
About This Quiz
The Treaty of Versailles signaled the end of the World War I. If you already know that pivotal fact, go on to prove that you know all the intriguing details behind one of the most controversial peace treaties in the history of the world. Our history challenge answers the what, where and why of the Versailles Treaty all in one cool quiz.
There are pertinent facts you'll need to prepare you for your info journey. Know that some political historians have cited the 1919 Versailles Treaty as an example of poor international diplomacy. We explain the all shocking reasons why inside this quiz. Architects of the final treaty document deliberately put full pressure on Germany to pay for all that went awry because of World War I, the bloodiest war ever. U.S. President Woodrow Wilson devised the peace treaty in his Fourteen Points plan, which he fashioned as an instrument for world peace. Many provisions from Wilson's plan were drafted into the Versailles Treaty, but there was one major difference between the two world peace schemes. Wilson never intended to go so hard on Germany, which was one of four Central Powers that the Allied Powers-the United States, Britain, France and Russia-defeated. As the major player of the Central Powers, Germany was made to pay for everything.
Witness the devastating deal Germany was served as a result of the Versailles Treaty. Scroll on, history awaits you!
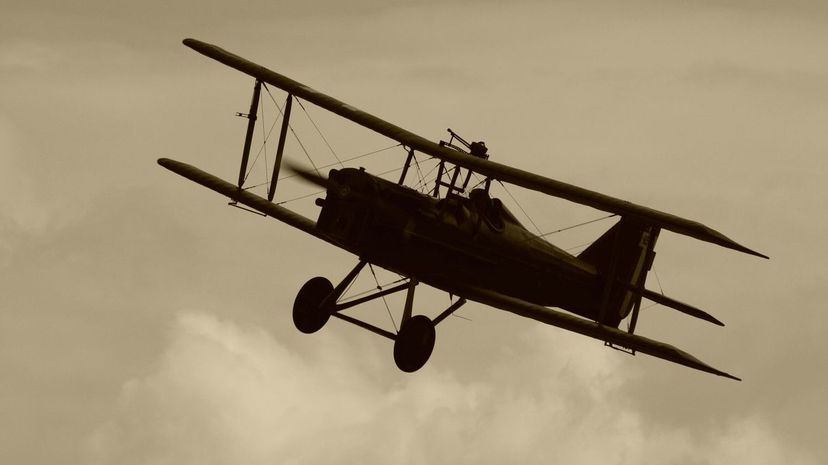

World War I, also known as the Great War, left three destroyed empires in its wake. Through the Treaty of Versailles, Allied nations rearranged territories of the major principality left standing among the vanquished, Germany.
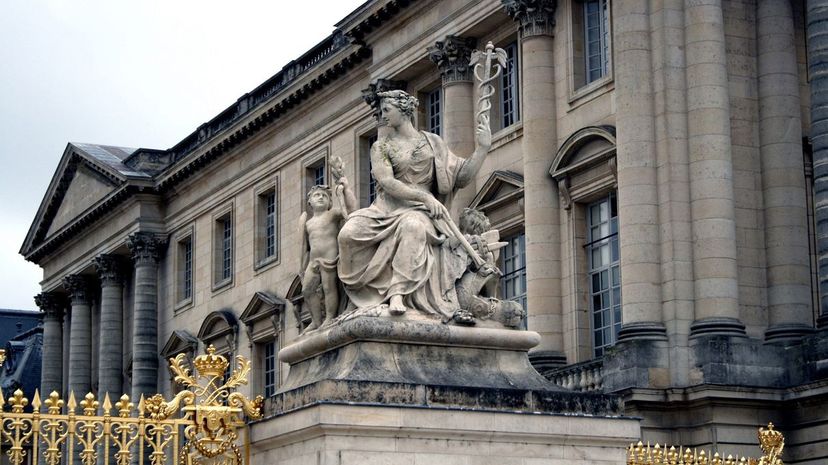

The Palace of Versailles in Paris is the former residence of Marie Antoinette and Louis XVI. Marie Antoinette, an Austrian, moved to the 700-room French palace at the age of 17 to become queen. Angry mobs of French citizens stormed the palace during the French Revolution.
At the end of World War I, victorious Allies imposed punitive war reparations on defeated Germany. Severe penalties that Germany incurred as a result of the Treaty of Versailles triggered circumstances that led to World War II.
Advertisement

The League of Nations was formed after World War I to help ensure that countries would defend each other against aggression. Though U.S. President Woodrow Wilson was a key framer of the Treaty of Versailles, the United States never joined the League of Nations.

