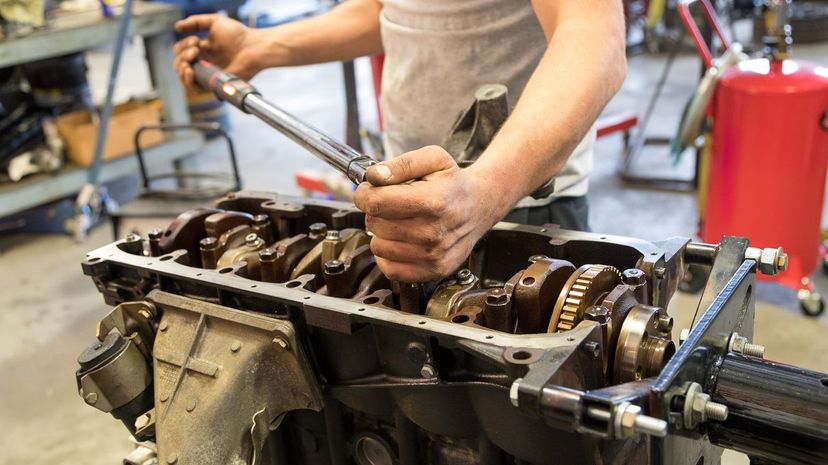

The crankcase lives up to its name and is the metal housing that holds in the crankshaft, the connecting rods, the crankshaft oil seal and the rest of the assembly. Open crank engines don't actually have a crankcase and are generally only seen in large engines like on ships.
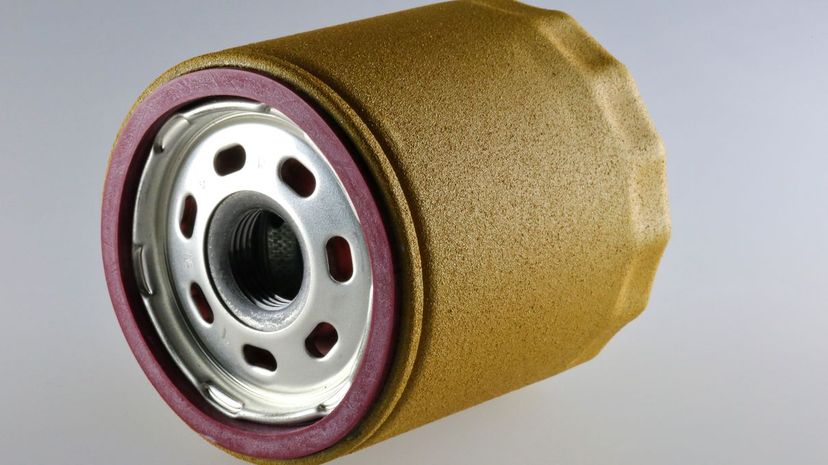

Oil filters remove the contaminants that may be in your oil. Since oil is cycled through the engine to keep it running clean and smooth, it will pick up debris and residue over time. The filer helps clean that out and, as such, needs to be replaced fairly regularly.
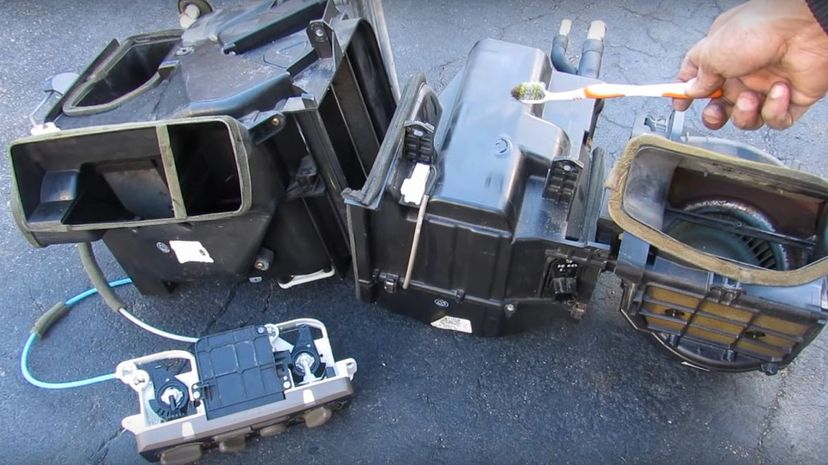