Fighting during World War I ended on Nov. 11, 1918. Signed on June 28, 1919, the Treaty of Versailles was the official end the war, which is renowned for being one of the deadliest wars in history. Historic military tactics failed utterly in the face of modern technology like the machine gun, grenade and poison gas.
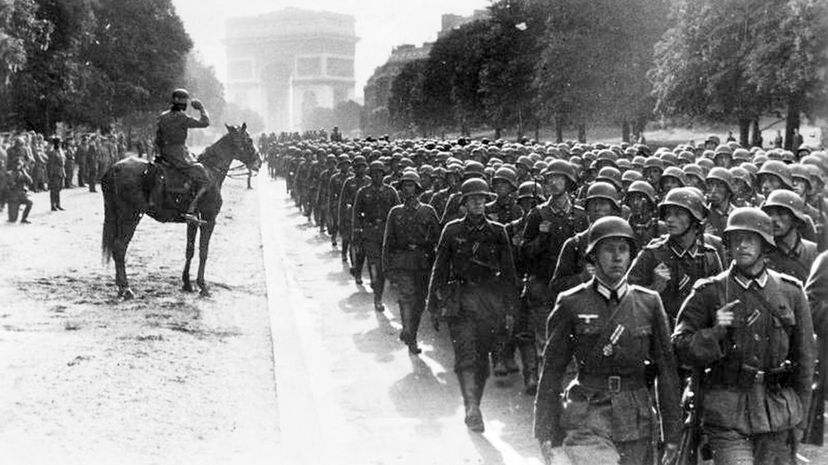

In 1940, Germany invaded France for the fifth time since 1814, before the two countries signed an armistice. Germany's Adolf Hitler insisted that the signing be held in the same railroad dining car in the Compiegne Forest, where Germany was made to sign the armistice that ended World War I.
Advertisement
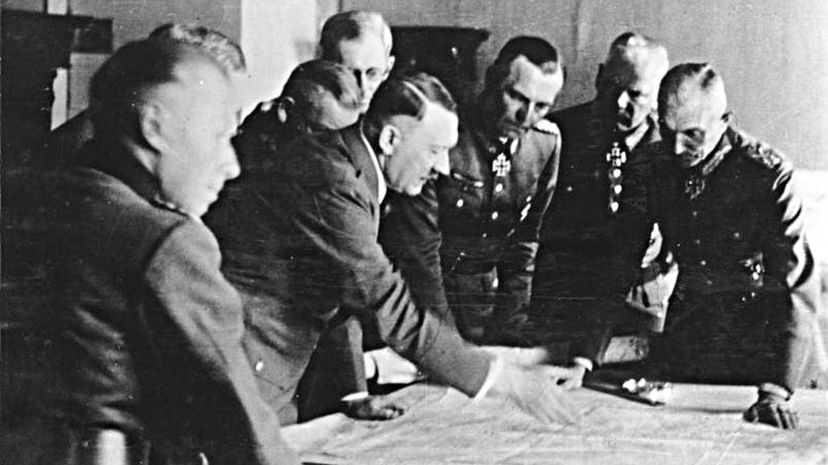

The Versailles Treaty imposed many harsh restrictions and penalties on Germany, including payment of war reparations. Ultimately, Germany withdrew from the League of Nations, as did its future World War II ally Italy. The League eventually disbanded when it could not prevent Hitler's rise.
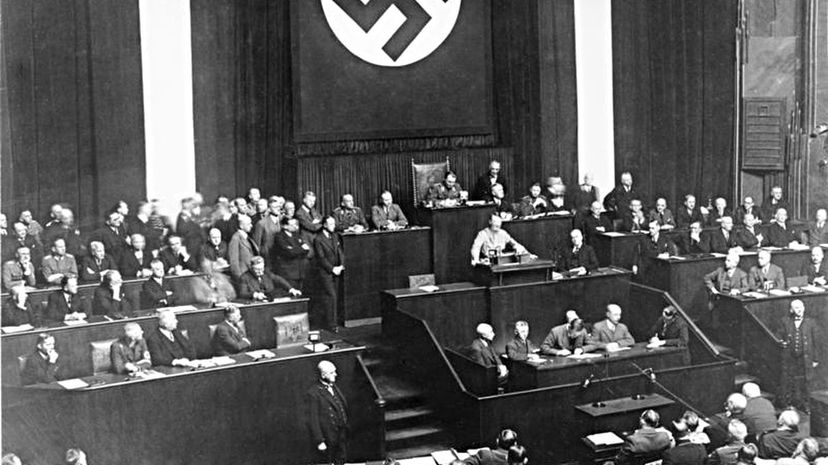