The car heater is a pretty simple device overall that makes efficient use of the excess heat from the engine. While much of the heat is vented through the exhaust or run through the coolant system, the heater allows a driver or passenger to control a ventilation system that redirects the heat into the car to keep you warm.
Advertisement
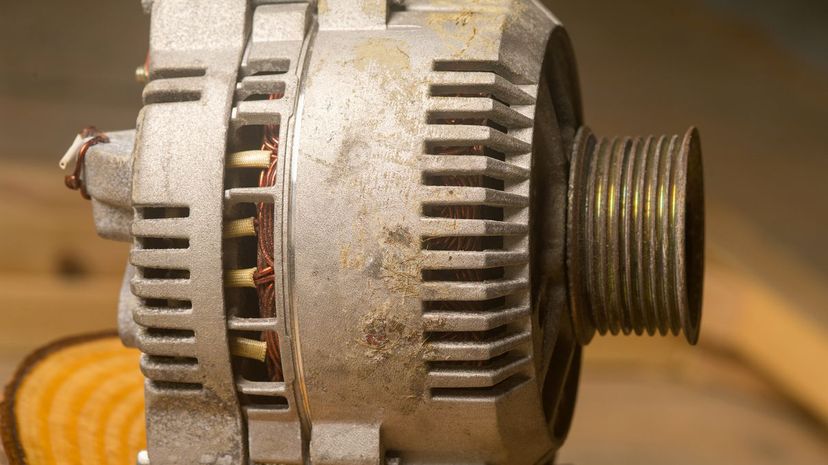

The reason your battery dies if you leave the lights on overnight but doesn't die if you drive for 3 days straight is that, when the car is running, the alternator keeps the battery charged. The Chrysler Valiant in 1960 was the first commercial car to have an alternator as a standard piece of equipment under the hood.
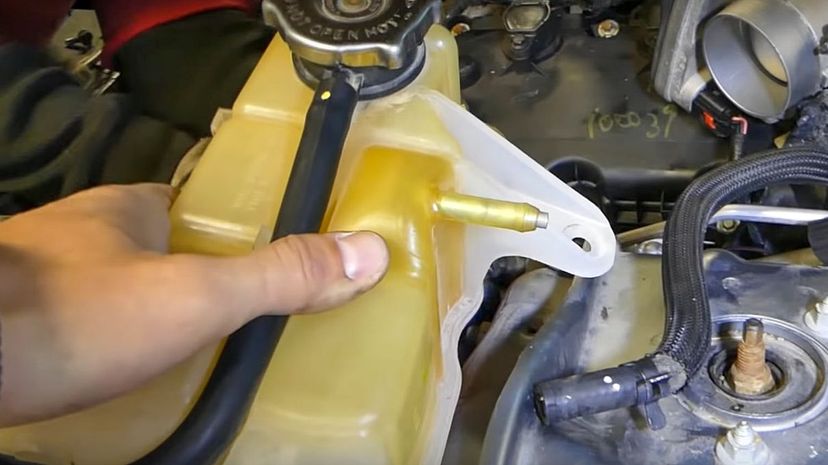