Former corporal of the German Army, Adolf Hitler, campaigned vigorously against the stipulations that the Treaty of Versailles imposed on Germany. Hitler's continuous protest among Germans, who were angered by the treaty, led to his success.
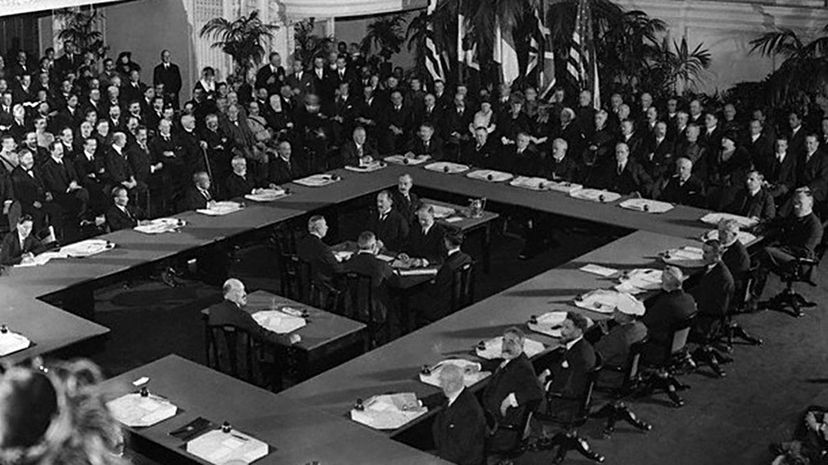

Though Lodge was chairman of the Foreign Relations Committee, President Woodrow Wilson, a Democrat, did not include the Republican in the U.S. delegation at the 1919 Paris Peace Conference. A Republican-controlled Senate further hindered Wilson's chances of ratifying the Versailles Treaty.
Advertisement

President Woodrow Wilson sought to end the prevalence of war through his Fourteen Points peace policy. Wilson's policy was a collection of terms that might prevent unchecked global aggression.
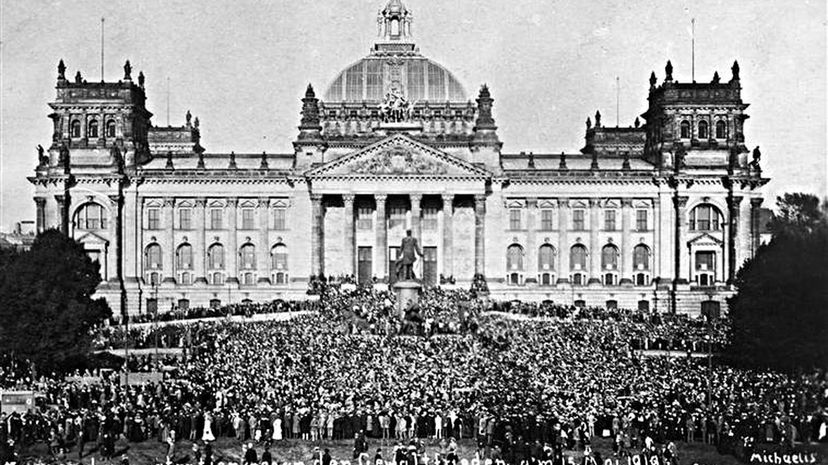

There'd been concern that the German National Assembly wouldn't ratify the 1919 Treaty of Versailles, considering that there existed powerful German statesmen who staunchly opposed its terms. General enmity among German leaders and citizens did not dissipate, but festered during the interwar period.
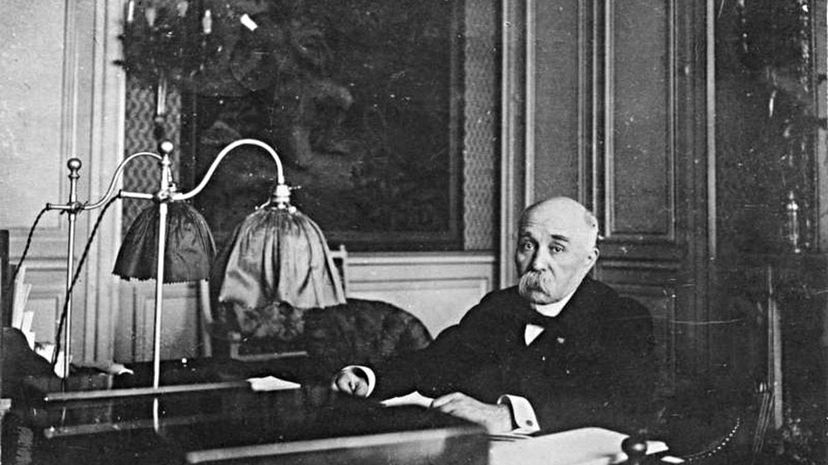