The reservoir tank in the engine is where coolant is stored to help keep the engine cool. It's worth noting that while water was often added to older engines it's a bad idea to just pour water into the tank in a modern engine. Coolant should be used instead to prevent damage.
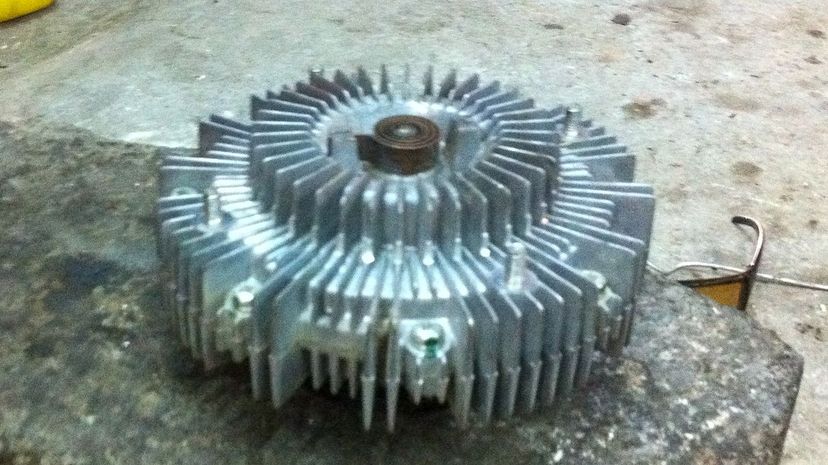

When your car is idling or operating at low speeds, the fan clutch draws in air through the radiator to keep the engine working at an optimal temperature. It spins pretty loosely at low temperatures, but as the temperature increases the clutch engages and the fan spins faster to provide more cooling.
Advertisement
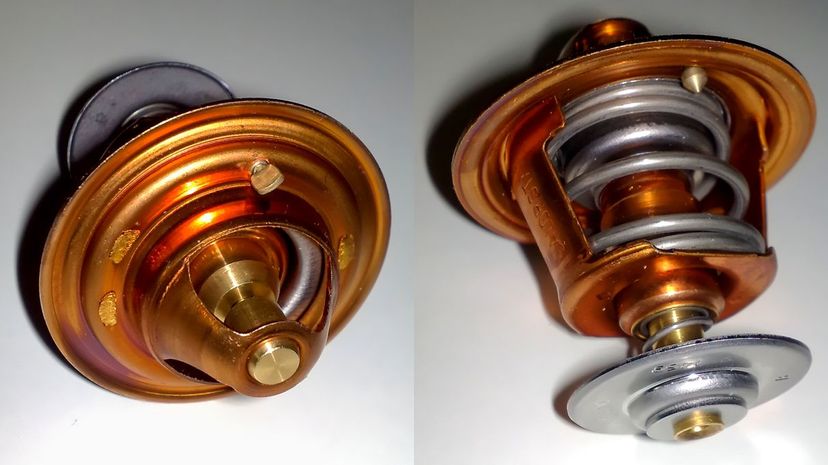

You don't want your car engine operating too hot as that can cause damage over time, so a thermostat is needed to monitor the temperature and keep things working in the optimal range.
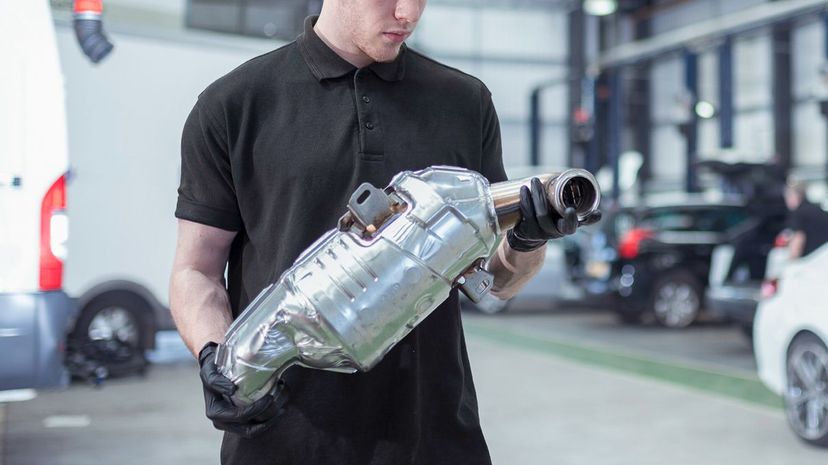

A catalytic converter makes use of what's called a redox reaction to reduce the amount of potentially toxic components spewed out by your exhaust. Converters have historically been targeted by thieves because they contain rare metals.
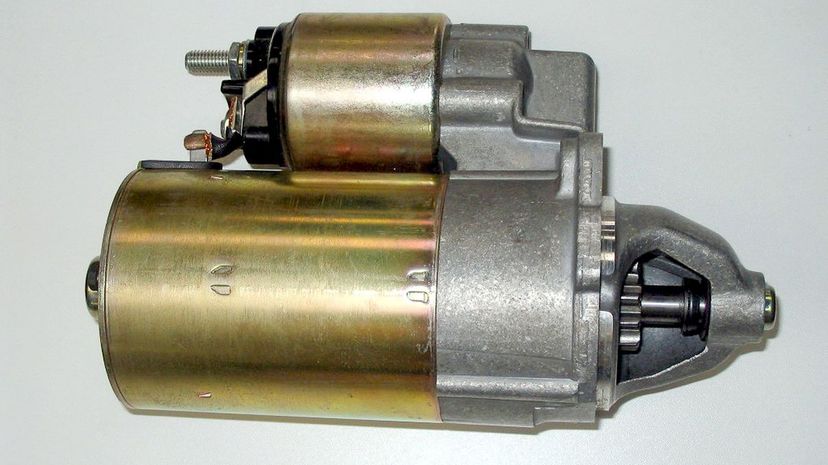

Before the engine runs, you need to do something to actually make it run. Old-timey cars were literally hand-cranked to get them going but the advent of the starter, which is only needed to get the engine moving into its self-sustaining four-stroke cycle, eliminated that older technology
Advertisement
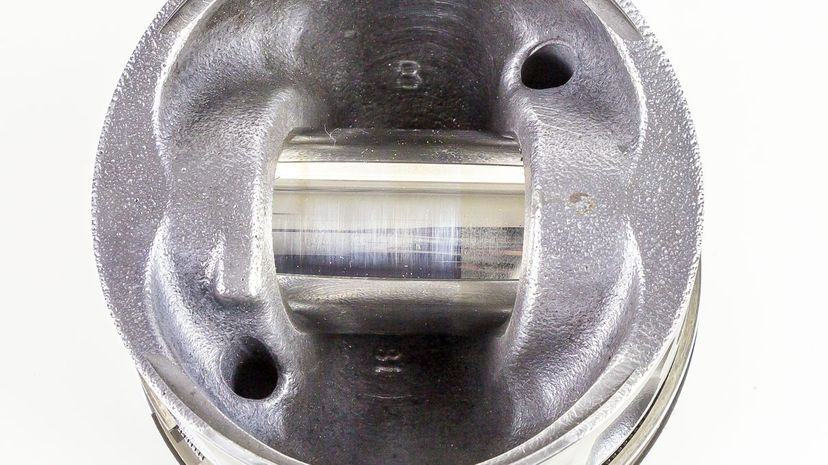
The gudgeon pin or wrist pin is the thing that connects a piston to a connecting rod in an engine. It allows the connecting rod to actually pivot as the piston pumps up and down. They can be either semi-floating or fully floating.
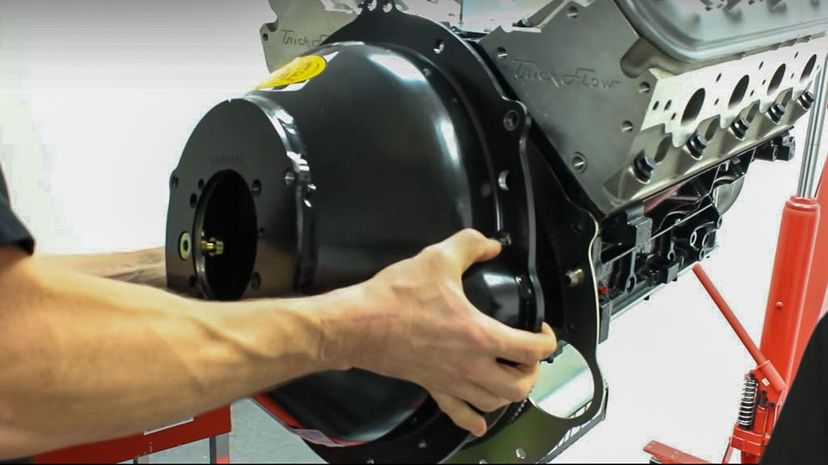