Georges Clemenceau, premier of France, David Lloyd George, prime minister of Great Britain, and U.S. President Woodrow Wilson dominated the conference of 1919. The Versailles Treaty that resulted was the first of five Paris peace treaties that reshaped the world after the Great War.
Advertisement
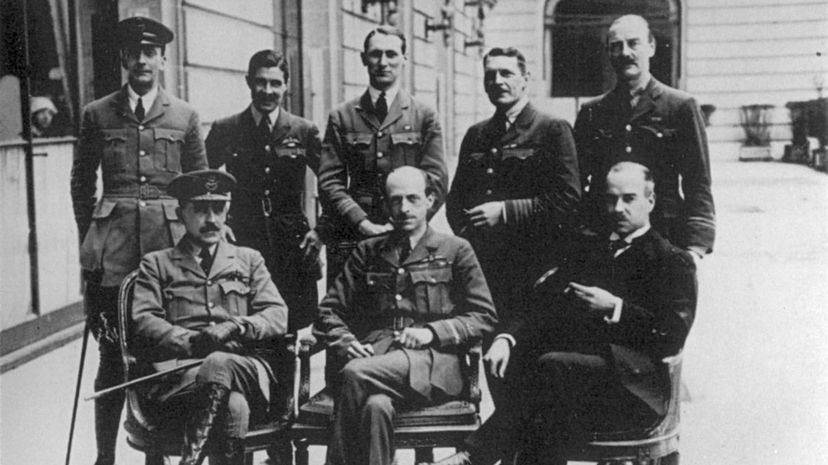

President Woodrow Wilson's calls for mercy on behalf of Germany at the peace talks were no match for the diplomatic "hawks" in the room. Both Britain's Lloyd George and France's Georges Clemenceau pushed for the harshest stipulations possible.

Versailles Conference members did not establish Yugoslavia or the first version of the entity, Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes. Montenegro-a Balkan state that had recently won independence-strongly objected to new Yugoslavia.

Though Germany was among other Central Powers nations, the Treaty of Versailles considered the major nation to be solely responsible for the First World War. The treaty aimed to cripple Germany militarily.
Advertisement

Formation of the League of Nations was a term included in the treaty. The League's single global mission was to end major conflicts among its members swiftly and with as little bloodshed as possible. The treaty was engineered to be the formal end to World War I and the beginning of world peace.

The struggle over a single Slavic principality was unanimously resolved at the end of the First World War. However, Western Versailles Conference members formally recognized the formation of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes as a remedy.
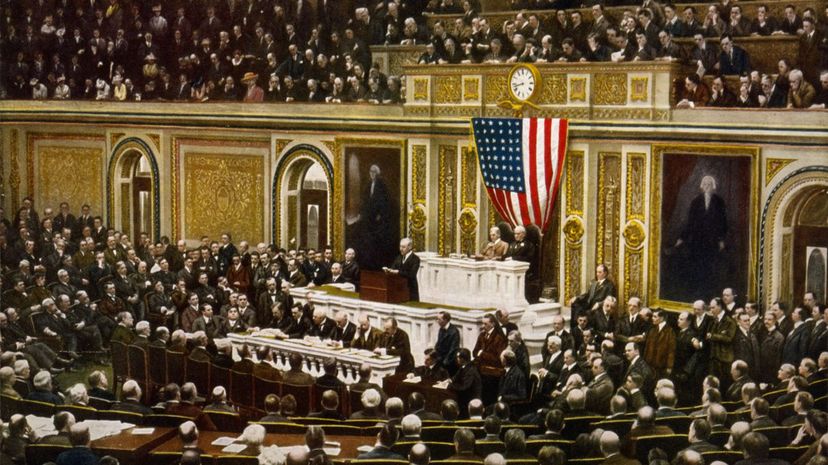
The United States never ratified the Treaty of Versailles, and therefore didn't join the League of Nations. A major issue among U.S. senators was the stipulation that the League, and not Congress, have the power to send U.S. troops to quell international conflicts.
Advertisement