The bell housing, so named because it's actually shaped kind of like a bell, is bolted to the engine block and covers the clutch assembly or the torque converter in your engine.
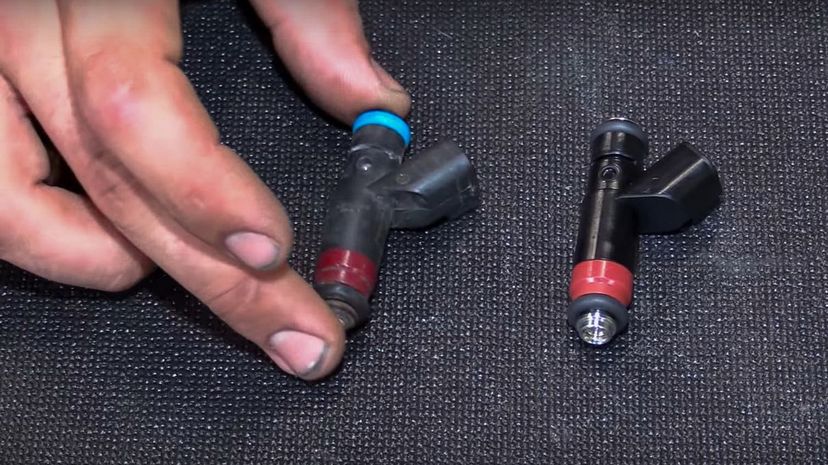

Fuel injectors replaced carburetors in many engines back in the 1980s. As the name implies, there is a nozzle that literally injects fuel into the combustion chamber, although some kinds may have multiple injectors rather than just one.
Advertisement
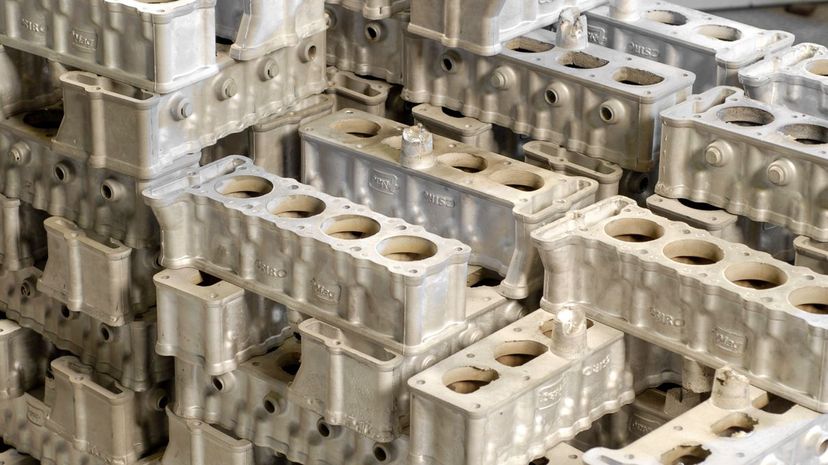

The engine block is sort of the housing for the entire engine. It's where the pistons pump in the cylinders, where the crank and camshaft are also held in more modern engines and where the combustion part of the combustion engine takes place.
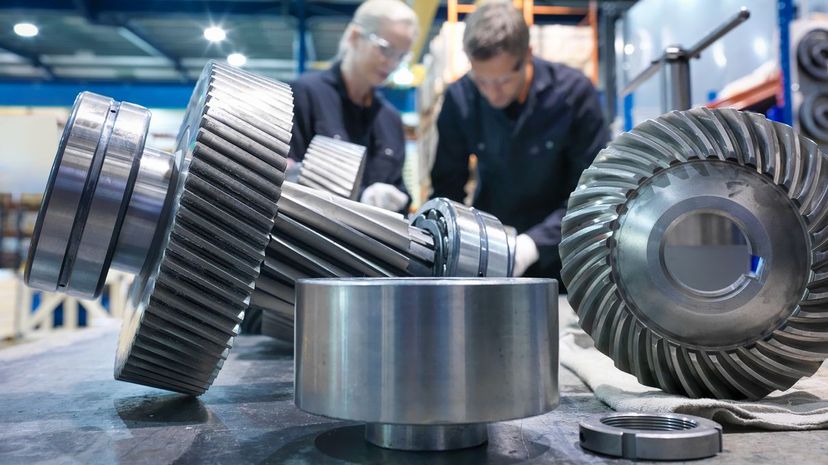