Most Democrats supported the Versailles Treaty, while Republicans were split. Sen. Lodge led the "Reservationists" among Republicans who desired the treaty's approval only if certain changes were adopted.
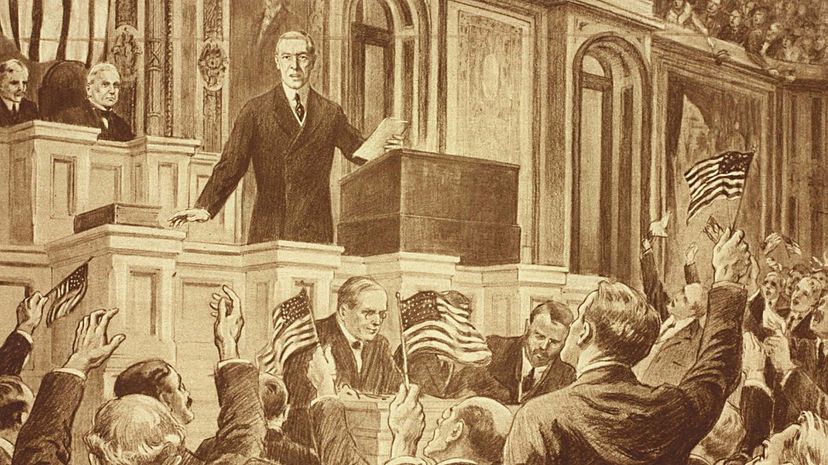
President Woodrow Wilson's presentation was the first time since 1789 that a U.S. president delivered a treaty to the Senate for ratification in person. Republican members of Congress were reluctant to surrender the power of the legislative body to the will of the League of Nations.
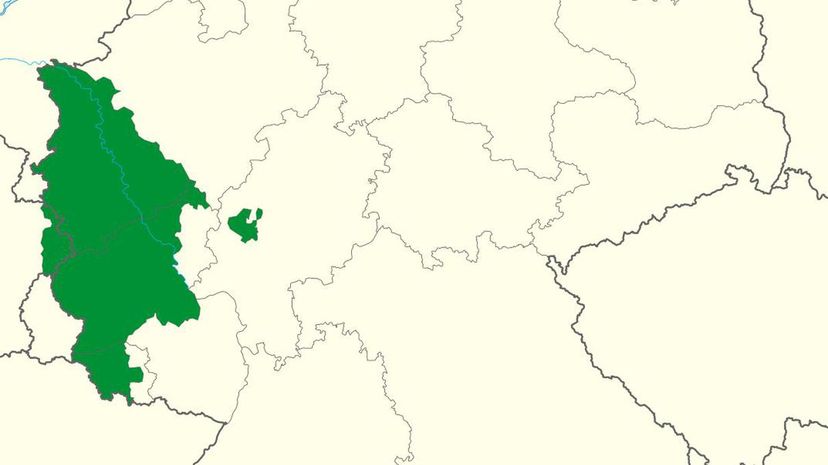
Germany was forced to give up Rhineland, which was a demilitarized zone that the League of Nations supervised. Germany also gave up the Danzig Corridor, including the bustling port city of Danzig.
Advertisement

At the end of the bloodiest battle in human history, U.S. President Woodrow Wilson eagerly sought a peaceful resolution. To prevent such barbarity from happening in the future, his League would solve issues through "cooperative diplomacy."

The final version of the Treaty of Versailles included the controversial Article 231, better known as the "war guilt clause." Germany was compelled to accept responsibility, ethical and financial, for World War I, or continue fighting.

Germany signed the Treaty of Versailles under the Weimar Republic, which made the governing body hugely unpopular among Germans who vehemently opposed the treaty's harsh provisions that devastated the nation's economy. Hitler's Nazi Party dissolved Weimar to institute the Third Reich in 1933.
Advertisement

Through the Treaty of Versailles, France sought to set in place strict punishments on neighboring Germany to safeguard its shared border. Annexed in 1870, the region of Alsace-Lorraine was returned to France as stipulated by the treaty.

United States senators who opposed the Versailles Treaty opposed President Woodrow Wilson's concept of "collective security." According to Wilson's plans for the League of Nations, member nations would lend military arsenals and troops in a joint effort if diplomacy ever failed.