The differential in your car allows the output to spin at different speeds so your wheels have proportional RPMs between the two of them as you drive. This makes turning a lot easier.
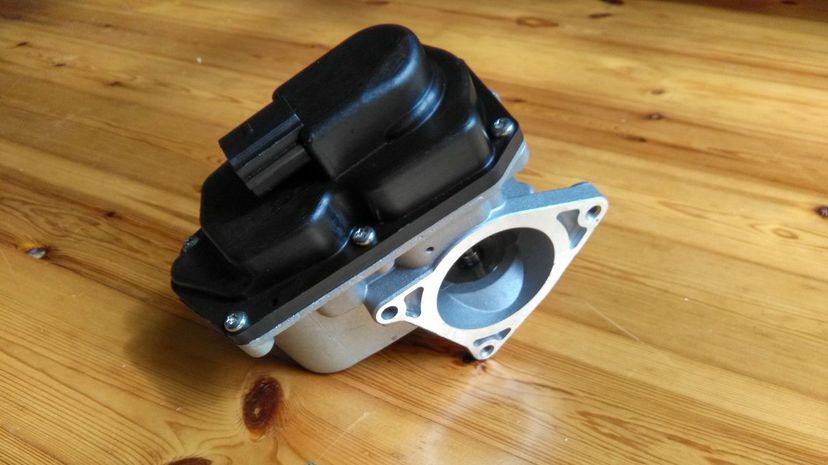

The EGR valve in an engine stands for "exhaust gas recirculation." It redirects a portion of the exhaust gases back into the engine to decrease combustion temperature and reduce the production of harmful nitrogen oxide gases as a result.
Advertisement
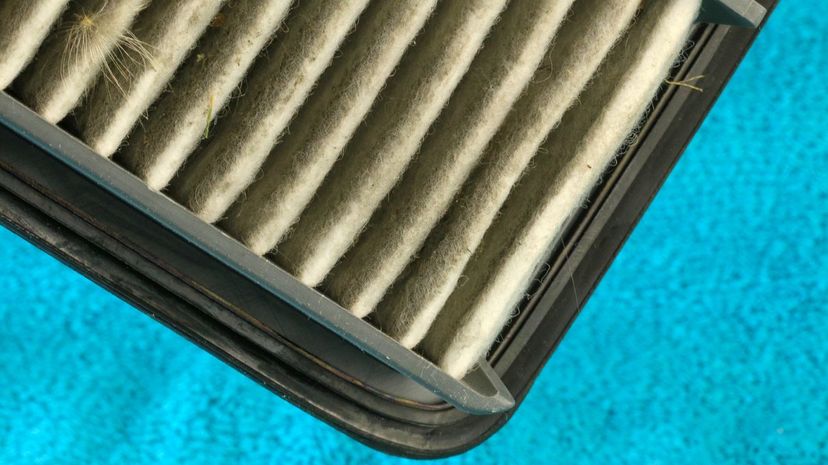

Your engine's air filter is one of the few parts of your engine that most people can visually inspect and replace all on their own without having to have a lot of technical knowledge. Manuals will recommend when they need to be changed although driving conditions, like frequently traveling on dirt roads, alter it a bit.
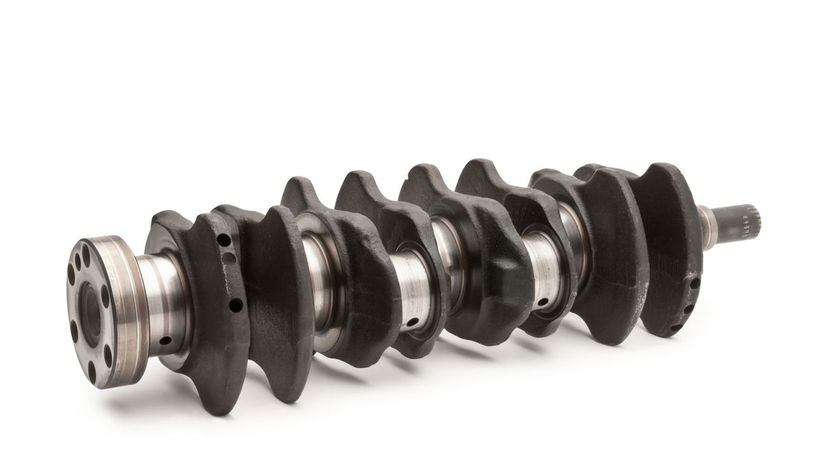

The crankshaft in your car basically takes the energy produced by the engine and makes it usable by the car's parts, such as allowing the belts to spin and operate various mechanisms like compressors. The pistons pumping up and down causes the crankshaft to spin.
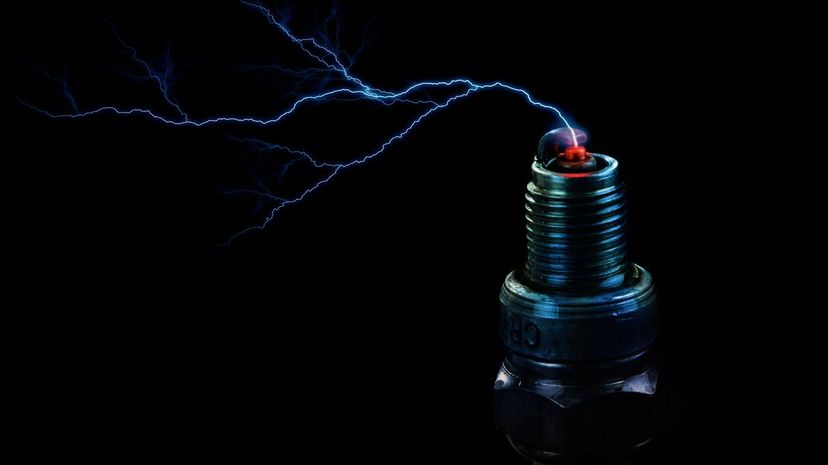

The spark made by a spark plug is what ignites the fuel mix to allow combustion to occur in a modern combustion engine. Modern plugs are often produced using some rare and valuable metals like platinum, gold, palladium and tungsten.
Advertisement
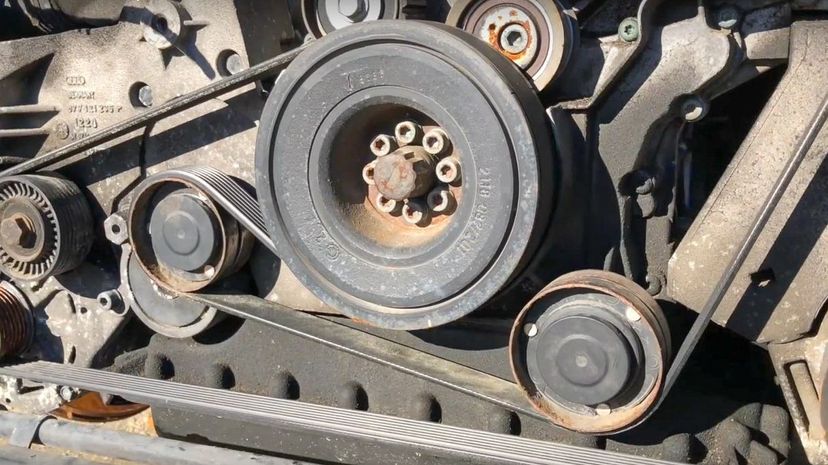

The drive belt is a pretty simple rubber belt in most modern cars that requires regular maintenance to ensure it's working right. It's attached to the alternator, the water pump, the air conditioning compressor, and the power steering pump, powering all of them as it cycles.