"Irreconcilables" did not want the treaty at all. Sen. Henry Lodge, leader of the "Reservationists," sent 14 reservations with the treaty to the Senate floor. Democrats, who had supported the treaty as delivered, rejected Lodge's scheme by siding with the Irreconcilables in a vote of 39 to 55.
Advertisement
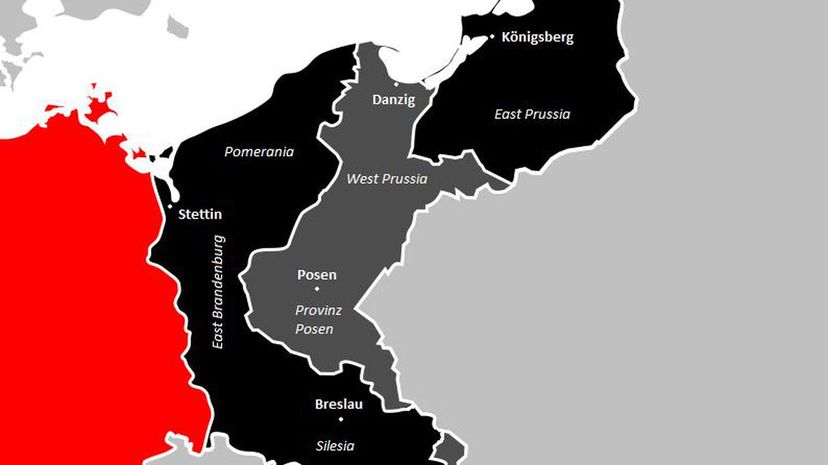
Germany returned approximately 27,027 square miles that it had acquired by the end of World War I. As a result, the German Empire shrank roughly 10%. Germany handed Prussia over to Poland, giving the country vital access to the Baltic Sea.

Members of the defeated Central Powers were Germany, the Ottoman Empire, Italy and Austria-Hungary. The Versailles Treaty recognized that Germany was the most powerful among the syndicate and penalized the nation accordingly. (The Axis Powers were the WWII group led by Germany.)

The Knox-Porter Resolution did for the United States what the Treaty of Versailles could not, in that it officially brought closure to World War I for the nation. President Warren G. Harding, Woodrow Wilson's Republican successor, signed the resolution into law on July 2, 1921.
Advertisement
Under Versailles Treaty provisions, Germany's colonies were redistributed. New Zealand took Samoa, Australia secured New Guinea, Britain seized Togoland and Tanganyika, Belgium won Ruanda-Urundi and France controlled Cameroon.

The International Labour Organization was established to fashion a widespread standard of global rights that included reasonable work conditions and basic protection for all people. The group has been a United Nations agency since the dissolution of the League of Nations.
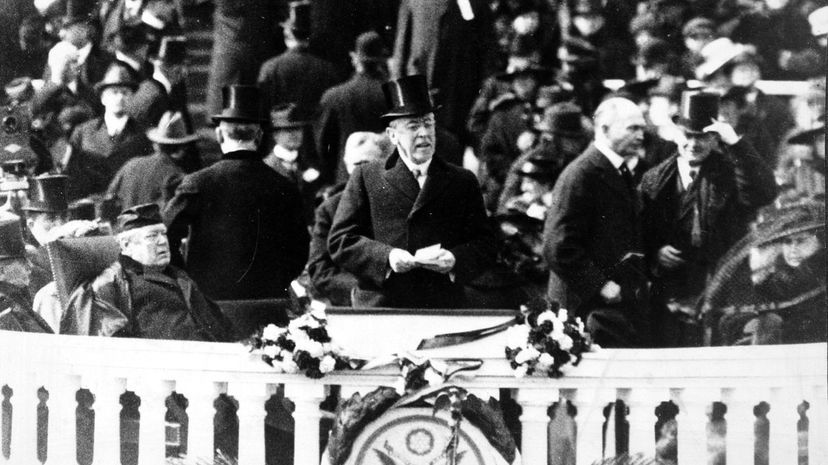

After he struggled to deliver his speech, President Wilson, who had just returned from representing the U.S. at the Paris Peace Conference, turned to Republicans and said, "It has come about by no plan of our conceiving ... We cannot turn back." Wilson's plea garnered faint applause.
Advertisement

In addition to land forfeitures, Germany was required to pay out approximately $30 billion in war reparations. The treaty also required Germany to reduce its army to 100,000 soldiers, and production of military weaponry was prohibited.

China's May Fourth university protest triggered the anti-imperialist Chinese Communist Party. During the protest, Chinese citizens reacted to the Allies denying the country land grabs and spoils of World War I although China was on the winning side.